Difference between revisions of "Cybersecurity"
m |
m |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
* [[Watch me Build a Cybersecurity Startup]] | [[Creatives#Siraj Raval|Siraj Raval]] | * [[Watch me Build a Cybersecurity Startup]] | [[Creatives#Siraj Raval|Siraj Raval]] | ||
* [https://fidelissecurity.com/resource/podcast/machine-learning-capabilities-ndr/ Machine-Learning Capabilities within Network Detection & Response (NDR) - Podcast | Fidelis Cybersecurity - COO, Craig Harber, and Data Science Manager, Abhishek Sharma] ...[https://fidelissecurity.com/resources/edu/network-security/extended-detection-response-xdr/ Extended Detection & Response (NDR)] | * [https://fidelissecurity.com/resource/podcast/machine-learning-capabilities-ndr/ Machine-Learning Capabilities within Network Detection & Response (NDR) - Podcast | Fidelis Cybersecurity - COO, Craig Harber, and Data Science Manager, Abhishek Sharma] ...[https://fidelissecurity.com/resources/edu/network-security/extended-detection-response-xdr/ Extended Detection & Response (NDR)] | ||
| − | * [https://bigbear.ai/ BigBear.AI] ... AI-powered analytics and cyber solutions | + | * [https://bigbear.ai/ BigBear.AI] ... AI-powered [[analytics]] and cyber solutions |
* [https://techxplore.com/news/2023-02-ai-based-tool-ddos.html A new AI-based tool to detect DDoS attacks | Ingrid Fadelli - TechXplore] | * [https://techxplore.com/news/2023-02-ai-based-tool-ddos.html A new AI-based tool to detect DDoS attacks | Ingrid Fadelli - TechXplore] | ||
* [https://media.defense.gov/2023/Feb/22/2003165170/-1/-1/0/CSI_BEST_PRACTICES_FOR_SECURING_YOUR_HOME_NETWORK.PDF Cybersecurity Information Sheet - Best Practices for Securing Your Home Network | US National Security Agency (NSA)] | * [https://media.defense.gov/2023/Feb/22/2003165170/-1/-1/0/CSI_BEST_PRACTICES_FOR_SECURING_YOUR_HOME_NETWORK.PDF Cybersecurity Information Sheet - Best Practices for Securing Your Home Network | US National Security Agency (NSA)] | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
* Malware detection: AI can be used to detect malware by analyzing its behavior and comparing it to known malware signatures. | * Malware detection: AI can be used to detect malware by analyzing its behavior and comparing it to known malware signatures. | ||
* Network intrusion detection: AI can be used to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access or data exfiltration. | * Network intrusion detection: AI can be used to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access or data exfiltration. | ||
| − | * User behavior analytics: AI can be used to track user behavior and identify suspicious activity, such as clicking on phishing links or downloading malicious files. | + | * User behavior [[analytics]]: AI can be used to track user behavior and identify suspicious activity, such as clicking on phishing links or downloading malicious files. |
* Vulnerability scanning: AI can be used to scan systems for known vulnerabilities. | * Vulnerability scanning: AI can be used to scan systems for known vulnerabilities. | ||
* Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR): AI can be used to automate security tasks, such as incident response and remediation. | * Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR): AI can be used to automate security tasks, such as incident response and remediation. | ||
| Line 205: | Line 205: | ||
<youtube>R9lkyJL2LlQ</youtube> | <youtube>R9lkyJL2LlQ</youtube> | ||
<b>How big data and AI saved the day: critical IP almost walked out the door | <b>How big data and AI saved the day: critical IP almost walked out the door | ||
| − | </b><br>Cybersecurity threats have evolved beyond what traditional SIEMs and firewalls can detect. We present case studies highlighting how: An advanced manufacturer was able to identify new insider threats, enabling them to protect their IP A media company’s security operations center was able to verify they weren’t the source of a high-profile media leak. The common thread across these real-world case studies is how businesses can expand their threat analysis using security analytics powered by artificial intelligence in a big data environment. Cybersecurity threats increasingly require the aggregation and analysis of multiple data