Difference between revisions of "Cybersecurity"
m (→eMail) |
m |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
* [[Telecommunications#5G Security|5G Security]] | * [[Telecommunications#5G Security|5G Security]] | ||
* [[Time]] ... [[Time#Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT)|PNT]] ... [[Time#Global Positioning System (GPS)|GPS]] ... [[Causation vs. Correlation#Retrocausality| Retrocausality]] ... [[Quantum#Delayed Choice Quantum Eraser|Delayed Choice Quantum Eraser]] ... [[Quantum]] | * [[Time]] ... [[Time#Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT)|PNT]] ... [[Time#Global Positioning System (GPS)|GPS]] ... [[Causation vs. Correlation#Retrocausality| Retrocausality]] ... [[Quantum#Delayed Choice Quantum Eraser|Delayed Choice Quantum Eraser]] ... [[Quantum]] | ||
| − | * [[Development]] ... [[Notebooks]] ... [[Development#AI Pair Programming Tools|AI Pair Programming]] ... [[Codeless Options, Code Generators, Drag n' Drop|Codeless | + | * [[Development]] ... [[Notebooks]] ... [[Development#AI Pair Programming Tools|AI Pair Programming]] ... [[Codeless Options, Code Generators, Drag n' Drop|Codeless]] ... [[Hugging Face]] ... [[Algorithm Administration#AIOps/MLOps|AIOps/MLOps]] ... [[Platforms: AI/Machine Learning as a Service (AIaaS/MLaaS)|AIaaS/MLaaS]] |
* [[Games - Security]] | * [[Games - Security]] | ||
* Useful Models [[...find outliers]]: | * Useful Models [[...find outliers]]: | ||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
* Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR): AI can be used to automate security tasks, such as incident response and remediation. | * Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR): AI can be used to automate security tasks, such as incident response and remediation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>j6S4_cZswWE</youtube> | ||
| + | <youtube>TIj4PBCzcEE</youtube> | ||
= Risk-based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) = | = Risk-based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) = | ||
| Line 244: | Line 247: | ||
<youtube>99hniQYB6VM</youtube> | <youtube>99hniQYB6VM</youtube> | ||
<b>Deep Learning For Realtime Malware Detection - Domenic Puzio and Kate Highnam | <b>Deep Learning For Realtime Malware Detection - Domenic Puzio and Kate Highnam | ||
| − | </b><br>Domain generation algorithm (DGA) malware makes callouts to unique web addresses to avoid detection by static rules engines. To counter this type of malware, we created an ensemble model that analyzes domains and evaluates if they were generated by a machine and thus potentially malicious. The ensemble consists of two deep learning models – a convolutional neural network and a long short-term memory network, both which were built using Keras and Tensorflow. These deep networks are flexible enough to learn complex patterns and do not require manual feature engineering. Deep learning models are also very difficult for malicious actors to reverse engineer, which makes them an ideal fit for cyber security use cases. The last piece of the ensemble is a natural-language processing model to assess whether the words in the domain make sense together. These three models are able to capture the structure and content of a domain, determining whether or not it comes from DGA malware with very high accuracy. These models have already been used to catch malware that vendor tools did not detect. Our system analyzes enterprise-scale network traffic in real time, renders predictions, and raises alerts for cyber security analysts to evaluate. Domenic Puzio is a Data Engineer with Capital One. He graduated from the University of Virginia with degrees in Mathematics and Computer Science. On his current project he is a core developer of a custom platform for ingesting, processing, and analyzing Capital One’s cyber-security data sources. Built entirely from opensource tools (NiFi, Kafka, Storm, Elasticsearch, Kibana), this framework processes hundreds of millions of events per hour. Currently, his focus is on the creation and productionization of machine learning models that provide enrichment to the data being streamed through the system. He is a contributor to two Apache projects. Kate Highnam has a background in Computer Science and Business, focusing on security, embedded devices, and accounting. At the University of Virginia, her thesis was a published industrial research paper containing an attack scenario and repair algorithm for drones deployed on missions with limited ground control contact. After joining Capital One as a Data Engineer, Kate has developed features within an internal DevOps Pipeline and Data Lake governance system. Currently, she builds machine learning models to assist cybersecurity experts and enhance defenses. | + | </b><br>Domain generation algorithm (DGA) malware makes callouts to unique web addresses to avoid detection by static rules engines. To counter this type of malware, we