Difference between revisions of "Loop"
m |
m (→Feedback Loop - Creating Consciousness) |
||
| (46 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
* [[Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Learning]] | * [[Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Learning]] | ||
* [[What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? | Artificial Intelligence (AI)]] ... [[Machine Learning (ML)]] ... [[Deep Learning]] ... [[Neural Network]] ... [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)|Reinforcement]] ... [[Learning Techniques]] | * [[What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? | Artificial Intelligence (AI)]] ... [[Machine Learning (ML)]] ... [[Deep Learning]] ... [[Neural Network]] ... [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)|Reinforcement]] ... [[Learning Techniques]] | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Perspective]] ... [[Context]] ... [[In-Context Learning (ICL)]] ... [[Transfer Learning]] ... [[Out-of-Distribution (OOD) Generalization]] |
| + | * [[Causation vs. Correlation]] ... [[Autocorrelation]] ...[[Convolution vs. Cross-Correlation (Autocorrelation)]] | ||
* [[Embedding]] ... [[Fine-tuning]] ... [[Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)|RAG]] ... [[Agents#AI-Powered Search|Search]] ... [[Clustering]] ... [[Recommendation]] ... [[Anomaly Detection]] ... [[Classification]] ... [[Dimensional Reduction]]. [[...find outliers]] | * [[Embedding]] ... [[Fine-tuning]] ... [[Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)|RAG]] ... [[Agents#AI-Powered Search|Search]] ... [[Clustering]] ... [[Recommendation]] ... [[Anomaly Detection]] ... [[Classification]] ... [[Dimensional Reduction]]. [[...find outliers]] | ||
* [[Algorithm Administration]] | * [[Algorithm Administration]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
* [[What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? | Artificial Intelligence (AI)]] ... [[Generative AI]] ... [[Machine Learning (ML)]] ... [[Deep Learning]] ... [[Neural Network]] ... [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)|Reinforcement]] ... [[Learning Techniques]] | * [[What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? | Artificial Intelligence (AI)]] ... [[Generative AI]] ... [[Machine Learning (ML)]] ... [[Deep Learning]] ... [[Neural Network]] ... [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)|Reinforcement]] ... [[Learning Techniques]] | ||
* [[Conversational AI]] ... [[ChatGPT]] | [[OpenAI]] ... [[Bing/Copilot]] | [[Microsoft]] ... [[Gemini]] | [[Google]] ... [[Claude]] | [[Anthropic]] ... [[Perplexity]] ... [[You]] ... [[phind]] ... [[Ernie]] | [[Baidu]] | * [[Conversational AI]] ... [[ChatGPT]] | [[OpenAI]] ... [[Bing/Copilot]] | [[Microsoft]] ... [[Gemini]] | [[Google]] ... [[Claude]] | [[Anthropic]] ... [[Perplexity]] ... [[You]] ... [[phind]] ... [[Ernie]] | [[Baidu]] | ||
| + | * [[Center and Circle Playbook]] ... 8-step stability guide | ||
* [https://medium.com/intuitionmachine/process-patterns-loops-and-emergence-dff1292cfa78 Process Patterns, Loops and Emergence | Carlos E. Perez - Medium] | * [https://medium.com/intuitionmachine/process-patterns-loops-and-emergence-dff1292cfa78 Process Patterns, Loops and Emergence | Carlos E. Perez - Medium] | ||
| Line 53: | Line 55: | ||
<youtube>ndQPdhf30rY</youtube> | <youtube>ndQPdhf30rY</youtube> | ||
<b>Mindset: OODA Loop by [[Creatives#John Richard Boyd|John Boyd]] | <b>Mindset: OODA Loop by [[Creatives#John Richard Boyd|John Boyd]] | ||
| − | </b><br>OODA Loop is an acronym which stands for Observe, Orient, Decide and Act. In this video I provide a historical, academic, and practical perspective to help shed some light on the topic. [[Creatives#John Richard Boyd|John Boyd]] is one of the greatest military strategist to have lived, and to understand OODA Loop it's import to put it into [[context]]. If you have any questions or have something to add, please comment down below. Like this content? Consider supporting me on Patreon where you will get exclusive access to unpublished videos, behind the scenes, coupons, and the satisfaction of supporting pro-freedom content. https://www.patreon.com/WeRunGuns Please LIKE, SHARE, and SUBSCRIBE if you enjoyed! | + | </b><br>OODA Loop is an acronym which stands for Observe, Orient, Decide and Act. In this video I provide a historical, academic, and practical [[perspective]] to help shed some light on the topic. [[Creatives#John Richard Boyd|John Boyd]] is one of the greatest military strategist to have lived, and to understand OODA Loop it's import to put it into [[context]]. If you have any questions or have something to add, please comment down below. Like this content? Consider supporting me on Patreon where you will get exclusive access to unpublished videos, behind the scenes, coupons, and the satisfaction of supporting pro-freedom content. https://www.patreon.com/WeRunGuns Please LIKE, SHARE, and SUBSCRIBE if you enjoyed! |
|} | |} | ||
|<!-- M --> | |<!-- M --> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 71: | ||
[https://www.google.com/search?q=loop+feedback+machine+learning+reinforcement ...Google search] | [https://www.google.com/search?q=loop+feedback+machine+learning+reinforcement ...Google search] | ||
| + | * [[Gaming]] ... [[Game-Based Learning (GBL)]] ... [[Games - Security|Security]] ... [[Game Development with Generative AI|Generative AI]] ... [[Metaverse#Games - Metaverse|Games - Metaverse]] ... [[Games - Quantum Theme|Quantum]] ... [[Game Theory]] ... [[Game Design | Design]] | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feedback Feedback | Wikipedia] | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feedback Feedback | Wikipedia] | ||
* [https://www.clarifai.com/blog/closing-the-loop-how-feedback-loops-help-to-maintain-quality-long-term-ai-results Closing the Loop: How Feedback Loops Help to Maintain Quality Long-Term AI Results | Natalie Fletcher - Clarifai] | * [https://www.clarifai.com/blog/closing-the-loop-how-feedback-loops-help-to-maintain-quality-long-term-ai-results Closing the Loop: How Feedback Loops Help to Maintain Quality Long-Term AI Results | Natalie Fletcher - Clarifai] | ||
| Line 147: | Line 150: | ||
<youtube>hhzysrZG8cU</youtube> | <youtube>hhzysrZG8cU</youtube> | ||
<b>Understanding Triple Loop Learning and it's impact on the Coaching Process | <b>Understanding Triple Loop Learning and it's impact on the Coaching Process | ||
| − | </b><br>The results that people achieve in life come from the actions that they take both at conscious and unconscious levels. Often a client will express a desire for change, and seek actionable steps from his coach to create that change. Taking positive actions can lead to positive changes and results, but may still fall short of being transformational. Coaches can help clients achieve real breakthrough when they understand how <b>Triple Loop Learning</b> occurs. For more, please visit us at https://www.coachmastersacademy.com/ | + | </b><br>The results that people achieve in life come from the actions that they take both at [[Consciousness|conscious]] and unconscious levels. Often a client will express a desire for change, and seek actionable steps from his coach to create that change. Taking positive actions can lead to positive changes and results, but may still fall short of being transformational. Coaches can help clients achieve real breakthrough when they understand how <b>Triple Loop Learning</b> occurs. For more, please visit us at https://www.coachmastersacademy.com/ |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| Line 176: | Line 179: | ||
* [https://simonsinek.com/product/start-with-why/ Start With Why | ][[Creatives#Simon Sinek|Simon Sinek]] ...[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Start_with_Why Wikipedia] | * [https://simonsinek.com/product/start-with-why/ Start With Why | ][[Creatives#Simon Sinek|Simon Sinek]] ...[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Start_with_Why Wikipedia] | ||
* [[Loop#Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop|Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop]] ...[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OODA_loop Wikipedia] | * [[Loop#Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop|Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop]] ...[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OODA_loop Wikipedia] | ||
| + | * [[Perspective]] ... [[Context]] ... [[In-Context Learning (ICL)]] ... [[Transfer Learning]] ... [[Out-of-Distribution (OOD) Generalization]] | ||
The Triple Golden OODA loop diagram depicts a hybrid of concepts from the Triple Loop concept inspired by Chris Argyris & Donald Schön's work on the Double Loop, [[Creatives#Simon Sinek|Simon Sinek]]'s Golden Circle in 'Start with Why', and [[Creatives#John Richard Boyd|Colonel John Boyd]]'s Observe, Orient, Decide and Act (OODA) Loop from his ‘A Discourse On Winning and Losing'. | The Triple Golden OODA loop diagram depicts a hybrid of concepts from the Triple Loop concept inspired by Chris Argyris & Donald Schön's work on the Double Loop, [[Creatives#Simon Sinek|Simon Sinek]]'s Golden Circle in 'Start with Why', and [[Creatives#John Richard Boyd|Colonel John Boyd]]'s Observe, Orient, Decide and Act (OODA) Loop from his ‘A Discourse On Winning and Losing'. | ||
| Line 185: | Line 189: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>qp0HIF3SfI4</youtube> |
<b>Start with WHY - Simon Sinek In Vegas | <b>Start with WHY - Simon Sinek In Vegas | ||
</b><br>IDLife NYC Those who lead inspire us. We follow those who lead because we want to and for selfish reasons. Those who start with "why" that have the ability to inspire those around them or find others who inspire them. | </b><br>IDLife NYC Those who lead inspire us. We follow those who lead because we want to and for selfish reasons. Those who start with "why" that have the ability to inspire those around them or find others who inspire them. | ||
| Line 255: | Line 259: | ||
[https://www.google.com/search?q=~Consciousness+feedback+Strange+loop+ai+machine+learning ...Google search] | [https://www.google.com/search?q=~Consciousness+feedback+Strange+loop+ai+machine+learning ...Google search] | ||