sources. Siloed tools and technologies serve their purpose, but can’t be applied to look across the ever-growing variety and volume of traffic. Big data technologies are a proven solution to aggregating and analyzing data across enormous volumes and varieties of data in a scalable way. However, as security professionals well know, more data doesn’t mean more leads or detection. In fact, all too often more data means slower threat hunting and more missed incidents. The solution is to leverage advanced analytical methods like machine learning. Machine learning is a powerful mathematical approach that can learn patterns in data to identify relevant areas to focus. By applying these methods, we can automatically learn baseline activity and detect deviations across all data sources to flag high-risk entities that behave differently from their peers or past activity. Speaker Roy Wilds Principal Data Scientist Interset | + | </b><br>Cybersecurity threats have evolved beyond what traditional SIEMs and firewalls can detect. We present case studies highlighting how: An advanced manufacturer was able to identify new insider threats, enabling them to protect their IP A media company’s security operations center was able to verify they weren’t the source of a high-profile media leak. The common thread across these real-world case studies is how businesses can expand their threat analysis using security [[analytics]] powered by artificial intelligence in a big data environment. Cybersecurity threats increasingly require the aggregation and analysis of multiple data sources. Siloed tools and technologies serve their purpose, but can’t be applied to look across the ever-growing variety and volume of traffic. Big data technologies are a proven solution to aggregating and analyzing data across enormous volumes and varieties of data in a scalable way. However, as security professionals well know, more data doesn’t mean more leads or detection. In fact, all too often more data means slower threat hunting and more missed incidents. The solution is to leverage advanced analytical methods like machine learning. Machine learning is a powerful mathematical approach that can learn patterns in data to identify relevant areas to focus. By applying these methods, we can automatically learn baseline activity and detect deviations across all data sources to flag high-risk entities that behave differently from their peers or past activity. Speaker Roy Wilds Principal Data Scientist Interset |
|} | |} | ||
|<!-- M --> | |<!-- M --> | ||
| Line 248: | Line 248: | ||
<youtube>PpiO0S-OQS0</youtube> | <youtube>PpiO0S-OQS0</youtube> | ||
<b>Thwart Fraud Using Graph Enhanced Artificial Intelligence | <b>Thwart Fraud Using Graph Enhanced Artificial Intelligence | ||
| − | </b><br>Amy Hodler, Analytics Program Manager at Neo4j and Scott Heath, Graph Practice Lead at Expero: This webinar will help you understand how successful financial services, banks and retailers are using graph technology and [[embedding]] intelligence to quickly identify risk and fraud patterns as they evolve. Fraudsters are now using more sophisticated and dynamic methods for credit card, money laundering and other types of fraud. Leveraging graph technology will allow you to see beyond individual data points and uncover difficult-to-detect patterns. Hear how to maximize time and resources with graph technology vs. traditional approaches. | + | </b><br>Amy Hodler, [[Analytics]] Program Manager at Neo4j and Scott Heath, Graph Practice Lead at Expero: This webinar will help you understand how successful financial services, banks and retailers are using graph technology and [[embedding]] intelligence to quickly identify risk and fraud patterns as they evolve. Fraudsters are now using more sophisticated and dynamic methods for credit card, money laundering and other types of fraud. Leveraging graph technology will allow you to see beyond individual data points and uncover difficult-to-detect patterns. Hear how to maximize time and resources with graph technology vs. traditional approaches. |
|} | |} | ||
|<!-- M --> | |<!-- M --> | ||
| Line 273: | Line 273: | ||
|| | || | ||
<youtube>m7htZ7PWQE8</youtube> | <youtube>m7htZ7PWQE8</youtube> | ||