created an ensemble model that analyzes domains and evaluates if they were generated by a machine and thus potentially malicious. The ensemble consists of two deep learning models – a convolutional neural network and a long short-term [[memory]] network, both which were built using Keras and Tensorflow. These deep networks are flexible enough to learn complex patterns and do not require manual feature engineering. Deep learning models are also very difficult for malicious actors to reverse engineer, which makes them an ideal fit for cyber security use cases. The last piece of the ensemble is a natural-language processing model to assess whether the words in the domain make sense together. These three models are able to capture the structure and content of a domain, determining whether or not it comes from DGA malware with very high accuracy. These models have already been used to catch malware that vendor tools did not detect. Our system analyzes enterprise-scale network traffic in real time, renders predictions, and raises alerts for cyber security analysts to evaluate. Domenic Puzio is a Data Engineer with Capital One. He graduated from the University of Virginia with degrees in Mathematics and Computer Science. On his current project he is a core developer of a custom platform for ingesting, processing, and analyzing Capital One’s cyber-security data sources. Built entirely from opensource tools (NiFi, Kafka, Storm, Elasticsearch, Kibana), this framework processes hundreds of millions of events per hour. Currently, his focus is on the creation and productionization of machine learning models that provide enrichment to the data being streamed through the system. He is a contributor to two Apache projects. Kate Highnam has a background in Computer Science and Business, focusing on security, embedded devices, and accounting. At the University of Virginia, her thesis was a published industrial research paper containing an attack scenario and repair algorithm for drones deployed on missions with limited ground control contact. After joining Capital One as a Data Engineer, Kate has developed features within an internal DevOps Pipeline and Data Lake governance system. Currently, she builds machine learning models to assist cybersecurity experts and enhance defenses. |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| Line 455: | Line 458: | ||
# Optionally, the character-level representation is passed through a small embedding model to generate a more sophisticated word embedding. | # Optionally, the character-level representation is passed through a small embedding model to generate a more sophisticated word embedding. | ||
# The resulting word embeddings are used as input for downstream NLP tasks. | # The resulting word embeddings are used as input for downstream NLP tasks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Out-Of-Vocabulary (OOV) == | ||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=ai+eMail+Out+Of+Vocabulary+OOV YouTube] | ||
| + | [https://www.quora.com/search?q=ai%20eMail%20Out%20Of%20Vocabulary%20OOV ... Quora] | ||
| + | [https://www.google.com/search?q=ai+eMail+Out+Of+Vocabulary+OOV ...Google search] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Out-of-vocabulary (OOV) refers to words or phrases that are not found in a predefined vocabulary or lexicon. These words can pose challenges for natural language processing (NLP) tasks, as the model may not be able to recognize or interpret them correctly. To handle OOV words, NLP systems can employ various techniques, such as: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Embedding|Word embedding]]: Representing words as vectors in a high-dimensional space, where similar words are located closer together. This allows the system to infer the meaning of OOV words based on their context and similarity to known words. | ||
| + | * [[Natural Language Processing (NLP)#Stemming (Morphological Similarity)|Morphological analysis]]: Breaking down words into their constituent morphemes (the smallest meaningful units of language), which can provide clues about the meaning of OOV words. | ||
| + | * [[Unsupervised|Unsupervised learning]]: Using unlabeled data to learn patterns and representations of words, including OOV words, without the need for explicit labeled examples. | ||
| + | * [[Context|Context-based prediction]]: Utilizing the surrounding words and context to predict the meaning or part of speech of an OOV word. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The handling of OOV words is an ongoing area of research in NLP, as it is crucial for developing robust and versatile language processing systems that can operate effectively in real-world scenarios. | ||
= Data Center Security = | = Data Center Security = | ||
| − | [https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=data+center+security+artificial+intelligence | + | [https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=ai+data+center+security+artificial+intelligence YouTube] |