| + | * [[Life~Meaning]] ... [[Consciousness]] ... [[Loop#Feedback Loop - Creating Consciousness|Creating Consciousness]] ... [[Quantum#Quantum Biology|Quantum Biology]] ... [[Orch-OR]] ... [[TAME]] ... [[Protein Folding & Discovery|Proteins]] | ||
| + | * [[Predictive Analytics#You’re Living Inside a Prediction: Toward Predictive AI Consciousness|You’re Living Inside a Prediction: Toward Predictive AI Consciousness]] | ||
| + | ** [[Simulation]] ... [[Simulated Environment Learning]] ... [[World Models]] ... [[Minecraft]]: [[Minecraft#Voyager|Voyager]] | ||
* [[Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) to Singularity]] ... [[Inside Out - Curious Optimistic Reasoning| Curious Reasoning]] ... [[Emergence]] ... [[Moonshots]] ... [[Explainable / Interpretable AI|Explainable AI]] ... [[Algorithm Administration#Automated Learning|Automated Learning]] | * [[Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) to Singularity]] ... [[Inside Out - Curious Optimistic Reasoning| Curious Reasoning]] ... [[Emergence]] ... [[Moonshots]] ... [[Explainable / Interpretable AI|Explainable AI]] ... [[Algorithm Administration#Automated Learning|Automated Learning]] | ||
* [https://www.popularmechanics.com/science/health/a10320/michio-kaku-and-the-mysteries-of-the-mind-16582552/ Michio Kaku and the Mysteries of the Mind | Alyson Sheppard - Popular Mechanics] ...The Future of the Mind: The Scientific Quest to Understand, Enhance, and Empower the Mind | * [https://www.popularmechanics.com/science/health/a10320/michio-kaku-and-the-mysteries-of-the-mind-16582552/ Michio Kaku and the Mysteries of the Mind | Alyson Sheppard - Popular Mechanics] ...The Future of the Mind: The Scientific Quest to Understand, Enhance, and Empower the Mind | ||
| Line 262: | Line 269: | ||
* [https://www.pulitzer.org/winners/douglas-r-hofstadter Godel, Escher, Bach: an Eternal Golden Braid | Douglas R. Hofstadter] | * [https://www.pulitzer.org/winners/douglas-r-hofstadter Godel, Escher, Bach: an Eternal Golden Braid | Douglas R. Hofstadter] | ||
** [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G%C3%B6del,_Escher,_Bach Gödel, Escher, Bach | Wikipedia] | ** [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G%C3%B6del,_Escher,_Bach Gödel, Escher, Bach | Wikipedia] | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
{|<!-- T --> | {|<!-- T --> | ||
| Line 269: | Line 277: | ||
|| | || | ||
<youtube>UEGx96PMiOo</youtube> | <youtube>UEGx96PMiOo</youtube> | ||
| − | <b>Michio Kaku: Feedback loops are creating | + | <b>Michio Kaku: Feedback loops are creating [[Consciousness]] | Big Think |
| − | </b><br>One of the great questions in all of science is where consciousness comes from. When it comes to consciousness, Kaku believes different species have different levels of consciousness, based on their feedback loops needed to survive in space, society, and time. According to the theoretical physicist, human beings' ability to use past experiences, memories, to predict the future makes us distinct among animals — and even robots (they're currently unable to understand, or operate within, a social hierarchy). Dr. Michio Kaku is the co-founder of string field theory, and is one of the most widely recognized scientists in the world today. He has written 4 New York Times Best Sellers, is the science correspondent for CBS This Morning and has hosted numerous science specials for BBC-TV, the Discovery/Science Channel. His radio show broadcasts to 100 radio stations every week. Dr. Kaku holds the Henry Semat Chair and Professorship in theoretical physics at the City College of New York (CUNY), where he has taught for over 25 years. He has also been a visiting professor at the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton, as well as New York University (NYU). | + | </b><br>One of the great questions in all of science is where [[consciousness]] comes from. When it comes to [[consciousness]], Kaku believes different species have different levels of [[consciousness]], based on their feedback loops needed to survive in space, society, and time. According to the theoretical physicist, human beings' ability to use past experiences, memories, to predict the future makes us distinct among animals — and even robots (they're currently unable to understand, or operate within, a social hierarchy). Dr. Michio Kaku is the co-founder of string field theory, and is one of the most widely recognized scientists in the world today. He has written 4 New York Times Best Sellers, is the science correspondent for CBS This Morning and has hosted numerous science specials for BBC-TV, the Discovery/Science Channel. His radio show broadcasts to 100 radio stations every week. Dr. Kaku holds the Henry Semat Chair and Professorship in theoretical physics at the City College of New York (CUNY), where he has taught for over 25 years. He has also been a visiting professor at the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton, as well as New York University (NYU). |
|} | |} | ||
|<!-- M --> | |<!-- M --> | ||
| Line 277: | Line 285: | ||
|| | || | ||
<youtube>lzn6QcITVaY</youtube> | <youtube>lzn6QcITVaY</youtube> | ||
| − | <b>Investigating Consciousness with Closed-Loop Neural Reinforcement | + | <b>Investigating [[Consciousness]] with Closed-Loop Neural Reinforcement |
| − | </b><br>Neuroscience Virtual Event 2018 Aurelio Cortese, PhD Researcher, ATR Institute International Aurelio received his MSc degree from the Life Sciences and Technologies faculty at EPFL in Switzerland (2012), while spending one year at the Max-Planck Institute of Psychiatry in Munich working on mice models of Alzheimer's disease and depression. He is now a researcher at ATR working with Mitsuo Kawato, with ongoing collaborations with Hakwan Lau's Lab at UCLA and Hong Kong University, and with Benedetto de Martino at UCL/Wellcome Trust (London, UK). Webinar: Investigating Consciousness with Closed-Loop Neural Reinforcement Abstract: | + | </b><br>[[Neuroscience]] Virtual Event 2018 Aurelio Cortese, PhD Researcher, ATR Institute International Aurelio received his MSc degree from the Life Sciences and Technologies faculty at EPFL in Switzerland (2012), while spending one year at the Max-Planck Institute of Psychiatry in Munich working on mice models of Alzheimer's disease and depression. He is now a researcher at ATR working with Mitsuo Kawato, with ongoing collaborations with Hakwan Lau's Lab at UCLA and Hong Kong University, and with Benedetto de Martino at UCL/Wellcome Trust (London, UK). Webinar: Investigating [[Consciousness]] with Closed-Loop Neural Reinforcement Abstract: |
| − | In consciousness studies, a longstanding controversy concerns whether activity in the prefrontal cortical (PFC) region of the brain is necessary to evoke conscious experiences. Similarly, there is contrasting evidence on whether subjective confidence directly reflects sensory evidence or may depend on a late-stage estimation, related to consciousness but dissociable from sensory processes. As of yet, in humans, experimental tools have lacked the power to resolve these issues convincingly. We overcome this difficulty by capitalizing on the recently developed method of decoded neurofeedback (DecNef), where the occurrence of distinct neural events (e.g., spatial activation patterns) is selectively rewarded. This closed-loop training thus has the power of reinforcing purely content-specific processes that typically lie below consciousness. In a series of recent studies, we employed DecNef to directly reinforce neural activation patterns in areas related to representations at different levels of complexity, from simpler (e.g. orientation in visual cortex) to more composite (e.g. confidence in PFC). In all cases, the manipulations resulted in clear behavioral or physiological changes. Nevertheless, during the training sessions, participants were never conscious about the content of these localized recurring activation patterns. | + | In [[consciousness]] studies, a longstanding controversy concerns whether activity in the prefrontal cortical (PFC) region of the brain is necessary to evoke [[Consciousness|conscious]] experiences. Similarly, there is contrasting evidence on whether subjective confidence directly reflects sensory evidence or may depend on a late-stage estimation, related to [[consciousness]] but dissociable from sensory processes. As of yet, in humans, experimental tools have lacked the power to resolve these issues convincingly. We overcome this difficulty by capitalizing on the recently developed method of decoded neurofeedback (DecNef), where the occurrence of distinct neural events (e.g., spatial activation patterns) is selectively rewarded. This closed-loop training thus has the power of reinforcing purely content-specific processes that typically lie below [[consciousness]]. In a series of recent studies, we employed DecNef to directly reinforce neural activation patterns in areas related to representations at different levels of complexity, from simpler (e.g. orientation in visual cortex) to more composite (e.g. confidence in PFC). In all cases, the manipulations resulted in clear behavioral or physiological changes. Nevertheless, during the training sessions, participants were never [[Consciousness|conscious]] about the content of these localized recurring activation patterns. |