| − | <b>Leveraging Machine Learning for Fraud Analytics (Cloud Next '18) | + | <b>Leveraging Machine Learning for Fraud [[Analytics]] (Cloud Next '18) |
| − | </b><br>We will showcase how we can build advance accelerators for Fraud Analytics solutions leveraging [[Google]] Stack. We will demonstrate how these accelerators fill the gaps that exists within other Fraud Analytics solutions currently available in the market today and how it can offer several benefits including real-time processing, increased accuracy, scalable database and high performance. MLAI102 Event schedule https://g.co/next18 Watch more Machine Learning & AI sessions here → https://bit.ly/2zGKfcg Next ‘18 All Sessions playlist https://bit.ly/Allsessions Subscribe to the [[Google]] Cloud channel! → https://bit.ly/NextSub | + | </b><br>We will showcase how we can build advance accelerators for Fraud [[Analytics]] solutions leveraging [[Google]] Stack. We will demonstrate how these accelerators fill the gaps that exists within other Fraud [[Analytics]] solutions currently available in the market today and how it can offer several benefits including real-time processing, increased accuracy, scalable database and high performance. MLAI102 Event schedule https://g.co/next18 Watch more Machine Learning & AI sessions here → https://bit.ly/2zGKfcg Next ‘18 All Sessions playlist https://bit.ly/Allsessions Subscribe to the [[Google]] Cloud channel! → https://bit.ly/NextSub |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
Revision as of 07:54, 9 July 2023
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- Cybersecurity ... OSINT ... Frameworks ... References ... Offense ... NIST ... DHS ... Screening ... Law Enforcement ... Government ... Defense ... Lifecycle Integration ... Products ... Evaluating
- Risk, Compliance and Regulation ... Ethics ... Privacy ... Law ... AI Governance ... AI Verification and Validation
- Prompt Injection Attack
- (Artificial) Immune System
- 5G Security
- Time ... PNT ... GPS ... Retrocausality ... Delayed Choice Quantum Eraser ... Quantum
- Development ... Notebooks ... AI Pair Programming ... Codeless, Generators, Drag n' Drop ... AIOps/MLOps ... AIaaS/MLaaS
- Games - Security
- Useful Models ...find outliers:
- Physical Layer Security (PLS)
- Time ... Retrocausality ... Delayed Choice Quantum Eraser ... Quantum
- Government’s AI Odyssey - A Candid Poll on AI and Machine Learning in the Federal Government | Government Business Council - AWS
- Bayesian Poisoning is a technique used by e-mail spammers to attempt to degrade the effectiveness of spam filters that rely on Bayesian spam filtering
- Detecting Malicious Requests with Keras & TensorFlow | Adam Kusey - Medium
- Best security software: How 12 cutting-edge tools tackle today's threats | CSO
- Excel ... Documents ... Database ... Graph ... LlamaIndex
- Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA)Is Trying Keep Adversaries From Corrupting AI Tools ... Could cyber adversaries be training the government’s artificial intelligence tools to fail? | Jack Corrigan - Nextgov
- TrojAI - Office of the Director of National Intelligence Office: Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity FedBizOpps.gov predict whether AI systems have been corrupted through so-called “Trojan attacks.”
- Adversarial Attacks on Graph Convolutional Network (GCN), Graph Neural Networks (Graph Nets), Geometric Deep Learning
- Breaking Down the Tencent 2018 Cybersecurity Report
- Chronicle combines all the best parts of Google and X culture
- Fraud and Anomaly Detection | Chris Nicholson - A.I. Wiki pathmind
- The Cyber Security Evaluation Tool (CSET®) | National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center ...provides a systematic, disciplined, and repeatable approach for evaluating an organization’s security posture
- Cyber Command, Microsoft take action against Trickbot botnet before Election Day | Shannon Vavra - cyberscoop
- An update on disruption of Trickbot Tom Burt | Microsoft ...The seven remaining servers are not traditional command-and-control servers but rather Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- FBI warning: Trickbot and ransomware attackers plan big hit on US hospitals | Liam Tung - ZDNet ...The FBI, CISA, HHS warning comes two weeks after Microsoft's partial takedown of the Trickbot botnet.
