Difference between revisions of "Data Science"
m |
m |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
* [[Data Science]] ... [[Data Governance|Governance]] ... [[Data Preprocessing|Preprocessing]] ... [[Feature Exploration/Learning|Exploration]] ... [[Data Interoperability|Interoperability]] ... [[Algorithm Administration#Master Data Management (MDM)|Master Data Management (MDM)]] ... [[Bias and Variances]] ... [[Benchmarks]] ... [[Datasets]] | * [[Data Science]] ... [[Data Governance|Governance]] ... [[Data Preprocessing|Preprocessing]] ... [[Feature Exploration/Learning|Exploration]] ... [[Data Interoperability|Interoperability]] ... [[Algorithm Administration#Master Data Management (MDM)|Master Data Management (MDM)]] ... [[Bias and Variances]] ... [[Benchmarks]] ... [[Datasets]] | ||
* [[Data Quality]] ...[[AI Verification and Validation|validity]], [[Evaluation - Measures#Accuracy|accuracy]], [[Data Quality#Data Cleaning|cleaning]], [[Data Quality#Data Completeness|completeness]], [[Data Quality#Data Consistency|consistency]], [[Data Quality#Data Encoding|encoding]], [[Data Quality#Zero Padding|padding]], [[Data Quality#Data Augmentation, Data Labeling, and Auto-Tagging|augmentation, labeling, auto-tagging]], [[Data Quality#Batch Norm(alization) & Standardization| normalization, standardization]], and [[Data Quality#Imbalanced Data|imbalanced data]] | * [[Data Quality]] ...[[AI Verification and Validation|validity]], [[Evaluation - Measures#Accuracy|accuracy]], [[Data Quality#Data Cleaning|cleaning]], [[Data Quality#Data Completeness|completeness]], [[Data Quality#Data Consistency|consistency]], [[Data Quality#Data Encoding|encoding]], [[Data Quality#Zero Padding|padding]], [[Data Quality#Data Augmentation, Data Labeling, and Auto-Tagging|augmentation, labeling, auto-tagging]], [[Data Quality#Batch Norm(alization) & Standardization| normalization, standardization]], and [[Data Quality#Imbalanced Data|imbalanced data]] | ||
| − | + | * [[Strategy & Tactics]] ... [[Project Management]] ... [[Best Practices]] ... [[Checklists]] ... [[Project Check-in]] ... [[Evaluation]] ... [[Evaluation - Measures|Measures]] | |
* [[What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? | Artificial Intelligence (AI)]] ... [[Machine Learning (ML)]] ... [[Deep Learning]] ... [[Neural Network]] ... [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)|Reinforcement]] ... [[Learning Techniques]] | * [[What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? | Artificial Intelligence (AI)]] ... [[Machine Learning (ML)]] ... [[Deep Learning]] ... [[Neural Network]] ... [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)|Reinforcement]] ... [[Learning Techniques]] | ||
* [[Risk, Compliance and Regulation]] ... [[Ethics]] ... [[Privacy]] ... [[Law]] ... [[AI Governance]] ... [[AI Verification and Validation]] | * [[Risk, Compliance and Regulation]] ... [[Ethics]] ... [[Privacy]] ... [[Law]] ... [[AI Governance]] ... [[AI Verification and Validation]] | ||
| − | * [[Excel]] ... [[LangChain#Documents|Documents]] ... [[Database]] ... [[Graph]] ... [[LlamaIndex]] | + | * [[Excel]] ... [[LangChain#Documents|Documents]] ... [[Database|Database; Vector & Relational]] ... [[Graph]] ... [[LlamaIndex]] |