| − | This raises a very interesting point: it is likely that consciousness requires more than just a local representation, however well defined. As already proposed, consciousness may rely on concomitant activations across frontoparietal networks. Frontal cortices could thus play a crucial role in bringing content to consciousness, by virtue of being also implicated in higher order representations. Approaches combining machine learning techniques with brain imaging and closed-loop training such as DecNef may offer a strong paradigm to further explore and understand consciousness and its real neural basis. | + | This raises a very interesting point: it is likely that [[consciousness]] requires more than just a local representation, however well defined. As already proposed, [[consciousness]] may rely on concomitant activations across frontoparietal networks. Frontal cortices could thus play a crucial role in bringing content to [[consciousness]], by virtue of being also implicated in higher order representations. Approaches combining machine learning techniques with brain imaging and closed-loop training such as DecNef may offer a strong paradigm to further explore and understand [[consciousness]] and its real neural basis. |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| Line 295: | Line 303: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>lXWhAPbBExY</youtube> |
| − | <b>Introduction to Brain and Consciousness 2.2 - Feedforward and Feedback Connections | + | <b>Introduction to Brain and [[Consciousness]] 2.2 - Feedforward and Feedback Connections |
</b><br>Synergos Narrated by Julia Donnell Written by Hakwan Lau Now, onto more details about the pathways. Again, getting the basic concepts is much more important than remembering all the specifics. When we say there’s a pathway, we imply there is a direction of information flow. And in fact there is. From the eyeball towards the brain, that is how perception happens. We call this direction feedforward, or bottom up. But interestingly, information also flows from the other direction. And we call these feedback, or top down signals. Directed/Edited by Justine Suh Cinematography/Sound Editing by Emily Kalish Key Grip and Sound by Santiago Rodriguez Herran Graphics & Subtitles by Peter Keating & Charmaine Wong FAIR USE NOTICE: This video contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. | </b><br>Synergos Narrated by Julia Donnell Written by Hakwan Lau Now, onto more details about the pathways. Again, getting the basic concepts is much more important than remembering all the specifics. When we say there’s a pathway, we imply there is a direction of information flow. And in fact there is. From the eyeball towards the brain, that is how perception happens. We call this direction feedforward, or bottom up. But interestingly, information also flows from the other direction. And we call these feedback, or top down signals. Directed/Edited by Justine Suh Cinematography/Sound Editing by Emily Kalish Key Grip and Sound by Santiago Rodriguez Herran Graphics & Subtitles by Peter Keating & Charmaine Wong FAIR USE NOTICE: This video contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 427: | Line 435: | ||
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = <span id="Feedback Loop - Homeostasis"></span>Feedback Loop - Allostasis & Homeostasis = | ||
| + | * [[Life~Meaning]] ... [[Consciousness]] ... [[Loop#Feedback Loop - Creating Consciousness|Creating Consciousness]] ... [[Quantum#Quantum Biology|Quantum Biology]] ... [[Orch-OR]] ... [[TAME]] ... [[Protein Folding & Discovery|Proteins]] | ||
| + | * [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ObpsPIp3n2U Adrenal Health, Stress Adaptation & Homeostasis |YourHormonesInc -] YouTube video | ||
| + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allostasis Allostasis | Wikipedia] | ||
| + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homeostasis Homeostasis | Wikipedia] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Allostasis''' the process of maintaining stability by changing the body’s operating settings in response to context and predicted demand—your brain and body anticipate needs (stress, exercise, threat, illness, time of day) and adjust hormones, autonomic output, and immune activity to match the situation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Before a speech: your heart rate rises, cortisol may increase, and blood pressure shifts before you start talking → '''Allostasis''''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Homeostasis''' is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Homeostasis operates primarily through [[negative feedback]] loops. When a variable changes, the body triggers a response to reverse that change to maintain equilibrium. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''After the speech ends: those values return toward baseline through feedback corrections → '''Homeostasis''''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <hr><center><i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Allostasis''' as the strategy (adapt to demand) and '''Homeostasis''' as the fine-tuning mechanics (keep variables in safe ranges). | ||
| + | |||
| + | </i></center><hr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' How they’re different ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Goal | ||
| + | : '''Homeostasis:''' keep a variable near a set range. | ||
| + | : '''Allostasis:''' keep the organism functioning well by adapting the set range and related systems to the moment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Timing | ||
| + | : '''Homeostasis:''' mostly reactive (corrects after deviation). | ||
| + | : '''Allostasis:''' often predictive/anticipatory (adjusts before or during expected demand). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Control style | ||
| + | : '''Homeostasis:''' local “thermostat” loops (negative feedback). | ||
| + | : '''Allostasis:''' coordinated, whole-system regulation (brain-driven orchestration across multiple systems). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Cost concept | ||
| + | : '''Homeostasis:''' not usually framed as “costly” unless failing. | ||
| + | : '''Allostasis:''' emphasizes wear-and-tear from chronic activation—''allostatic load''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Homeostatic Control System ''' | ||
| + | A homeostatic control system consists of three functional components: | ||
| + | # '''Receptor (Sensor):''' Detects a change in the environment (stimulus). | ||
| + | # '''Control Center:''' Processes the information and signals the effector (e.g., the [[brain]]). | ||
| + | # '''Effector:''' Carries out the necessary adjustment to restore balance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The term was coined by physiologist [[Walter Bradford Cannon]] in 1926. It is derived from the Greek words: | ||
| + | * ''hómoios'' ({{lang|grc|ὅμοιος}}), meaning "similar" | ||
| + | * ''stásis'' ({{lang|grc|στάσις}}), meaning "standing still" | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Homeostasis & Allostasis: An Evolutionary Perspective With Consciousness ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Life survives by keeping its internal conditions in a workable range. Early life mostly did this with '''Homeostasis''' (reactive feedback). As nervous systems evolved, organisms gained '''Allostasis''' (predictive, context-sensitive regulation). What we call '''[[conscious]] experience''' may be one of the tools that helps organisms coordinate allostatic control across the whole body—especially when tradeoffs, uncertainty, or social complexity are involved. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Homeostasis came first: the ancient “stay alive” machinery ''' | ||
| + | '''Homeostasis''' is evolution’s baseline: keep core variables (ions, pH, temperature, glucose, oxygen, hydration) within survivable bounds. | ||
| + | * '''Single cells:''' membrane pumps, ion channels, osmotic regulation, energy balance (ATP) — fast local loops. | ||
| + | * '''Multicellular life:''' internal transport (circulation), compartment control, hormonal signaling — keeping the “internal ocean” stable enough for specialized tissues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Key evolutionary point:''' Homeostasis works best when the environment is fairly predictable and when local feedback loops can correct deviations quickly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Allostasis emerged with nervous systems: “stability through change” ''' | ||
| + | '''Allostasis''' is what you get when an organism can anticipate, learn, and coordinate multiple systems at once. | ||
| + | * '''Prediction:''' adjust physiology ''before'' demand hits (fight/flight, exercise, cold exposure, feeding). | ||
| + | * '''Coordination:''' align heart, lungs, immune tone, attention, and behavior toward the same goal. | ||
| + | * '''Tradeoffs:''' choose a “good enough” body state for the situation (e.g., temporarily raise blood pressure to escape, even if it’s not ideal long-term). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Key evolutionary point:''' Allostasis becomes valuable when: | ||
| + | * the environment is variable, | ||
| + | * the organism is mobile, | ||
| + | * the organism must make fast choices under uncertainty. | ||
| + | * and playing dead | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Where [[consciousness]] fits: interoception + choice under uncertainty ''' | ||
| + | A useful way to connect [[consciousness]] to regulation is '''interoception''' — sensing internal body states (heartbeat, breathing, gut signals, temperature, inflammation, hormonal state). | ||
| + | * Much interoceptive control is '''unconscious''' (reflex loops in the brainstem/hypothalamus). | ||
| + | * Some interoceptive information becomes '''[[consciousness|conscious]] feelings''' (hunger, thirst, nausea, calm, anxiety, “wired/tired,” pain). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''One evolutionary hypothesis:''' [[consciousness]] helps Allostasis when the organism needs '''flexible control''' across time: | ||
| + | * planning (“If I keep running, will I overheat?”) | ||
| + | * learning (“That food made me sick—avoid it.”) | ||
| + | * social prediction (“If I challenge him, what happens next?”) | ||
| + | * conflict resolution (“I’m scared, but I still need to do this.”) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' A layered control stack: from reflex → feeling → deliberation ''' | ||
| + | You can think of regulation as a stack of increasingly “expensive” control systems: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Layer A: Local Homeostasis (fast, automatic) | ||