| − | [https://www.google.com/search?q=data+center+security+artificial+intelligence+ | + | [https://www.quora.com/search?q=ai%20data%20center%20security%20artificial%20intelligence ... Quora] |
| + | [https://www.google.com/search?q=ai+data+center+security+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | ||
| + | [https://news.google.com/search?q=ai+data+center+security+artificial+intelligence ...Google News] | ||
| + | [https://www.bing.com/news/search?q=ai+data+center+security+artificial+intelligence&qft=interval%3d%228%22 ...Bing News] | ||
{|<!-- T --> | {|<!-- T --> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:03, 16 June 2024
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- Cybersecurity ... OSINT ... Frameworks ... References ... Offense ... NIST ... DHS ... Screening ... Law Enforcement ... Government ... Defense ... Lifecycle Integration ... Products ... Evaluating
- Zero Trust
- Cybersecurity Conferences
- Risk, Compliance and Regulation ... Ethics ... Privacy ... Law ... AI Governance ... AI Verification and Validation
- Prompt Injection Attack
- (Artificial) Immune System
- 5G Security
- Time ... PNT ... GPS ... Retrocausality ... Delayed Choice Quantum Eraser ... Quantum
- Development ... Notebooks ... AI Pair Programming ... Codeless ... Hugging Face ... AIOps/MLOps ... AIaaS/MLaaS
- Games - Security
- Useful Models ...find outliers:
- Physical Layer Security (PLS)
- Time ... Retrocausality ... Delayed Choice Quantum Eraser ... Quantum
- Government’s AI Odyssey - A Candid Poll on AI and Machine Learning in the Federal Government | Government Business Council - AWS
- Bayesian Poisoning is a technique used by e-mail spammers to attempt to degrade the effectiveness of spam filters that rely on Bayesian spam filtering
- Detecting Malicious Requests with Keras & TensorFlow | Adam Kusey - Medium
- Best security software: How 12 cutting-edge tools tackle today's threats | CSO
- Excel ... Documents ... Database; Vector & Relational ... Graph ... LlamaIndex
- Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA)Is Trying Keep Adversaries From Corrupting AI Tools ... Could cyber adversaries be training the government’s artificial intelligence tools to fail? | Jack Corrigan - Nextgov
- TrojAI - Office of the Director of National Intelligence Office: Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity FedBizOpps.gov predict whether AI systems have been corrupted through so-called “Trojan attacks.”
- Adversarial Attacks on Graph Convolutional Network (GCN), Graph Neural Networks (Graph Nets), Geometric Deep Learning
- Breaking Down the Tencent 2018 Cybersecurity Report
- Chronicle combines all the best parts of Google and X culture
- Fraud and Anomaly Detection | Chris Nicholson - A.I. Wiki pathmind
- The Cyber Security Evaluation Tool (CSET®) | National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center ...provides a systematic, disciplined, and repeatable approach for evaluating an organization’s security posture
- Cyber Command, Microsoft take action against Trickbot botnet before Election Day | Shannon Vavra - cyberscoop
- An update on disruption of Trickbot Tom Burt | Microsoft ...The seven remaining servers are not traditional command-and-control servers but rather Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- FBI warning: Trickbot and ransomware attackers plan big hit on US hospitals | Liam Tung - ZDNet ...The FBI, CISA, HHS warning comes two weeks after Microsoft's partial takedown of the Trickbot botnet.
- European ransomware group strikes US hospital networks, analysts warn | Sean Lyngaas - cyberscoop ..UNC1878 has been deploying Ryuk ransomware and taking multiple hospital IT networks offline ...suspected ransomware attacks this week on hospitals in New York, Oregon and Vermont, and perhaps other states.
- Cybersecurity as we know it will be 'a thing of the past in the next decade,' says Cloudflare's COO, as security moves towards a 'water treatment' model | Rosalie Chan - Business Insider ... cybersecurity systems will weed out bad actors earlier in their attacks
- Watch me Build a Cybersecurity Startup | Siraj Raval
- Machine-Learning Capabilities within Network Detection & Response (NDR) - Podcast | Fidelis Cybersecurity - COO, Craig Harber, and Data Science Manager, Abhishek Sharma ...Extended Detection & Response (NDR)
- A new AI-based tool to detect DDoS attacks | Ingrid Fadelli - TechXplore
- Cybersecurity Information Sheet - Best Practices for Securing Your Home Network | US National Security Agency (NSA)
- AI can identify passwords by sound of keys being pressed, study suggests | Nicola Davis - The Guardian ... with more than 90% accuracy
- The Untold Story of the Boldest Supply-Chain Hack Ever | Kim Zetter - Wired ... The attackers were in thousands of corporate and government networks. They might still be there now. Behind the scenes of the SolarWinds investigation.