| − | * [[Algorithm Administration#Hyperparameter|Hyperparameter]] | + | * [[Backpropagation]] ... [[Feed Forward Neural Network (FF or FFNN)|FFNN]] ... [[Forward-Forward]] ... [[Activation Functions]] ...[[Softmax]] ... [[Loss]] ... [[Boosting]] ... [[Gradient Descent Optimization & Challenges|Gradient Descent]] ... [[Algorithm Administration#Hyperparameter|Hyperparameter]] ... [[Manifold Hypothesis]] ... [[Principal Component Analysis (PCA)|PCA]] |
| − | * [[Analytics]] ... [[Visualization]] ... [[Graphical Tools for Modeling AI Components|Graphical Tools | + | * [[Analytics]] ... [[Visualization]] ... [[Graphical Tools for Modeling AI Components|Graphical Tools]] ... [[Diagrams for Business Analysis|Diagrams]] & [[Generative AI for Business Analysis|Business Analysis]] ... [[Requirements Management|Requirements]] ... [[Loop]] ... [[Bayes]] ... [[Network Pattern]] |
| − | * [[Development]] ... [[Notebooks]] ... [[Development#AI Pair Programming Tools|AI Pair Programming]] ... [[Codeless Options, Code Generators, Drag n' Drop|Codeless | + | * [[Development]] ... [[Notebooks]] ... [[Development#AI Pair Programming Tools|AI Pair Programming]] ... [[Codeless Options, Code Generators, Drag n' Drop|Codeless]] ... [[Hugging Face]] ... [[Algorithm Administration#AIOps/MLOps|AIOps/MLOps]] ... [[Platforms: AI/Machine Learning as a Service (AIaaS/MLaaS)|AIaaS/MLaaS]] |
| − | * [[Train, Validate, and Test]] | + | * [[AI Solver]] ... [[Algorithms]] ... [[Algorithm Administration|Administration]] ... [[Model Search]] ... [[Discriminative vs. Generative]] ... [[Train, Validate, and Test]] |
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_science Data Science | Wikipedia] | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_science Data Science | Wikipedia] | ||
* [https://towardsdatascience.com/introduction-to-statistics-e9d72d818745 Data science concepts you need to know! Part 1 | Michael Barber - Towards Data Science] | * [https://towardsdatascience.com/introduction-to-statistics-e9d72d818745 Data science concepts you need to know! Part 1 | Michael Barber - Towards Data Science] | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<youtube>yqmiViOXlk8</youtube> | <youtube>yqmiViOXlk8</youtube> | ||
<youtube>WrJWXxcxguc</youtube> | <youtube>WrJWXxcxguc</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = <span id="People, Process, Product... and Data"></span>People, Process, Product... and Data = | ||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=ai+People+Proces+Product+Data YouTube search...] | ||
| + | [https://www.google.com/search?q=ai+People+Proces+Product+Data ...Google search] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [https://marcuslemonis.com/business/3ps-of-business Marcus Lemonis Business Learning Center] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Marcus Lemonis businessman, television personality, and philanthropist, popularized the concept of the "Three P's of Business Success": People, Process, and Product. According to Lemonis, these three elements are the cornerstone of everything inside a business, and managing them effectively is critical to growing and succeeding in business. By focusing on these three key areas, businesses can improve their chances of success and growth. Marcus Lemonis uses these principles in his reality television show "The Profit," where he invests his own cash in struggling businesses and helps them turn around and succeed. Here's a breakdown of each of the Three P's: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <b>People</b>: the employees, customers, and other stakeholders involved in the business. Managing people effectively involves hiring the right people, training them well, and creating a positive work environment that fosters productivity and innovation. | ||