| + | : Cells and organs self-regulate (ion balance, local blood flow, basic reflexes). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Layer B: Body-wide Allostasis (coordinated, mostly automatic) | ||
| + | : Brainstem + hypothalamus + autonomic and endocrine systems shift setpoints based on context (stress response, circadian rhythm, fever response). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ; Layer C: [[consciousness|Conscious]] control (slow, flexible, meaning-driven) | ||
| + | : Cortex can simulate futures, apply goals/values, and reshape behavior to prevent future instability (choose shelter, negotiate, delay gratification, seek help). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Why it matters:''' [[consciousness]] is not required for most homeostatic corrections—but it may be crucial for complex allostatic problems where the “right” action depends on goals, predictions, and social context. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Emotions as “Allostatic programs” ''' | ||
| + | From this lens, emotions aren’t random “extras.” They can be seen as packaged action-and-body-state programs: | ||
| + | * '''Fear''' biases attention + raises arousal to escape threats. | ||
| + | * '''Anger''' mobilizes energy for confrontation and boundary enforcement. | ||
| + | * '''Sadness''' can promote withdrawal/conservation and social support seeking. | ||
| + | * '''Joy/interest''' can promote exploration and learning when safe. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These states are Allostatic because they change physiology and behavior together to manage risk and opportunity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' When the system misfires: Allostatic load ''' | ||
| + | Allostasis is powerful, but it has a cost when it’s chronically engaged: | ||
| + | * persistent stress physiology | ||
| + | * disrupted sleep/circadian rhythms | ||
| + | * metabolic strain | ||
| + | * inflammatory changes | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Allostatic load''' is the “wear-and-tear” that shows up when the body keeps paying short-term survival costs without recovery—often a mismatch between ancient regulatory systems and modern persistent stressors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Takeaway ''' | ||
| + | * '''Homeostasis''' is the ancient reactive core: correct deviations to protect life. | ||
| + | * '''Allostasis''' is the evolved upgrade: predict, coordinate, and adapt setpoints to meet situations. | ||
| + | * '''[[Consciousness]]''' may be one of evolution’s tools for higher-level Allostatic control—helping an organism integrate internal signals with goals, learning, and social reality when simple reflexes aren’t enough. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Examples ''' | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Process !! Scenario !! Homeostatic Response | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="2"| '''[[Thermoregulation]]''' | ||
| + | | Hyperthermia (Too hot) | ||
| + | | [[Perspiration|Sweating]] (evaporative cooling) and [[vasodilation]] (widening of blood vessels to release heat). | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Hypothermia (Too cold) | ||
| + | | [[Shivering]] (muscle heat generation) and [[vasoconstriction]] (narrowing of blood vessels to conserve heat). | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="2"| '''[[Blood sugar regulation|Glucoregulation]]''' | ||
| + | | Hyperglycemia (High blood sugar) | ||
| + | | The [[pancreas]] releases '''[[insulin]]''', causing cells to absorb glucose. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Hypoglycemia (Low blood sugar) | ||
| + | | The pancreas releases '''[[glucagon]]''', causing the [[liver]] to release stored glucose. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''[[Osmoregulation]]''' | ||
| + | | Dehydration | ||
| + | | The [[kidney|kidneys]] concentrate urine to conserve water; the [[hypothalamus]] stimulates thirst. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== <span id="Vagus Nerve"></span>Vagus Nerve ==== | ||
| + | Vagus nerve acts like a two-way control cable between your organs and your brainstem—constantly measuring internal conditions and then nudging things back toward “normal.” Most vagus fibers are sensory (afferent)—they carry status updates from your organs up to the brain (often cited around ~80% afferent). Those signals primarily land in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in the medulla, a major “autonomic dashboard” that integrates input from the cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive systems. Then the brain sends motor (efferent) vagal output back down (via nuclei like the nucleus ambiguus and dorsal motor nucleus) to adjust organs—usually in a calming, “rest-and-digest” direction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b><i>Organ state changes → vagal sensory input → NTS integrates → vagal output → organ function shifts → state normalizes</i></b> | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Blood pressure & heart-rate control (baroreflex) - Sensors in major arteries detect stretch/pressure and signal the brainstem; the NTS then helps drive vagal output that slows the heart when pressure is high (and relaxes vagal braking when pressure is low). | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Breathing–heart coordination (respiratory sinus arrhythmia) - Your heart rate naturally speeds a bit on inhale and slows on exhale; that rhythm reflects tight coupling between respiration networks and cardiac vagal control pathways. | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Gut “status,” satiety, and digestion (vagovagal reflexes) - Vagal sensory neurons detect things like stomach stretch and digestive signals and report to the brainstem; vagal output helps tune motility and secretion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | # The “inflammatory reflex” (immune homeostasis) - There’s evidence for a vagus-linked reflex where vagal signaling can dampen excessive cytokine release (often described as the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway), involving acetylcholine signaling and α7 nicotinic receptors on immune cells in experimental models | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>p9XHI_26cPE</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==== <span id="AlphaFold 2"></span>AlphaFold 2 ==== | ||
| + | [[Protein Folding & Discovery|DeepMind AlphaFold]] can help researchers understand receptors/ion channels/drug targets that sit upstream of autonomic signaling. (think adrenergic + muscarinic GPCRs, serotonin receptors, nicotinic receptors, cardiac ion channels like hERG/Kv11.1, etc.). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''3D structure when no experimental model exists:''' [[Protein Folding & Discovery|DeepMind AlphaFold]] can generate a workable 3D fold for hard targets (especially membrane proteins), giving researchers a structural starting point for autonomic-relevant receptors and channels. | ||
| + | * '''Druggable pocket mapping:''' With a predicted structure, researchers can identify and compare likely orthosteric/allosteric pockets and map known functional residues to guide selectivity and SAR hypotheses. | ||
| + | * '''Signaling-complex hypotheses:''' [[Protein Folding & Discovery|DeepMind AlphaFold]] (including multimer approaches) can model receptor–transducer interfaces (e.g., GPCR–G protein) to propose coupling-selectivity determinants and testable interaction residues. | ||
| + | * '''Complexes with ligands/ions (AlphaFold 3):''' [[Protein Folding & Discovery|DeepMind AlphaFold 3]] can propose bound geometries for proteins with small molecules, ions, and modified residues, helping frame how upstream autonomic targets may engage drugs or cofactors. | ||
| + | * '''Channel gating and state-dependent binding:''' Structural models can suggest pore architecture and gating features that help explain why some drugs bind preferentially to specific channel states relevant to excitability control. | ||
| + | * '''Variant-to-mechanism interpretation:''' By placing mutations on a structure, researchers can hypothesize whether variants affect folding/trafficking, ligand binding, gating, or signaling interfaces and then design focused validation assays. | ||
| + | * '''Faster experimental design and interpretation:''' [[Protein Folding & Discovery|DeepMind AlphaFold]] models help pick construct boundaries and stabilizing changes and can speed cryo-EM/mutagenesis planning by providing a structural scaffold for iterative testing. | ||
= Recursion = | = Recursion = | ||
| Line 588: | Line 766: | ||
* [https://www.packetlabs.net/purple-team/ Purple Team: When Red and Blue Teams Work Together | Packetlabs] | * [https://www.packetlabs.net/purple-team/ Purple Team: When Red and Blue Teams Work Together | Packetlabs] | ||
| − | Modern security organizations create new capabilities within an overall cyber defense team by organizing themselves around a fundamental concept of an “OODA loop” — enabling teams to quickly make necessary decisions as they are responding to live or simulated incidents. ... Handling incidents effectively requires this sort of cyclical and quick decision making. In this quick-decision cycle, the IR team becomes the Blue Team, the “attackers” comprise the Red Team and run attack scenarios, and an even more novel third team called the Purple Team proactively hunts the attackers. This structure allows organizations to “train like they fight,” enabling them to prepare for increasingly more advanced adversarial techniques....Purple Teams help optimize security detection processes within an organization by reproducing attacks, determining if successful detection of these attacks occurred, and exposing existing deficiencies within the organization’s IR plan. [https://medium.com/@bogov/improving-cyber-defense-by-purple-team-using-ooda-loop-ae0459bbe734 Improving Cyber Defense by Purple Team using OODA loop | Ozren (Oz) Bogovac - Medium] | + | Modern security organizations create new capabilities within an overall cyber defense team by organizing themselves around a fundamental concept of an “OODA loop” — enabling teams to quickly make necessary decisions as they are responding to live or [[Simulation | simulated incidents]]. ... Handling incidents effectively requires this sort of cyclical and quick decision making. In this quick-decision cycle, the IR team becomes the Blue Team, the “attackers” comprise the Red Team and run attack scenarios, and an even more novel third team called the Purple Team proactively hunts the attackers. This structure allows organizations to “train like they fight,” enabling them to prepare for increasingly more advanced adversarial techniques....Purple Teams help optimize security detection processes within an organization by reproducing attacks, determining if successful detection of these attacks occurred, and exposing existing deficiencies within the organization’s IR plan. [https://medium.com/@bogov/improving-cyber-defense-by-purple-team-using-ooda-loop-ae0459bbe734 Improving Cyber Defense by Purple Team using OODA loop | Ozren (Oz) Bogovac - Medium] |