- SolarWinds ... AIOps-powered Anomaly-Based Alerts... AIOps-powered observability provides predictive intelligence to help manage complex hybrid IT environments and enables a shift toward autonomous operations
- Applications:
- BigBear.AI ... AI-powered analytics and cyber solutions
- New Cyber ... supporting Risk Management Framework (RMF) & Zero Trust and Insider Threat
- GATE | Gate CyberTech ... defeat wiretapping, peeking, keylogging, phishing, and dictionary attacks ... Demo
- CyFormer AI/ML Cybersecurity Toolkit ... Data is analyzed and then translated through CyFormer’s natural language processing engine resulting in actionable anomaly reports. The CyFormer model can identify events outside of the normal baseline, tag those events, and then send JSON alerts to analysts.
- Generative AI
- ChatGPT is enabling script kiddies to write functional malware | Dan Goodwin - ARS Technica ...For a beta, ChatGPT isn't all that bad at writing fairly decent malware.
- ChatGPT Used to Develop New Malicious Tools | Check Point Research
- ChatGPT Creates Polymorphic Malware | Alessandro Mascellino - InfoSecurity ... researchers at CyberArk
- Hackers are selling a service that bypasses ChatGPT restrictions on malware ChatGPT | Dan Goodin - ARS Technica... restrictions on the creation of illicit content are easy to circumvent.
- AI Can Crack Most Common Passwords In Less Than A Minute | Zhiye Liu - Tom's Hardware
- Integrating ChatGPT & Generative AI Within Cybersecurity Best Practices | Mani Nagothu - Sentinel One
- Google brings generative AI to cybersecurity | Kyle Wiggers - TechCrunch ...Google's Cloud Security AI Workbench, a cybersecurity suite powered by a specialized “security” AI language model called Sec-PaLM. An offshoot of Google’s PaLM
- After WormGPT, FraudGPT Emerges to Help Scammers Steal Your Data | Michael Kan - PC Magazine ... hackers are seizing the opportunity to create AI-powered chatbots to facilitate cybercrime and scams.
- Fifty minutes to hack ChatGPT: Inside the DEF CON competition to break AI | Elias Groll - Cyberscoop ... More than 2,000 hackers attacked cutting-edge chatbots to discover vulnerabilities — and demonstrated the challenges for red-teaming AI -- Anthropic, Cohere, Google, Hugging Face, Microsoft, Meta, NVIDIA, OpenAI and Stability AI
AI can assist with cybersecurity functions in many ways. It can reinforce cyber threat intelligence by searching for characteristics of cyberattacks, strengthening defenses, analyzing data to authenticate users, and discovering clues as to the identity of specific cyberattackers. AI can also analyze massive quantities of risk data to speed up response times and augment under-resourced security operations. AI technologies like machine learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP) can provide rapid insights to cut through the noise of daily alerts, drastically reducing response times.
AI can explain the behavior of malicious scripts
AI can help address many challenges in cybersecurity, such as the massive amounts of data that no amount of humans can help protect and the hundreds and thousands of devices to protect a single organization. AI improves its knowledge to “understand” cybersecurity threats and cyber risk by consuming billions of data artifacts. It analyzes relationships between threats like malicious files, suspicious IP addresses or insiders in seconds or minutes. In addition, experts can learn a lot about vulnerabilities in their network or software and the threat actors who try to attack it by using AI to set up honeypots on decoy servers.
AI is being used in a variety of ways to improve cybersecurity. Some of the most common applications of AI in cybersecurity include:
- Malware detection: AI can be used to detect malware by analyzing its behavior and comparing it to known malware signatures.