- European ransomware group strikes US hospital networks, analysts warn | Sean Lyngaas - cyberscoop ..UNC1878 has been deploying Ryuk ransomware and taking multiple hospital IT networks offline ...suspected ransomware attacks this week on hospitals in New York, Oregon and Vermont, and perhaps other states.
- Cybersecurity as we know it will be 'a thing of the past in the next decade,' says Cloudflare's COO, as security moves towards a 'water treatment' model | Rosalie Chan - Business Insider ... cybersecurity systems will weed out bad actors earlier in their attacks
- Watch me Build a Cybersecurity Startup | Siraj Raval
- Machine-Learning Capabilities within Network Detection & Response (NDR) - Podcast | Fidelis Cybersecurity - COO, Craig Harber, and Data Science Manager, Abhishek Sharma ...Extended Detection & Response (NDR)
- BigBear.AI ... AI-powered analytics and cyber solutions
- A new AI-based tool to detect DDoS attacks | Ingrid Fadelli - TechXplore
- Cybersecurity Information Sheet - Best Practices for Securing Your Home Network | US National Security Agency (NSA)
- GATE | Gate CyberTech ... defeat wiretapping, peeking, keylogging, phishing, and dictionary attacks ... Demo
- Generative AI
- ChatGPT is enabling script kiddies to write functional malware | Dan Goodwin - ARS Technica ...For a beta, ChatGPT isn't all that bad at writing fairly decent malware.
- ChatGPT Used to Develop New Malicious Tools | Check Point Research
- ChatGPT Creates Polymorphic Malware | Alessandro Mascellino - InfoSecurity ... researchers at CyberArk
- Hackers are selling a service that bypasses ChatGPT restrictions on malware ChatGPT | Dan Goodin - ARS Technica... restrictions on the creation of illicit content are easy to circumvent.
- AI Can Crack Most Common Passwords In Less Than A Minute | Zhiye Liu - Tom's Hardware
- Integrating ChatGPT & Generative AI Within Cybersecurity Best Practices | Mani Nagothu - Sentinel One
- Google brings generative AI to cybersecurity | Kyle Wiggers - TechCrunch ...Google's Cloud Security AI Workbench, a cybersecurity suite powered by a specialized “security” AI language model called Sec-PaLM. An offshoot of Google’s PaLM model
AI can assist with cybersecurity functions in many ways. It can reinforce cyber threat intelligence by searching for characteristics of cyberattacks, strengthening defenses, analyzing data to authenticate users, and discovering clues as to the identity of specific cyberattackers. AI can also analyze massive quantities of risk data to speed up response times and augment under-resourced security operations. AI technologies like machine learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP) can provide rapid insights to cut through the noise of daily alerts, drastically reducing response times.
AI can explain the behavior of malicious scripts
AI can help address many challenges in cybersecurity, such as the massive amounts of data that no amount of humans can help protect and the hundreds and thousands of devices to protect a single organization. AI improves its knowledge to “understand” cybersecurity threats and cyber risk by consuming billions of data artifacts. It analyzes relationships between threats like malicious files, suspicious IP addresses or insiders in seconds or minutes. In addition, experts can learn a lot about vulnerabilities in their network or software and the threat actors who try to attack it by using AI to set up honeypots on decoy servers.
AI is being used in a variety of ways to improve cybersecurity. Some of the most common applications of AI in cybersecurity include:
- Malware detection: AI can be used to detect malware by analyzing its behavior and comparing it to known malware signatures.
- Network intrusion detection: AI can be used to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access or data exfiltration.
- User behavior analytics: AI can be used to track user behavior and identify suspicious activity, such as clicking on phishing links or downloading malicious files.
- Vulnerability scanning: AI can be used to scan systems for known vulnerabilities.
- Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR): AI can be used to automate security tasks, such as incident response and remediation.