<img src="https://cdn.packetlabs.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/10115222/purple-team-fig2.png" width="700"> | <img src="https://cdn.packetlabs.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/10115222/purple-team-fig2.png" width="700"> | ||
| Line 632: | Line 810: | ||
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| + | = Operating Systems as a Loop - (Event-Driven Mental Model) = | ||
| + | A useful mental model is that ''Windows is mostly a waiting loop'' that wakes up to handle events. It is not usually a "busy loop" burning CPU; it typically blocks (sleeps) until something needs attention. Windows is essentially an ''event-driven loop'' that mostly sleeps, and hardware interrupts (like mouse movement) are one of the main ways the system gets woken up to do work. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' The Core Pattern ''' | ||
| + | Windows (and many apps running on it) follow this cycle: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # '''Wait''' for something to happen (input, timer, disk, network, etc.) | ||
| + | # '''Identify''' what happened | ||
| + | # '''Dispatch''' work to the right component (driver, OS service, app/window) | ||
| + | # '''Return to waiting''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''' What “Interruptions” Really Mean --'''The word "interruption" often refers to a hardware interrupt. Hardware Interrupts (Fast “Wake Up!” Signals). An interrupt is the hardware's way of telling the CPU: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :''"Pause what you're doing briefly—this needs immediate attention."'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Interrupts are used for things like: | ||
| + | * Mouse/keyboard activity | ||
| + | * Timer ticks | ||
| + | * Disk I/O completion | ||
| + | * Network packets arriving | ||
| + | * USB device changes | ||
Latest revision as of 07:11, 19 January 2026
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- Analytics ... Visualization ... Graphical Tools ... Diagrams & Business Analysis ... Requirements ... Loop ... Bayes ... Network Pattern
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) ... Machine Learning (ML) ... Deep Learning ... Neural Network ... Reinforcement ... Learning Techniques
- Perspective ... Context ... In-Context Learning (ICL) ... Transfer Learning ... Out-of-Distribution (OOD) Generalization
- Causation vs. Correlation ... Autocorrelation ...Convolution vs. Cross-Correlation (Autocorrelation)
- Embedding ... Fine-tuning ... RAG ... Search ... Clustering ... Recommendation ... Anomaly Detection ... Classification ... Dimensional Reduction. ...find outliers
- Algorithm Administration
- Policy ... Policy vs Plan ... Constitutional AI ... Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO) ... Policy Gradient (PG) ... Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
- Agents ... Robotic Process Automation ... Assistants ... Personal Companions ... Productivity ... Email ... Negotiation ... LangChain
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) ... Generative AI ... Machine Learning (ML) ... Deep Learning ... Neural Network ... Reinforcement ... Learning Techniques
- Conversational AI ... ChatGPT | OpenAI ... Bing/Copilot | Microsoft ... Gemini | Google ... Claude | Anthropic ... Perplexity ... You ... phind ... Ernie | Baidu
- Center and Circle Playbook ... 8-step stability guide
- Process Patterns, Loops and Emergence | Carlos E. Perez - Medium
Contents
- 1 Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop
- 2 Feedback Loop
- 3 Multi-Loop Learning
- 4 Triple Golden OODA
- 5 Feedback Loop - Peer Learning
- 6 Feedback Loop - Creating Consciousness
- 7 Feedback Loop - Scientific Discovery
- 8 Feedback Loop - Stock Market Predictions
- 9 Feedback Loop - The AI Economist
- 10 Feedback Loop - Synthetic
- 11 Feedback Loop - Allostasis & Homeostasis
- 12 Recursion
- 13 Unintended Feedback Loop
- 14 Using the OODA Loop - Purple Team with Cybersecurity
- 15 OODA Loop - Security Approaches
- 16 Operating Systems as a Loop - (Event-Driven Mental Model)
Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop
YouTube search... ...Google search
The OODA loop is the cycle: Observe–Orient–Decide–Act ...emphasized that "the loop" is actually a set of interacting loops that are to be kept in continuous operation... developed by military strategist and United States Air Force Colonel John Boyd. Boyd applied the concept to the combat operations process, often at the operational level during military campaigns. It is now also often applied to understand commercial operations and learning processes. The approach explains how agility can overcome raw power in dealing with human opponents. It is especially applicable to cyber security and cyberwarfare. Wikipedia ... A Discourse On Winning and Losing | John R. Boyd - Air University Press
We’ve historically focused automation efforts on the “Act” portion but the real potential for new technologies is to address the prior 3 steps: Improving Observation: Improve the data itself with better sensing accuracy, timeliness, relevance, etc or improve our ability to use the data with higher throughput learning processes Improving Orientation: Improve the classification of the current state and the prediction of future states
Improving Decision: Improve the ability to choose between paths via better objective functions. How Artificial Intelligence is Closing the Loop with Better Predictions | Erik Trautman - HackerNoon]
|
|
Feedback Loop
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Gaming ... Game-Based Learning (GBL) ... Security ... Generative AI ... Games - Metaverse ... Quantum ... Game Theory ... Design
- Feedback | Wikipedia
- Closing the Loop: How Feedback Loops Help to Maintain Quality Long-Term AI Results | Natalie Fletcher - Clarifai
- So, What Actually Is a Feedback Loop? | Tina Nord - Ultimate Knowledge ...With feedback loops, a system is constantly in dialogue with itself.
- AI in the Feedback Loop: A Survey of Alternative Approaches | Karl-ErikÅrzén - ScienceDirect ...paper gives special attention to fuzzy control and expert control.
- Feedback Loops in Machine Learning | Ankur Goyal - Impair ...in spite of the immense benefits that Machine Learning offers, this technology has been very slow to take off, particularly in the enterprise world. At Impira, we believe a key reason for this is the lack of well-designed feedback loops that serve to continuously improve machine learning models.
- HP200A | Wikipedia ...oscillator to use a simple light bulb as the temperature-dependent resistor in its feedback network. Walt Disney bought eight HP200A for use in the production of Fantasia
- The Air Force Research Lab wants tools, techniques and innovative ideas for shortening the OODA Loop. | Aaron Boyd - Nextgov
any process where the outputs of a system are plugged back in and used as iterative inputs. Feedback loops exist just about everywhere. In nature, the evolutionary "arms race" between predators and prey is a classic example. In business, the practice of taking customer feedback (the output of a product or service) and using it to improve future processes is another commonly used feedback loop. Today, rapid advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are helping businesses do more with data. These systems — and their ability to analyze an inhuman amount of data — allow businesses to adjust algorithms, workflows and processes on the fly. Get More Out Of Feedback Loops With AI | Arka Dhar - Forbes
|
|
Multi-Loop Learning
YouTube search... ...Google search
- How Artificial Intelligence Will Redefine Management | V. Kolbjørnsrud, R. Amico and R.J. Thomas
- Chris Argyris: theories of action, double-loop learning and organizational learning | Infed.org
- Donald Schon (Schön): learning, reflection and change | Infed.org
- Organisational learning: a critical review | Catherine L. Wang, Pervaiz K. Ahmed
- Single and double loop learning | Organizational Learning
- Double-loop learning | Wikipedia
- Re-Framing Perspectives | Patrick A. Trottier - The Institute Of Emergent Organizational Development and Emergent Change®
- Working visually: Record, Reflect, Reframe, Part 1 Part 2 | Kim S van den Berg
- Different Kinds of Learning (Loops of Learning) Adapted from “Field Guide to Consulting and Organizational Development”

|
|
|
|
|
|
Triple Golden OODA
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Context ... the next AI frontier
- Multi-Loop Learning
- Start With Why | Simon Sinek ...Wikipedia
- Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop ...Wikipedia
- Perspective ... Context ... In-Context Learning (ICL) ... Transfer Learning ... Out-of-Distribution (OOD) Generalization
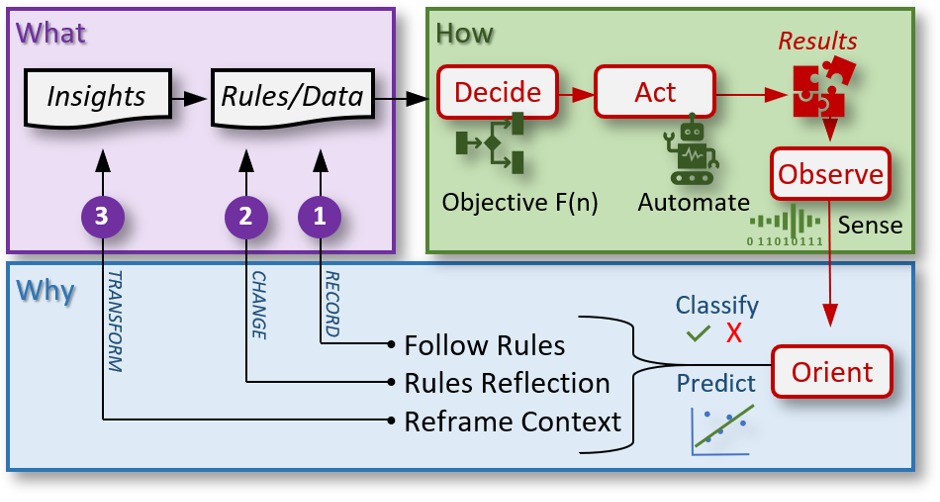
The Triple Golden OODA loop diagram depicts a hybrid of concepts from the Triple Loop concept inspired by Chris Argyris & Donald Schön's work on the Double Loop, Simon Sinek's Golden Circle in 'Start with Why', and Colonel John Boyd's Observe, Orient, Decide and Act (OODA) Loop from his ‘A Discourse On Winning and Losing'.