- Network intrusion detection: AI can be used to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access or data exfiltration.
- User behavior analytics: AI can be used to track user behavior and identify suspicious activity, such as clicking on phishing links or downloading malicious files.
- Vulnerability scanning: AI can be used to scan systems for known vulnerabilities.
- Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR): AI can be used to automate security tasks, such as incident response and remediation.
Contents
Risk-based Vulnerability Management (RBVM)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fraud Detection
- Introduction to Fraud Detection Systems | Miguel Gonzalez-Fierro, Microsoft
- AI for Health Insurance Fraud Detection – Current Applications | Niccolo Mejia
|
|
|
|
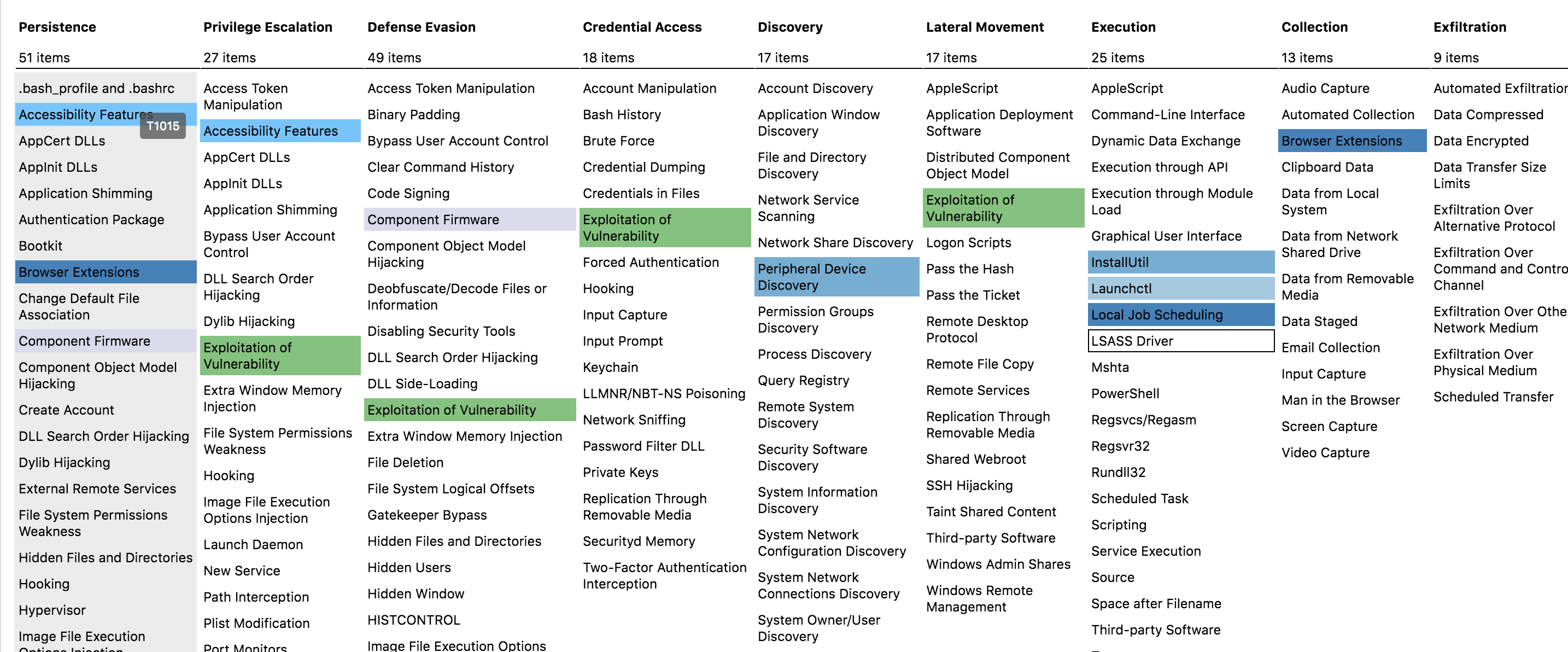
MITRE ATT&CK™
Youtube search... ...Google search
- ATT&CK™ Navigator | MITRE ...measure your threat detection
- ATT&CK™ Homepage | MITRE
- ATT&CK™ Resources | MITRE
- Cybersecurity Frameworks, Architectures & Roadmaps
- MITRE ATT&CK™ Framework: Everything You Need to Know | Jeff Petters - Varonis
- DETT&CT: MAPPING YOUR BLUE TEAM TO MITRE ATT&CK™ | Marcus Bakker and Ruben Bouman - MB Secure ...DEtect Tactics, Techniques & Combat Threats
- Remapping Red Canary with ATT&CK sub-techniques | B. Donohue, K. Nickels, and M. Graeber - Atomic Red Team; a library of simple tests that every security team can execute to test their defenses.