Contents
Risk-based Vulnerability Management (RBVM)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fraud Detection
- Introduction to Fraud Detection Systems | Miguel Gonzalez-Fierro, Microsoft
- AI for Health Insurance Fraud Detection – Current Applications | Niccolo Mejia
|
|
|
|
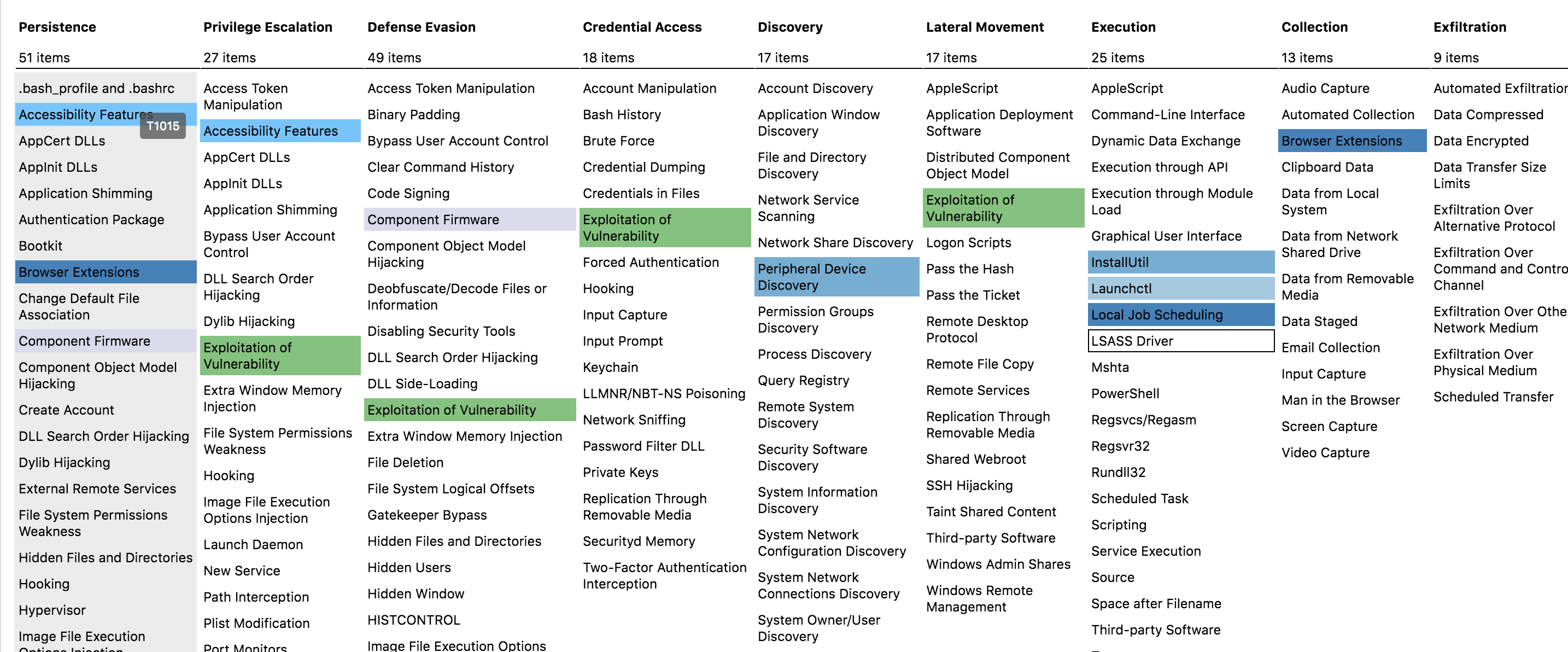
MITRE ATT&CK™
Youtube search... ...Google search
- ATT&CK™ Navigator | MITRE ...measure your threat detection
- ATT&CK™ Homepage | MITRE
- ATT&CK™ Resources | MITRE
- Cybersecurity Frameworks, Architectures & Roadmaps
- MITRE ATT&CK™ Framework: Everything You Need to Know | Jeff Petters - Varonis
- DETT&CT: MAPPING YOUR BLUE TEAM TO MITRE ATT&CK™ | Marcus Bakker and Ruben Bouman - MB Secure ...DEtect Tactics, Techniques & Combat Threats
- Remapping Red Canary with ATT&CK sub-techniques | B. Donohue, K. Nickels, and M. Graeber - Atomic Red Team; a library of simple tests that every security team can execute to test their defenses.