|
|
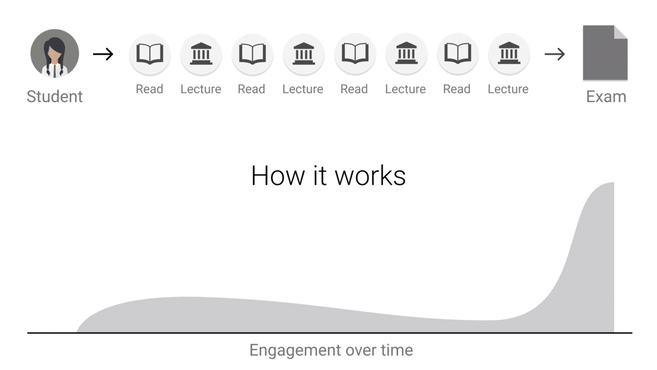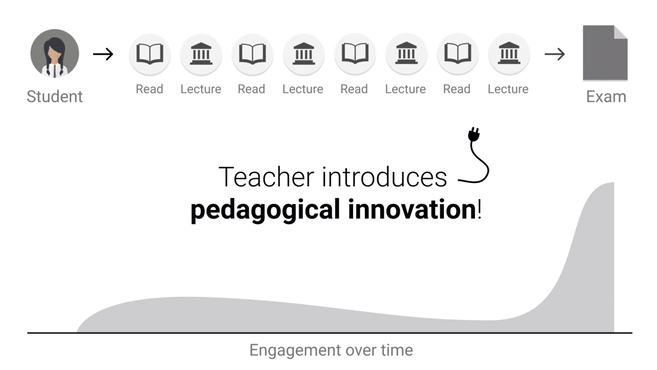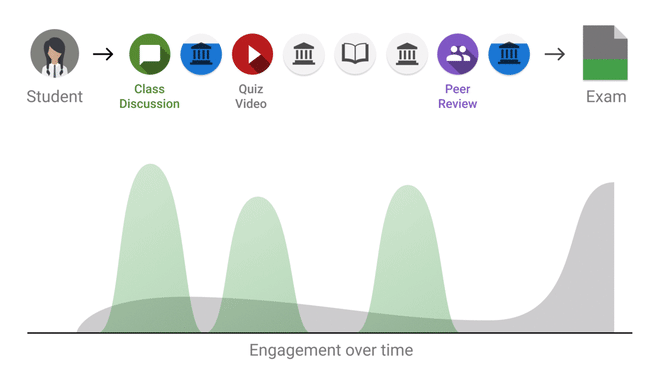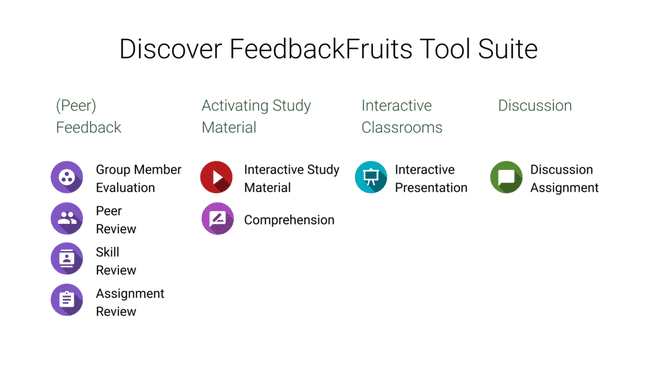
Feedback Loop - Peer Learning
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Education
- Decentralized: Federated & Distributed Learning
- FeedbackFruits
- The NIPS experiment | Eric Price - A blog on machine learning very broadly construed by Moritz Hardt
|
|
|
|
Feedback Loop - Creating Consciousness
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Life~Meaning ... Consciousness ... Creating Consciousness ... Quantum Biology ... Orch-OR ... TAME ... Proteins
- You’re Living Inside a Prediction: Toward Predictive AI Consciousness
- Simulation ... Simulated Environment Learning ... World Models ... Minecraft: Voyager
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) to Singularity ... Curious Reasoning ... Emergence ... Moonshots ... Explainable AI ... Automated Learning
- Michio Kaku and the Mysteries of the Mind | Alyson Sheppard - Popular Mechanics ...The Future of the Mind: The Scientific Quest to Understand, Enhance, and Empower the Mind
- A Theory of Consciousness | Tyler Neylon - Medium
- Do Loops Explain Consciousness? | Martin Gardner - AMS.org ...Review of I Am a Strange Loop
- Strange Loop | Wikipedia ...The "strangeness" of a strange loop comes from our way of perception
- Godel, Escher, Bach: an Eternal Golden Braid | Douglas R. Hofstadter
|
|
|
|
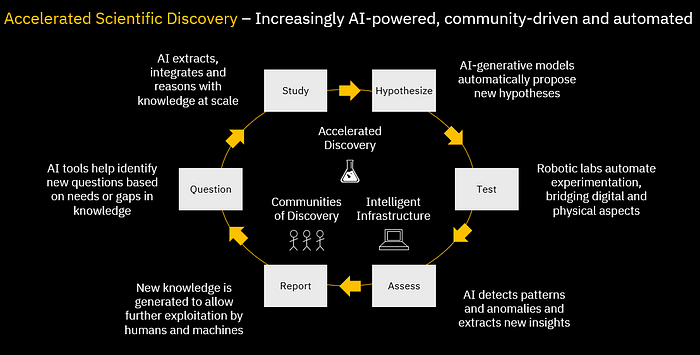
Feedback Loop - Scientific Discovery
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Scientific discovery must be redefined. Quantum and AI can help | Dario Gil - World Economic Forum
- Can Artificial Intelligence Make Scientific Discoveries? | Kartik Hosanagar - The Scientist
- Can artificial intelligence lead scientific discoveries? | University of Konstanz - EurekAlert!
The paradigm shift will be from AI used for analysing the data which has already been obtained, to AI deciding what to measure next. Why Artificial Intelligence Will Enable New Scientific Discoveries - Andrew Briggs - Graphcore
Quantum Computing and AI to Enable Our Sustainable Future | Katia Moskvitch - IBM

|
|
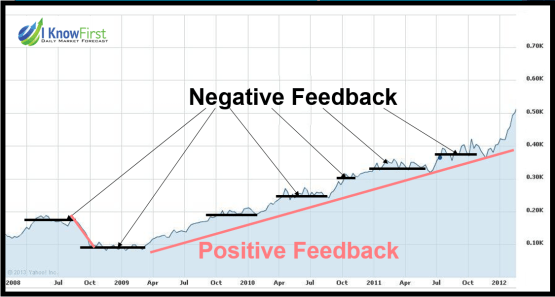
Feedback Loop - Stock Market Predictions
YouTube search... ...Google search
Why you can beat the market, even when it does not seem so. The importance of loops, patterns, and predictable events. Random events are don’t measure risks, and should not affect your decision making. Some traders follow the trend, and some go against it. At I Know First we work on algorithmic strategies which are neither, we simply try an assess where the next opportunity is and provide stock market predictions. If this means to do what everyone else does, than why not. If it means going against when everyone else does, this is also fine. The tricky part is determining where this opportunities are, this article will discuss how to find opportunities in what can seem as total randomness. Markets are Complex, but not Unpredictable! There are two major misconceptions about the stock market. The first one is connected to the classical economic theory which claims markets to be efficient, and as such unpredictable. In this case trying to select one stock over another becomes useless, as no opportunity is ever better than the other. Both stocks are perfectly priced according to their opportunity and risk, with everyone having all information. However, the truth of the matter is that some people profit trading stocks while others lose – this by itself proves the market to be inefficient, and thus exploitable. While US markets are very efficient, and most information is available, not everyone interprets this information the same. Stock Market Predictions: Where In The Feedback Loop Is Your Portfolio? | I Know First
|
Feedback Loop - The AI Economist
YouTube search... ...Google search
Optimal Tax Design as Learned Reward Design Using Reinforcement Learning. Reinforcement learning is a powerful framework in which agents learn from experience collected through trial-and-error. We use model-free RL, in which agents do not use any prior world knowledge or modeling assumptions. Another benefit of RL is that agents can optimize for any objective. In our setting, this means that a tax policy can be learned that optimizes any social objective, and without knowledge of workers’ utility functions or skills. The AI Economist: Improving Equality and Productivity with AI-Driven Tax Policies | S. Zheng, A. Trott, S. Srinivasa, N. Naik, M. Gruesbeck, D. Parkes, and R. Socher - Einstein.ai]

|
Feedback Loop - Synthetic
YouTube search... ...Google search
|
Feedback Loop - Allostasis & Homeostasis
- Life~Meaning ... Consciousness ... Creating Consciousness ... Quantum Biology ... Orch-OR ... TAME ... Proteins
- Adrenal Health, Stress Adaptation & Homeostasis |YourHormonesInc - YouTube video
- Allostasis | Wikipedia
- Homeostasis | Wikipedia
- Allostasis the process of maintaining stability by changing the body’s operating settings in response to context and predicted demand—your brain and body anticipate needs (stress, exercise, threat, illness, time of day) and adjust hormones, autonomic output, and immune activity to match the situation.