| + | * <b>Process</b>: the systems and procedures that a business uses to create and deliver its products or services. Managing processes effectively involves streamlining operations, eliminating waste, and continuously improving efficiency and quality. | ||
| + | * <b>Product</b>: the goods or services that a business offers to its customers. Managing products effectively involves developing high-quality products that meet customer needs and preferences, and continuously innovating to stay ahead of the competition. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <hr><center><b> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ... and Data | ||
| + | |||
| + | </b></center><hr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | As businesses increasingly rely on data and AI technologies to drive growth and innovation, Marcus Lemonis' strategy can be enhanced by incorporating a stronger focus on data-driven decision-making and AI integration. Here's how his Three P's framework can be adapted to this new landscape: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <b>People</b>: In addition to understanding and managing employees and customers, businesses should also focus on leveraging <i>data</i> to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends. This can help in personalizing marketing efforts, improving customer experiences, and driving customer loyalty | ||
| + | * <b>Process</b>: <i>Data</i> can play a crucial role in optimizing business processes. By collecting and analyzing <i>data</i>, businesses can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. AI technologies can be used to automate repetitive tasks, streamline operations, and enhance overall efficiency | ||
| + | * <b>Product</b>: <i>Data</i> and AI can be used to inform product development and innovation. By analyzing market trends, customer feedback, and competitor insights, businesses can identify new product opportunities, optimize existing offerings, and stay ahead of the competition | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>u2q-QF8TDGA</youtube> | ||
= What is Data Science = | = What is Data Science = | ||
| Line 97: | Line 125: | ||
<youtube>D0B1JZMCMLo</youtube> | <youtube>D0B1JZMCMLo</youtube> | ||
<b>Data Science in 30 Minutes: Predicting Content Demand with Machine Learning | <b>Data Science in 30 Minutes: Predicting Content Demand with Machine Learning | ||