- Using the OODA Loop - Purple Team with Cybersecurity
knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations. The ATT&CK™ knowledge base is used as a foundation for the development of specific threat models and methodologies in the private sector, in government, and in the cybersecurity product and service community.

|
|
|
|
|
|
Open Source Tools
Youtube search... ...Google search
- National Security Agency (NSA)
- Ghidra A software reverse engineering (SRE) suite of tools developed by NSA's Research Directorate in support of the Cybersecurity mission Ghidra.org
- The NSA Makes Ghidra, a Powerful Cybersecurity Tool, Open Source | Lily Hay Newman - Wired
- DataWave is an ingest/query framework that leverages Apache Accumulo to provide fast, secure data access.
- Free Open Source Software Cybersecurity | DataShield
- 47 powerful open-source app sec tools you should consider | Mike Perrow - Vertica - TechBeacon
|
|
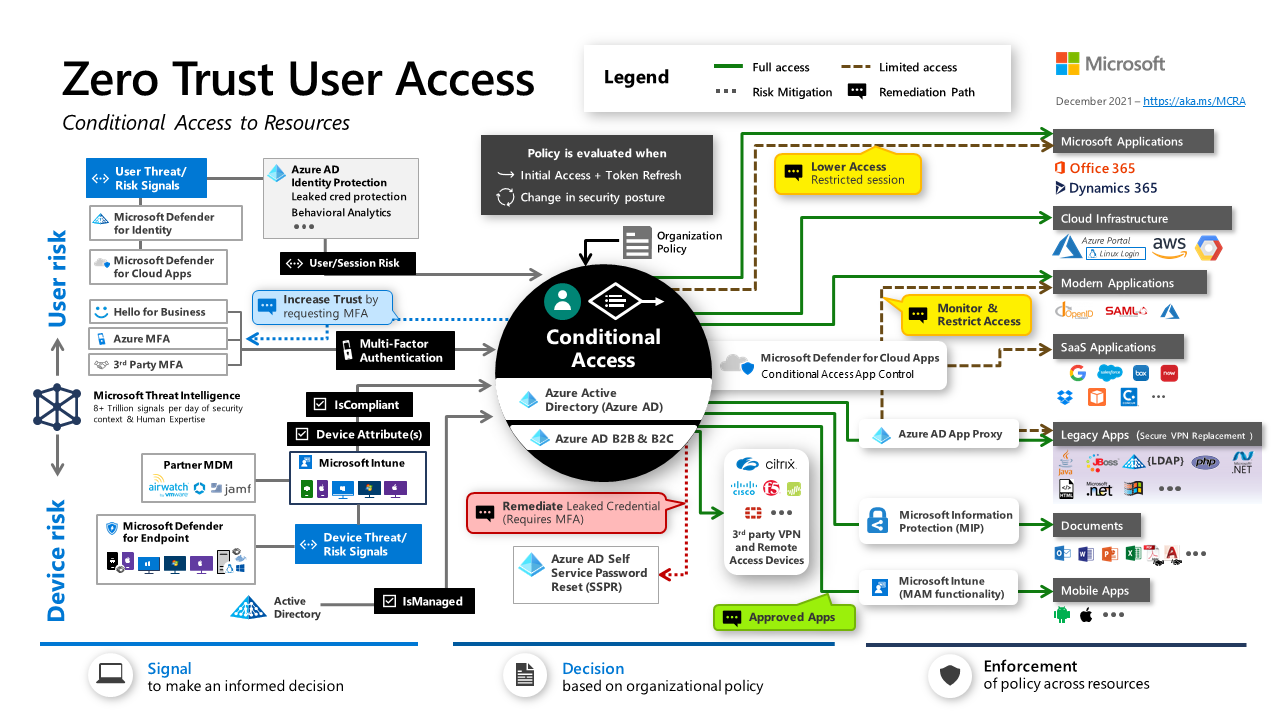
Zero Trust
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- Zero Trust Architecture | NIST
- Conditional Access design principles and dependencies | Microsoft
- Zero trust security model | Wikipedia
Zero Trust architecture is a cybersecurity approach that assumes breaches will occur and uses risk-based access controls to limit the damage from an attack. Instead of only guarding an organization’s perimeter, Zero Trust architecture protects each file, email, and network by authenticating every identity and device. Rather than just securing one network, Zero Trust architecture also helps secure remote access, personal devices, and third-party apps. The principles of Zero Trust are: Verify explicitly, Use least privileged access, Assume breach and Require end-to-end encryption.