Before a speech: your heart rate rises, cortisol may increase, and blood pressure shifts before you start talking → Allostasis
- Homeostasis is the state of steady internal, physical, and chemical conditions maintained by living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Homeostasis operates primarily through negative feedback loops. When a variable changes, the body triggers a response to reverse that change to maintain equilibrium.
After the speech ends: those values return toward baseline through feedback corrections → Homeostasis
Allostasis as the strategy (adapt to demand) and Homeostasis as the fine-tuning mechanics (keep variables in safe ranges).
How they’re different
- Goal
- Homeostasis: keep a variable near a set range.
- Allostasis: keep the organism functioning well by adapting the set range and related systems to the moment.
- Timing
- Homeostasis: mostly reactive (corrects after deviation).
- Allostasis: often predictive/anticipatory (adjusts before or during expected demand).
- Control style
- Homeostasis: local “thermostat” loops (negative feedback).
- Allostasis: coordinated, whole-system regulation (brain-driven orchestration across multiple systems).
- Cost concept
- Homeostasis: not usually framed as “costly” unless failing.
- Allostasis: emphasizes wear-and-tear from chronic activation—allostatic load.
Homeostatic Control System A homeostatic control system consists of three functional components:
- Receptor (Sensor): Detects a change in the environment (stimulus).
- Control Center: Processes the information and signals the effector (e.g., the brain).
- Effector: Carries out the necessary adjustment to restore balance.
The term was coined by physiologist Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. It is derived from the Greek words:
- hómoios (Template:Lang), meaning "similar"
- stásis (Template:Lang), meaning "standing still"
Homeostasis & Allostasis: An Evolutionary Perspective With Consciousness
Life survives by keeping its internal conditions in a workable range. Early life mostly did this with Homeostasis (reactive feedback). As nervous systems evolved, organisms gained Allostasis (predictive, context-sensitive regulation). What we call conscious experience may be one of the tools that helps organisms coordinate allostatic control across the whole body—especially when tradeoffs, uncertainty, or social complexity are involved.
Homeostasis came first: the ancient “stay alive” machinery Homeostasis is evolution’s baseline: keep core variables (ions, pH, temperature, glucose, oxygen, hydration) within survivable bounds.
- Single cells: membrane pumps, ion channels, osmotic regulation, energy balance (ATP) — fast local loops.
- Multicellular life: internal transport (circulation), compartment control, hormonal signaling — keeping the “internal ocean” stable enough for specialized tissues.
Key evolutionary point: Homeostasis works best when the environment is fairly predictable and when local feedback loops can correct deviations quickly.
Allostasis emerged with nervous systems: “stability through change” Allostasis is what you get when an organism can anticipate, learn, and coordinate multiple systems at once.
- Prediction: adjust physiology before demand hits (fight/flight, exercise, cold exposure, feeding).
- Coordination: align heart, lungs, immune tone, attention, and behavior toward the same goal.
- Tradeoffs: choose a “good enough” body state for the situation (e.g., temporarily raise blood pressure to escape, even if it’s not ideal long-term).
Key evolutionary point: Allostasis becomes valuable when:
- the environment is variable,
- the organism is mobile,
- the organism must make fast choices under uncertainty.
- and playing dead
Where consciousness fits: interoception + choice under uncertainty A useful way to connect consciousness to regulation is interoception — sensing internal body states (heartbeat, breathing, gut signals, temperature, inflammation, hormonal state).
- Much interoceptive control is unconscious (reflex loops in the brainstem/hypothalamus).
- Some interoceptive information becomes conscious feelings (hunger, thirst, nausea, calm, anxiety, “wired/tired,” pain).
One evolutionary hypothesis: consciousness helps Allostasis when the organism needs flexible control across time:
- planning (“If I keep running, will I overheat?”)
- learning (“That food made me sick—avoid it.”)
- social prediction (“If I challenge him, what happens next?”)
- conflict resolution (“I’m scared, but I still need to do this.”)
A layered control stack: from reflex → feeling → deliberation You can think of regulation as a stack of increasingly “expensive” control systems:
- Layer A
- Local Homeostasis (fast, automatic)
- Cells and organs self-regulate (ion balance, local blood flow, basic reflexes).
- Layer B
- Body-wide Allostasis (coordinated, mostly automatic)
- Brainstem + hypothalamus + autonomic and endocrine systems shift setpoints based on context (stress response, circadian rhythm, fever response).
- Layer C
- Conscious control (slow, flexible, meaning-driven)
- Cortex can simulate futures, apply goals/values, and reshape behavior to prevent future instability (choose shelter, negotiate, delay gratification, seek help).
Why it matters: consciousness is not required for most homeostatic corrections—but it may be crucial for complex allostatic problems where the “right” action depends on goals, predictions, and social context.
Emotions as “Allostatic programs” From this lens, emotions aren’t random “extras.” They can be seen as packaged action-and-body-state programs:
- Fear biases attention + raises arousal to escape threats.
- Anger mobilizes energy for confrontation and boundary enforcement.
- Sadness can promote withdrawal/conservation and social support seeking.
- Joy/interest can promote exploration and learning when safe.
These states are Allostatic because they change physiology and behavior together to manage risk and opportunity.
When the system misfires: Allostatic load Allostasis is powerful, but it has a cost when it’s chronically engaged:
- persistent stress physiology
- disrupted sleep/circadian rhythms
- metabolic strain
- inflammatory changes
Allostatic load is the “wear-and-tear” that shows up when the body keeps paying short-term survival costs without recovery—often a mismatch between ancient regulatory systems and modern persistent stressors.
Takeaway
- Homeostasis is the ancient reactive core: correct deviations to protect life.
- Allostasis is the evolved upgrade: predict, coordinate, and adapt setpoints to meet situations.
- Consciousness may be one of evolution’s tools for higher-level Allostatic control—helping an organism integrate internal signals with goals, learning, and social reality when simple reflexes aren’t enough.
Examples
| Process | Scenario | Homeostatic Response |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoregulation | Hyperthermia (Too hot) | Sweating (evaporative cooling) and vasodilation (widening of blood vessels to release heat). |
| Hypothermia (Too cold) | Shivering (muscle heat generation) and vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels to conserve heat). | |
| Glucoregulation | Hyperglycemia (High blood sugar) | The pancreas releases insulin, causing cells to absorb glucose. |
| Hypoglycemia (Low blood sugar) | The pancreas releases glucagon, causing the liver to release stored glucose. | |
| Osmoregulation | Dehydration | The kidneys concentrate urine to conserve water; the hypothalamus stimulates thirst. |
Vagus Nerve
Vagus nerve acts like a two-way control cable between your organs and your brainstem—constantly measuring internal conditions and then nudging things back toward “normal.” Most vagus fibers are sensory (afferent)—they carry status updates from your organs up to the brain (often cited around ~80% afferent). Those signals primarily land in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in the medulla, a major “autonomic dashboard” that integrates input from the cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive systems. Then the brain sends motor (efferent) vagal output back down (via nuclei like the nucleus ambiguus and dorsal motor nucleus) to adjust organs—usually in a calming, “rest-and-digest” direction.
Organ state changes → vagal sensory input → NTS integrates → vagal output → organ function shifts → state normalizes
- Blood pressure & heart-rate control (baroreflex) - Sensors in major arteries detect stretch/pressure and signal the brainstem; the NTS then helps drive vagal output that slows the heart when pressure is high (and relaxes vagal braking when pressure is low).