| − | </b><br>Netflix is well-known for its data-driven recommendations that seek to customize the user experience for every subscriber. But data science at Netflix extends far beyond that - from optimizing streaming and content caching to informing decisions about the TV shows and films available on the service. The talk covered work done by Becky and the Content Data Science team at Netflix, which seeks to evaluate where Netflix should spend their next content dollar using machine learning and [[Predictive Analytics|predictive models]]. The Data Incubator is a data science education company based in NYC, DC, and SF with both corporate training as well as recruiting services. For data science corporate training, we offer customized, in-house corporate training solutions in data and analytics. For data science hiring, we run a free 8 week fellowship training PhDs to become data scientists. The fellowship selects 2% of its 2000+ quarterly applicants and is free for Fellows. Hiring companies (including EBay, Capital One, Pfizer) pay a recruiting fee only if they successfully hire. You can read about us on Harvard Business Review, VentureBeat, or The Next Web, or read about our alumni at LinkedIn, Palantir or the NYTimes. About the speakers: | + | </b><br>Netflix is well-known for its data-driven recommendations that seek to customize the user experience for every subscriber. But data science at Netflix extends far beyond that - from optimizing streaming and content caching to informing decisions about the TV shows and films available on the service. The talk covered work done by Becky and the Content Data Science team at Netflix, which seeks to evaluate where Netflix should spend their next content dollar using machine learning and [[Predictive Analytics|predictive models]]. The Data Incubator is a data science education company based in NYC, DC, and SF with both corporate training as well as recruiting services. For data science corporate training, we offer customized, in-house corporate training solutions in data and analytics. For data science hiring, we run a free 8 week fellowship training PhDs to become data scientists. The fellowship selects 2% of its 2000+ quarterly applicants and is free for Fellows. Hiring companies (including EBay, Capital One, Pfizer) pay a recruiting fee only if they successfully hire. You can read about us on Harvard Business Review, VentureBeat, or The Next Web, or read about our alumni at LinkedIn, [[Palantir]] or the NYTimes. About the speakers: Dr. Becky Tucker is a Senior Data Scientist at Netflix, a streaming media and entertainment company based in Los Gatos, CA. She holds a PhD in Physics from Caltech. At Netflix, Becky works on models that predict the demand for TV shows and movies. Michael Li founded The Data Incubator, a New York-based training program that turns talented PhDs from academia into workplace-ready data scientists and quants. The program is free to Fellows, employers engage with the Incubator as hiring partners. |
| − | Dr. Becky Tucker is a Senior Data Scientist at Netflix, a streaming media and entertainment company based in Los Gatos, CA. She holds a PhD in Physics from Caltech. At Netflix, Becky works on models that predict the demand for TV shows and movies. | ||
| − | Michael Li founded The Data Incubator, a New York-based training program that turns talented PhDs from academia into workplace-ready data scientists and quants. The program is free to Fellows, employers engage with the Incubator as hiring partners. | ||
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| Line 222: | Line 248: | ||
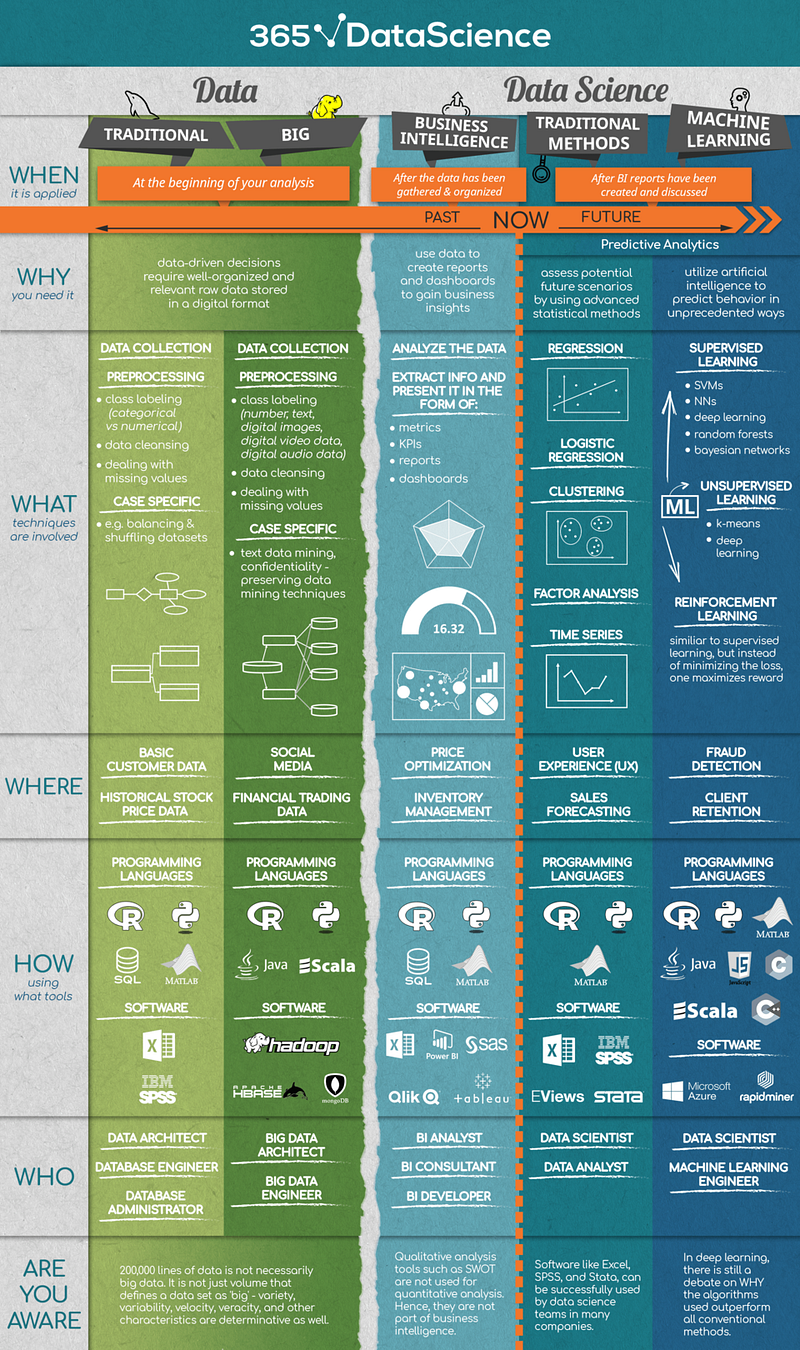