Part of... software-defined networking (SD-WAN) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). SASE delivers wide-area networking with cybersecurity both on-site and in the cloud as DoD expands its reliance on cloud data storage. One of the key tenants of zero trust involves identity. Thunderdome will use identity verification, including public key infrastructure (PKI), which uses a certificate to validate data being sent from one point to another, and identity credentialing and access management (ICAM). ICAM verifies a person’s identity and links them to their allowed access privileges. - Thunderdome hits its targets, DISA moves to next phase of zero trust | Alexandra Lohr - Federal New Network
|
|
|
|
AI-Driven Patch Management
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- 5 ways AI-driven patch management is driving the future of cybersecurity | Louis Columbus - VentureBeat
- Revolutionizing Patch Management: Meeting Modern Infrastructure and Workspace Needs | E-SPIN
Also, AI models help in the automatic analysis of patch risk and carry out the complete life-cycle of each version release. AI-driven patch management helps in automatically identifying new patch or application release with the help of AI-models. Based on this automated discovery of the new patch, the new version update will take place across all servers and applications. AI-based patch management relies in part on algorithms that need a continual stream of data in order to keep “learning” and assessing patch vulnerabilities. There are several benefits of using AI in patch management. AI-driven patch management enables you to automate your entire application version change management. This automation is made possible with the use of advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. Also, AI models help in the automatic analysis of patch risk and carry out the complete life-cycle of each version release. Automating patch management while capitalizing on diverse datasets and integrating it into an RBVM platform is a perfect use case of AI in cybersecurity. Leading AI-based patch management systems can interpret vulnerability assessment telemetry and prioritize risks by patch type, system and endpoint.
There are several companies that use AI-driven patch management technology. Some of these companies include Atera, Automox, BMC Client Management Patch powered by Ivanti, Canonical, ConnectWise, Flexera, GFI, ITarian, Ivanti, Jamf, Kaseya, ManageEngine, N-able, NinjaOne, SecPod, SysWard, Syxsense and Tanium
Asset Risk Management (ARM): Physical Layer
- Sepio ... Asset Risk Management that works for you. Manage your asset risks with granular controls based on true Asset DNA
- Sepio and NIST Cybersecurity Framework Compliance
The Sepio solution compares an asset’s DNA profile and Asset Risk Factor (ARF) score with your preset rules and directly connects it to an enforced policy. Any changes to an asset are accounted for, and the appropriate policy applied. Assets that breach the preset rules or get recognized as known attack tools by Sepio’s are immediately blocked, enabling instant and automated risk mitigation.Sepio’s patented machine learning technology revolutionizes asset visibility across your enterprise network and endpoints, providing effortless and continuous monitoring down to the peripherals. Sepio’s Asset DNA accurately identifies all assets based on their physical nature, ensuring that your organization can trust each device’s identity and detect any unauthorized or rogue devices. From unseen and actively evasive assets to spoofed devices, compromised hardware, and unauthorized assets connected to your network, Sepio’s improved asset visibility feature eliminates blind spots and provides comprehensive visibility into your IT/OT/IoT/peripheral assets. In addition to enhancing security, asset visibility is crucial for compliance with cybersecurity regulations. With Asset DNA, organizations can quickly identify any non-compliant devices throughout their network, down to the endpoint’s peripherals.
Data Center Security
Youtube search... ...Google search
|
|
|
|
|
|