- Breathing–heart coordination (respiratory sinus arrhythmia) - Your heart rate naturally speeds a bit on inhale and slows on exhale; that rhythm reflects tight coupling between respiration networks and cardiac vagal control pathways.
- Gut “status,” satiety, and digestion (vagovagal reflexes) - Vagal sensory neurons detect things like stomach stretch and digestive signals and report to the brainstem; vagal output helps tune motility and secretion.
- The “inflammatory reflex” (immune homeostasis) - There’s evidence for a vagus-linked reflex where vagal signaling can dampen excessive cytokine release (often described as the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway), involving acetylcholine signaling and α7 nicotinic receptors on immune cells in experimental models
AlphaFold 2
DeepMind AlphaFold can help researchers understand receptors/ion channels/drug targets that sit upstream of autonomic signaling. (think adrenergic + muscarinic GPCRs, serotonin receptors, nicotinic receptors, cardiac ion channels like hERG/Kv11.1, etc.).
- 3D structure when no experimental model exists: DeepMind AlphaFold can generate a workable 3D fold for hard targets (especially membrane proteins), giving researchers a structural starting point for autonomic-relevant receptors and channels.
- Druggable pocket mapping: With a predicted structure, researchers can identify and compare likely orthosteric/allosteric pockets and map known functional residues to guide selectivity and SAR hypotheses.
- Signaling-complex hypotheses: DeepMind AlphaFold (including multimer approaches) can model receptor–transducer interfaces (e.g., GPCR–G protein) to propose coupling-selectivity determinants and testable interaction residues.
- Complexes with ligands/ions (AlphaFold 3): DeepMind AlphaFold 3 can propose bound geometries for proteins with small molecules, ions, and modified residues, helping frame how upstream autonomic targets may engage drugs or cofactors.
- Channel gating and state-dependent binding: Structural models can suggest pore architecture and gating features that help explain why some drugs bind preferentially to specific channel states relevant to excitability control.
- Variant-to-mechanism interpretation: By placing mutations on a structure, researchers can hypothesize whether variants affect folding/trafficking, ligand binding, gating, or signaling interfaces and then design focused validation assays.
- Faster experimental design and interpretation: DeepMind AlphaFold models help pick construct boundaries and stabilizing changes and can speed cryo-EM/mutagenesis planning by providing a structural scaffold for iterative testing.
Recursion
YouTube search... ...Google search

|
|
|
|
Unintended Feedback Loop
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Bias and Variances
- Unintended consequences from existing AI | Wikipedia
- Weapons of Math Destruction: How Big Data Increases Inequality and Threatens Democracy | Cathy O'Neil
- The Toxic Potential of YouTube’s Feedback Loop | Guillaume Chaslot - Wired
- The Unintended Consequences of Machine Learning | Frank Kane - Sundog Education - KDnuggets
- Dangerous Feedback Loops in ML | David Blaszka - Towards Data Science
- The Negative Feedback Loop: Technology Needs To Know When It Gets Things Wrong | Fiona McEvoy - You The Data ...This is not a secret problem. AI developers are painfully aware that there is currently no straightforward way to combat biased data or solicit full feedback. However, increasingly they are making efforts to harvest this critical information wherever and however they can. Not just in the name of ethics, but also to ensure that their creations perform as accurately as possible.

Models that are an integrated part of a product experience, or what we referred to as data products, often involve feedback loops. When done right, feedback loops can help us to create better experiences. However, feedback loops can also create unintended negative consequences, such as bias or inaccurate model performance measurements... Getting Better at Machine Learning | Robert Chang - Medium
Leaders hoping to shift their posture from hindsight to foresight need to better understand the types of risks they are taking on, their interdependencies, and their underlying causes... Confronting the risks of artificial intelligence | B. Cheatham, K. Javanmardian, and H. Samandari - Mckinsey & Company
One of the key features of live ML systems is that they often end up influencing their own behavior if they update over time. This leads to a form of analysis debt, in which it is difficult to predict the behavior of a given model before it is released. These feedback loops can take different forms, but they are all more difficult to detect and address if they occur gradually over time, as may be the case when models are updated infrequently.
- Direct Feedback Loops. A model may directly influence the selection of its own future training data. It is common practice to use standard supervised algorithms, although the theoretically correct solution would be to use bandit algorithms. The problem here is that bandit algorithms (such as contextual bandits) do not necessarily scale well to the size of action spaces typically required for real-world problems. It is possible to mitigate these effects by using some amount of randomization, or by isolating certain parts of data from being influenced by a given model.
- Hidden Feedback Loops. Direct feedback loops are costly to analyze, but at least they pose a statistical challenge that ML researchers may find natural to investigate. A more difficult case is hidden feedback loops, in which two systems influence each other indirectly through the world. One example of this may be if two systems independently determine facets of a web page, such as
one selecting products to show and another selecting related reviews. Improving one system may lead to changes in behavior in the other, as users begin clicking more or less on the other components in reaction to the changes. Note that these hidden loops may exist between completely disjoint systems. Consider the case of two stock-market prediction models from two different investment companies. Improvements (or, more scarily, bugs) in one may influence the bidding and buying behavior of the other. Hidden Technical Debt in Machine Learning Systems | D. Sculley, G. Holt, D. Golovin, E. Davydov, T. Phillips, D. Ebner, V. Chaudhary, M. Young, J. Crespo, and D. Dennison - Google


When the system is retrained on future data, it may become not less but more detrimental to historically disadvantaged groups. In order to build AI systems that are aligned with desirable long-term societal outcomes, we need to understand when and why such negative feedback loops occur, and we need to learn how to prevent them. When bias begets bias: A source of negative feedback loops in AI systems | Lydia T. Liu - University of California, Berkeley - Microsoft Research Blog
|
|
Unintended Feedback Loop - Filter Bubbles
YouTube search... ...Google search
In December 2009, Google began customizing its search results for all users, and we entered a new era of personalization. With little notice or fanfare, our online experience is changing, as the websites we visit are increasingly tailoring themselves to us. In this engaging and visionary book, MoveOn.org board president Eli Pariser lays bare the personalization that is already taking place on every major website, from Facebook to AOL to ABC News. As Pariser reveals, this new trend is nothing short of an invisible revolution in how we consume information, one that will shape how we learn, what we know, and even how our democracy works. The Filter Bubble | Eli Pariser
In news media, echo chamber is a metaphorical description of a situation in which beliefs are amplified or reinforced by communication and repetition inside a closed system. Filter Bubble | Wikipedia
|
|
|
|
Using the OODA Loop - Purple Team with Cybersecurity
YouTube search... ...Google search
- MITRE ATT&CK™
- The Cyber OODA Loop, How Your Attacker Should Help You Design Your Defense | Tony Sager - The Center for Internet Security - NIST
- The 4 Phases of Effective Incident Response Decision Making | Andrew Cook - Praetorian
- OODA and Cybersecurity | INFOSEC
- Red Team VS Blue Team: What’s The Difference? | Jason Firch - PurpleSec
- Purple Team: When Red and Blue Teams Work Together | Packetlabs
Modern security organizations create new capabilities within an overall cyber defense team by organizing themselves around a fundamental concept of an “OODA loop” — enabling teams to quickly make necessary decisions as they are responding to live or simulated incidents. ... Handling incidents effectively requires this sort of cyclical and quick decision making. In this quick-decision cycle, the IR team becomes the Blue Team, the “attackers” comprise the Red Team and run attack scenarios, and an even more novel third team called the Purple Team proactively hunts the attackers. This structure allows organizations to “train like they fight,” enabling them to prepare for increasingly more advanced adversarial techniques....Purple Teams help optimize security detection processes within an organization by reproducing attacks, determining if successful detection of these attacks occurred, and exposing existing deficiencies within the organization’s IR plan. Improving Cyber Defense by Purple Team using OODA loop | Ozren (Oz) Bogovac - Medium

|
|
OODA Loop - Security Approaches
YouTube search... ...Google search
|
|
Operating Systems as a Loop - (Event-Driven Mental Model)
A useful mental model is that Windows is mostly a waiting loop that wakes up to handle events. It is not usually a "busy loop" burning CPU; it typically blocks (sleeps) until something needs attention. Windows is essentially an event-driven loop that mostly sleeps, and hardware interrupts (like mouse movement) are one of the main ways the system gets woken up to do work.
The Core Pattern Windows (and many apps running on it) follow this cycle:
- Wait for something to happen (input, timer, disk, network, etc.)
- Identify what happened
- Dispatch work to the right component (driver, OS service, app/window)
- Return to waiting
What “Interruptions” Really Mean --The word "interruption" often refers to a hardware interrupt. Hardware Interrupts (Fast “Wake Up!” Signals). An interrupt is the hardware's way of telling the CPU:
- "Pause what you're doing briefly—this needs immediate attention."
Interrupts are used for things like:
- Mouse/keyboard activity
- Timer ticks
- Disk I/O completion
- Network packets arriving
- USB device changes