- Using the OODA Loop - Purple Team with Cybersecurity
knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations. The ATT&CK™ knowledge base is used as a foundation for the development of specific threat models and methodologies in the private sector, in government, and in the cybersecurity product and service community.

|
|
|
|
|
|
Open Source Tools
Youtube search... ...Google search
- National Security Agency (NSA)
- Ghidra A software reverse engineering (SRE) suite of tools developed by NSA's Research Directorate in support of the Cybersecurity mission Ghidra.org
- The NSA Makes Ghidra, a Powerful Cybersecurity Tool, Open Source | Lily Hay Newman - Wired
- DataWave is an ingest/query framework that leverages Apache Accumulo to provide fast, secure data access.
- Free Open Source Software Cybersecurity | DataShield
- 47 powerful open-source app sec tools you should consider | Mike Perrow - Vertica - TechBeacon
|
|
AI-Driven Patch Management
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- 5 ways AI-driven patch management is driving the future of cybersecurity | Louis Columbus - VentureBeat
- Revolutionizing Patch Management: Meeting Modern Infrastructure and Workspace Needs | E-SPIN
Also, AI models help in the automatic analysis of patch risk and carry out the complete life-cycle of each version release. AI-driven patch management helps in automatically identifying new patch or application release with the help of AI-models. Based on this automated discovery of the new patch, the new version update will take place across all servers and applications. AI-based patch management relies in part on algorithms that need a continual stream of data in order to keep “learning” and assessing patch vulnerabilities. There are several benefits of using AI in patch management. AI-driven patch management enables you to automate your entire application version change management. This automation is made possible with the use of advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. Also, AI models help in the automatic analysis of patch risk and carry out the complete life-cycle of each version release. Automating patch management while capitalizing on diverse datasets and integrating it into an RBVM platform is a perfect use case of AI in cybersecurity. Leading AI-based patch management systems can interpret vulnerability assessment telemetry and prioritize risks by patch type, system and endpoint.
There are several companies that use AI-driven patch management technology. Some of these companies include Atera, Automox, BMC Client Management Patch powered by Ivanti, Canonical, ConnectWise, Flexera, GFI, ITarian, Ivanti, Jamf, Kaseya, ManageEngine, N-able, NinjaOne, SecPod, SysWard, Syxsense and Tanium
Asset Risk Management (ARM): Physical Layer
- Sepio ... Asset Risk Management that works for you. Manage your asset risks with granular controls based on true Asset DNA
- Sepio and NIST Cybersecurity Framework Compliance
The Sepio solution compares an asset’s DNA profile and Asset Risk Factor (ARF) score with your preset rules and directly connects it to an enforced policy. Any changes to an asset are accounted for, and the appropriate policy applied. Assets that breach the preset rules or get recognized as known attack tools by Sepio’s are immediately blocked, enabling instant and automated risk mitigation.Sepio’s patented machine learning technology revolutionizes asset visibility across your enterprise network and endpoints, providing effortless and continuous monitoring down to the peripherals. Sepio’s Asset DNA accurately identifies all assets based on their physical nature, ensuring that your organization can trust each device’s identity and detect any unauthorized or rogue devices. From unseen and actively evasive assets to spoofed devices, compromised hardware, and unauthorized assets connected to your network, Sepio’s improved asset visibility feature eliminates blind spots and provides comprehensive visibility into your IT/OT/IoT/peripheral assets. In addition to enhancing security, asset visibility is crucial for compliance with cybersecurity regulations. With Asset DNA, organizations can quickly identify any non-compliant devices throughout their network, down to the endpoint’s peripherals.