[https://towardsdatascience.com/the-what-where-and-how-of-data-science-6dda1af98671 The What, Where and How of Data Science | Iliya Valchanov] | [https://towardsdatascience.com/the-what-where-and-how-of-data-science-6dda1af98671 The What, Where and How of Data Science | Iliya Valchanov] | ||
| − | <img src="https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1*z5VIYRsdFI-b8WPVyFPeWQ.png" width=" | + | <img src="https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1*z5VIYRsdFI-b8WPVyFPeWQ.png" width="1000"> |
Latest revision as of 20:50, 26 April 2024
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- Data Science ... Governance ... Preprocessing ... Exploration ... Interoperability ... Master Data Management (MDM) ... Bias and Variances ... Benchmarks ... Datasets
- Data Quality ...validity, accuracy, cleaning, completeness, consistency, encoding, padding, augmentation, labeling, auto-tagging, normalization, standardization, and imbalanced data
- Strategy & Tactics ... Project Management ... Best Practices ... Checklists ... Project Check-in ... Evaluation ... Measures
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) ... Machine Learning (ML) ... Deep Learning ... Neural Network ... Reinforcement ... Learning Techniques
- Risk, Compliance and Regulation ... Ethics ... Privacy ... Law ... AI Governance ... AI Verification and Validation
- Excel ... Documents ... Database; Vector & Relational ... Graph ... LlamaIndex
- Backpropagation ... FFNN ... Forward-Forward ... Activation Functions ...Softmax ... Loss ... Boosting ... Gradient Descent ... Hyperparameter ... Manifold Hypothesis ... PCA
- Analytics ... Visualization ... Graphical Tools ... Diagrams & Business Analysis ... Requirements ... Loop ... Bayes ... Network Pattern
- Development ... Notebooks ... AI Pair Programming ... Codeless ... Hugging Face ... AIOps/MLOps ... AIaaS/MLaaS
- AI Solver ... Algorithms ... Administration ... Model Search ... Discriminative vs. Generative ... Train, Validate, and Test
- Data Science | Wikipedia
- Data science concepts you need to know! Part 1 | Michael Barber - Towards Data Science
- Data Fallacies to Avoid - An Illustrated Collection of Mistakes People Often Make When Analyzing Data - Tom Bransby
Contents
Data Strategy
People, Process, Product... and Data
YouTube search... ...Google search
Marcus Lemonis businessman, television personality, and philanthropist, popularized the concept of the "Three P's of Business Success": People, Process, and Product. According to Lemonis, these three elements are the cornerstone of everything inside a business, and managing them effectively is critical to growing and succeeding in business. By focusing on these three key areas, businesses can improve their chances of success and growth. Marcus Lemonis uses these principles in his reality television show "The Profit," where he invests his own cash in struggling businesses and helps them turn around and succeed. Here's a breakdown of each of the Three P's:
- People: the employees, customers, and other stakeholders involved in the business. Managing people effectively involves hiring the right people, training them well, and creating a positive work environment that fosters productivity and innovation.