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- Embedding ... Fine-tuning ... RAG ... Search ... Clustering ... Recommendation ... Anomaly Detection ... Classification ... Dimensional Reduction. ...find outliers
- Google unveils new next generation security system to keep your Gmail account safe | Sead Fadilpašić - TechRadar ... RETVec promises to cut down on Gmail spam and reduce false positives
RETVec is short for Resilient and Efficient Text Vectorizer, with vectorization being a “methodology in natural language processing to map words or phrases from a corresponding vector of real numbers” and then using those to run further analysis, predictions, and word similarities Understanding NLP Word Embeddings — Text Vectorization | Prabhu - Toward Data Science
With RETVec, Gmail will be better at spotting spam emails hiding invisible characters, LEET substitution (3xpl4in3d instead of explained, for example), intentional typos, and more. Harmful email messages will have a tough time making it into inboxes. Leet speak, also known as hackspeak or simply leet, is the substitution of a word's letters with numbers or special characters. "Leet" is derived from the word "elite"
RETVec's character encoding scheme is based on the idea that words can be represented by their constituent characters. This allows RETVec to handle out-of-vocabulary (OOV) words and typos, which are common challenges for traditional word-based vectorizers. RETVec's character encoder first maps each character to a unique identifier. Then, it applies a series of transformations to these identifiers to capture local context and word-level information. The resulting character-level representation is then used to generate the word embedding.
Optional Embedding Model - In addition to the character encoding scheme, RETVec can also incorporate a small embedding model to learn more sophisticated word representations. This embedding model is trained using pairwise metric learning, which helps to improve the resilience of the word embeddings to typos and adversarial attacks.
Pipeline - the overall RETVec pipeline can be summarized as follows:
- Input text is preprocessed to remove punctuation, whitespace, and other non-alphanumeric characters.
- The text is segmented into individual words.
- For each word, its constituent characters are encoded using RETVec's character encoder.
- Optionally, the character-level representation is passed through a small embedding model to generate a more sophisticated word embedding.
- The resulting word embeddings are used as input for downstream NLP tasks.
Out-Of-Vocabulary (OOV)
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search
Out-of-vocabulary (OOV) refers to words or phrases that are not found in a predefined vocabulary or lexicon. These words can pose challenges for natural language processing (NLP) tasks, as the model may not be able to recognize or interpret them correctly. To handle OOV words, NLP systems can employ various techniques, such as:
- Word embedding: Representing words as vectors in a high-dimensional space, where similar words are located closer together. This allows the system to infer the meaning of OOV words based on their context and similarity to known words.
- Morphological analysis: Breaking down words into their constituent morphemes (the smallest meaningful units of language), which can provide clues about the meaning of OOV words.
- Unsupervised learning: Using unlabeled data to learn patterns and representations of words, including OOV words, without the need for explicit labeled examples.
- Context-based prediction: Utilizing the surrounding words and context to predict the meaning or part of speech of an OOV word.
The handling of OOV words is an ongoing area of research in NLP, as it is crucial for developing robust and versatile language processing systems that can operate effectively in real-world scenarios.
Data Center Security
YouTube ... Quora ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Vault
Solutions:
- VectorZero's cloud-based cybersecurity solution, Active Data Vault, uses AI to provide high-assurance, secure confidential computing. The AI-enabled security solution encrypts data in transit, at rest, and during use while data is active, ensuring that even the company's software service providers do not have keys to the data. VectorZero Technologies LLC has pioneered a new class of AI-enabled security-as-a-service software. The solution uses thousands of security controls integrated into one software solution. VectorZero is a company that provides a high-assurance, high-utility data vault powered by advanced key management, post-quantum encryption, and edge-to-cloud chain of trust.
- Skyflow offers a Generative AI data privacy solution with their Large Language Model (LLM) Privacy Vault. It provides comprehensive privacy-preserving solutions that let companies prevent the leakage of sensitive data into LLMs. The LLM Privacy Vault is designed to protect sensitive data by using Generative AI to create synthetic data that can be used for testing and development purposes.
Concept