- Process: the systems and procedures that a business uses to create and deliver its products or services. Managing processes effectively involves streamlining operations, eliminating waste, and continuously improving efficiency and quality.
- Product: the goods or services that a business offers to its customers. Managing products effectively involves developing high-quality products that meet customer needs and preferences, and continuously innovating to stay ahead of the competition.
... and Data
As businesses increasingly rely on data and AI technologies to drive growth and innovation, Marcus Lemonis' strategy can be enhanced by incorporating a stronger focus on data-driven decision-making and AI integration. Here's how his Three P's framework can be adapted to this new landscape:
- People: In addition to understanding and managing employees and customers, businesses should also focus on leveraging data to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends. This can help in personalizing marketing efforts, improving customer experiences, and driving customer loyalty
- Process: Data can play a crucial role in optimizing business processes. By collecting and analyzing data, businesses can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. AI technologies can be used to automate repetitive tasks, streamline operations, and enhance overall efficiency
- Product: Data and AI can be used to inform product development and innovation. By analyzing market trends, customer feedback, and competitor insights, businesses can identify new product opportunities, optimize existing offerings, and stay ahead of the competition
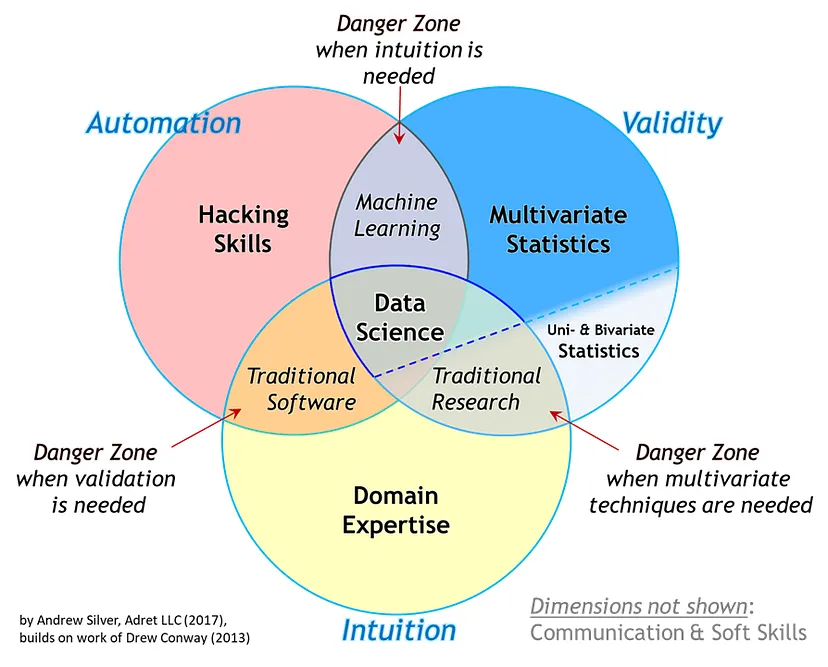
What is Data Science
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Analysis using ChatGPT
YouTube search... ...Google search
|
|
|
|
Structured, Semi-Structured, and Unstructured
YouTube search... ...Google search
- What’s The Difference Between Structured, Semi-Structured And Unstructured Data? | Bernard Marr - Forbes
- Difference between Structured, Semi-structured and Unstructured data | Ashish Vishwakarma - GeeksForGeeks
|
|
|
|
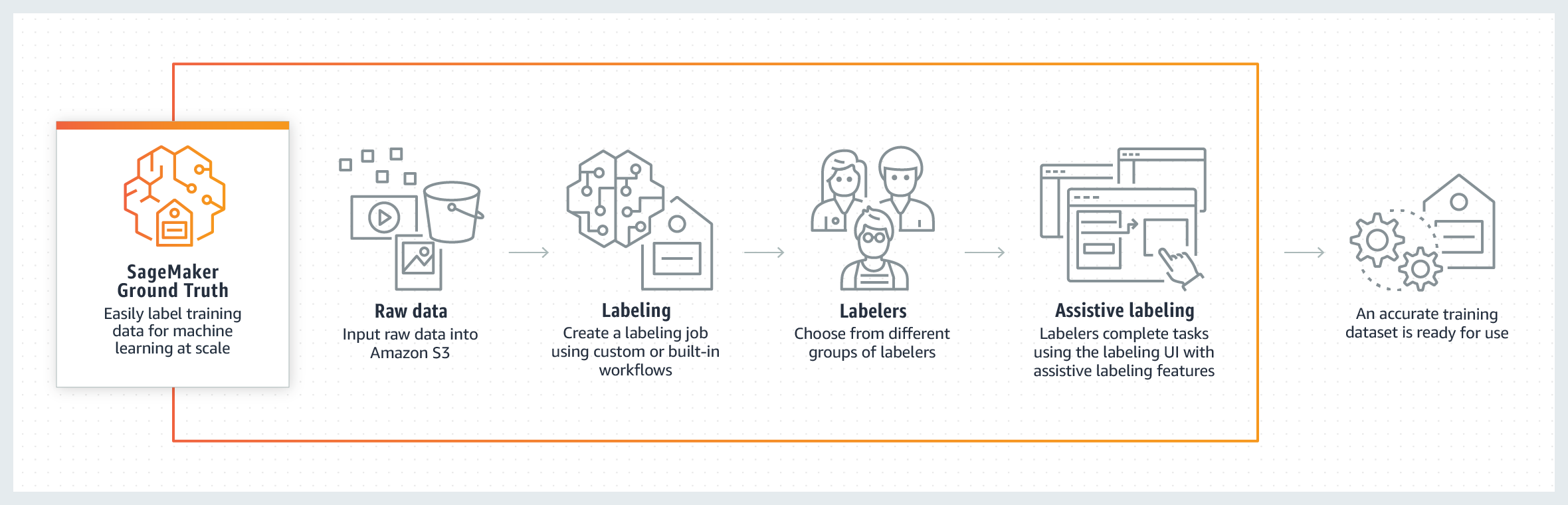
Ground Truth
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Ground Truth Gold — Intelligent data labeling and annotation | The Hive - Medium
- Ground Truth | SageMaker - Amazon
Ground truth is a term used in various fields to refer to information provided by direct observation (i.e. empirical evidence) as opposed to information provided by inference. "Ground truth" may be seen as a conceptual term relative to the knowledge of the truth concerning a specific question. It is the ideal expected result. Wikipedia
You might have heard the term “ground truth” rolling around the ML/AI space, but what does it mean? Newsflash: Ground truth isn’t true. It’s an ideal expected result (according to the people in charge). In other words, it’s a way to boil down the opinions of project owners by creating a set of examples with output labels that those owners found palatable. It might involve hand-labeling example datapoints or putting sensors “on the ground” (in a curated real-world location) to collect desirable answer data for training your system. What is “Ground Truth” in AI? (A warning.) | Cassie Kozyrkov - Towards Data Science
|
|
The What, Where and How of Data Science | Iliya Valchanov