Difference between revisions of "Best Practices"
m |
m |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|title=PRIMO.ai | |title=PRIMO.ai | ||
|titlemode=append | |titlemode=append | ||
| − | |keywords=artificial, intelligence, machine, learning, models | + | |keywords=ChatGPT, artificial, intelligence, machine, learning, GPT-4, GPT-5, NLP, NLG, NLC, NLU, models, data, singularity, moonshot, Sentience, AGI, Emergence, Moonshot, Explainable, TensorFlow, Google, Nvidia, Microsoft, Azure, Amazon, AWS, Hugging Face, OpenAI, Tensorflow, OpenAI, Google, Nvidia, Microsoft, Azure, Amazon, AWS, Meta, LLM, metaverse, assistants, agents, digital twin, IoT, Transhumanism, Immersive Reality, Generative AI, Conversational AI, Perplexity, Bing, You, Bard, Ernie, prompt Engineering LangChain, Video/Image, Vision, End-to-End Speech, Synthesize Speech, Speech Recognition, Stanford, MIT |description=Helpful resources for your journey with artificial intelligence; videos, articles, techniques, courses, profiles, and tools |
| − | |description=Helpful resources for your journey with artificial intelligence; videos, articles, techniques, courses, profiles, and tools | + | |
| + | <!-- Google tag (gtag.js) --> | ||
| + | <script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=G-4GCWLBVJ7T"></script> | ||
| + | <script> | ||
| + | window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || []; | ||
| + | function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);} | ||
| + | gtag('js', new Date()); | ||
| + | |||
| + | gtag('config', 'G-4GCWLBVJ7T'); | ||
| + | </script> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [ | + | [https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=ai+Best+Practice YouTube search...] |
| − | [ | + | [https://www.quora.com/search?q=ai%20Best%20Practice ... Quora search] |
| + | [https://www.google.com/search?q=ai+Best+Practice ...Google search] | ||
| + | [https://news.google.com/search?q=ai+Best+Practice ...Google News] | ||
| + | [https://www.bing.com/news/search?q=ai+Best+Practice&qft=interval%3d%228%22 ...Bing News] | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Strategy & Tactics]] ... [[Project Management]] ... [[Best Practices]] ... [[Checklists]] ... [[Project Check-in]] ... [[Evaluation]] ... [[Evaluation - Measures|Measures]] |
| − | + | * [[Leadership]] | |
| − | + | * [[Risk, Compliance and Regulation]] ... [[Ethics]] ... [[Privacy]] ... [[Law]] ... [[AI Governance]] ... [[AI Verification and Validation]] | |
| − | + | * [[Data Science]] ... [[Data Governance|Governance]] ... [[Data Preprocessing|Preprocessing]] ... [[Feature Exploration/Learning|Exploration]] ... [[Data Interoperability|Interoperability]] ... [[Algorithm Administration#Master Data Management (MDM)|Master Data Management (MDM)]] ... [[Bias and Variances]] ... [[Benchmarks]] ... [[Datasets]] | |
| − | + | * [https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/guides/rules-of-ml Rules of Machine Learning: Best Practices for ML Engineering | Martin Zinkevich - ][[Google]] | |
| − | + | * [https://cloud.google.com/solutions/machine-learning/best-practices-for-ml-performance-cost Best practices for performance and cost optimization for machine learning |] [[Google]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * [[ | ||
| − | * [[ | ||
| − | |||
{|<!-- T --> | {|<!-- T --> | ||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
| Line 47: | Line 42: | ||
<b>Best Practices of In-Platform AI/ML Webinar | <b>Best Practices of In-Platform AI/ML Webinar | ||
</b><br>Productive use of machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies is impossible without a platform that allows autonomous functioning of AI/ML mechanisms. In-platform AI/ML has a number of advantages that can be obtained via best practices by InterSystems. On this webinar, we will present: • MLOps as the natural paradigm for in-platform AI/ML | </b><br>Productive use of machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies is impossible without a platform that allows autonomous functioning of AI/ML mechanisms. In-platform AI/ML has a number of advantages that can be obtained via best practices by InterSystems. On this webinar, we will present: • MLOps as the natural paradigm for in-platform AI/ML | ||
| − | • A full cycle of AI/ML content development and in-platform deployment (including bidirectional integration of Jupyter with InterSystems IRIS) | + | • A full cycle of AI/ML content [[development]] and in-platform deployment (including bidirectional integration of Jupyter with InterSystems IRIS) |
• New toolset added to ML Toolkit: integration and orchestration for Julia mathematical modeling environment | • New toolset added to ML Toolkit: integration and orchestration for Julia mathematical modeling environment | ||
• Automated AI/ML model selection and parameter determination via an SQL query | • Automated AI/ML model selection and parameter determination via an SQL query | ||
| Line 54: | Line 49: | ||
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{|<!-- T --> | {|<!-- T --> | ||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube>-- | + | <youtube>p2gvo0RCdSY</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>3 Best Practices for Overcoming AI Obstacles to Build the Future-ready Enterprise |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), an IT services, consulting and business solutions organization that has been partnering with the world’s largest businesses in their transformation journeys for the last 50 years. A part of the Tata group, India's largest multinational business group, TCS has over 436,000 of the world’s best-trained consultants in 46 countries. The company is listed on the BSE (formerly Bombay Stock Exchange) and the NSE (National Stock Exchange) in India. |
| + | |} | ||
| + | |<!-- M --> | ||
| + | | valign="top" | | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | <youtube>66TgH0YV4eA</youtube> | ||
| + | <b>Visualization Best Practices for Explainable AI | ||
| + | </b><br>How do you know if a machine learning model is trustworthy or potentially biased? One of the top trends in analytics is the rise of explainable AI, the practice of presenting transparent views into how algorithms make decisions. In this session, we will dive deeper into understanding and explaining machine learning terms and charts to the business using Tableau. We will walk through real-world examples from healthcare, retail, marketing, banking, and other industries. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| + | {|<!-- T --> | ||
| + | | valign="top" | | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | <youtube>85e-bkN-5Es</youtube> | ||
| + | <b>Conversational AI: Best Practices for Building Bots | ||
| + | </b><br>Conversational digital affordances are fast becoming a norm for users everywhere – from the office to the kitchen; from the car to the living room. We can type, tap or talk to all manner of device, apps, bots and agents to do all manner of things. When designed well, conversational AI experiences are natural, intuitive and efficient. In this session, we’ll provide practical guidance for building great bots. We’ll put the guidance to work using the Bot Builder v4 SDK, bot [[development]] tools and [[Microsoft]] Cognitive Services. | ||
|} | |} | ||
|<!-- M --> | |<!-- M --> | ||
| Line 70: | Line 78: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>9Zag7uhjdYo</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>007. Machine learning best practices we've learned from hundreds of competitions - Ben Hamner |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>Ben Hamner is Chief Scientist at Kaggle, leading its data science and [[development]] teams. He is the principal architect of many of Kaggle's most advanced machine learning projects including current work in Eagle Ford and GE's flight arrival prediction and optimization modeling. |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 87: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>4cqbblDhhGc</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>Geo for Good 2019: Machine Learning Best Practices |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>With the pace of modern machine learning, building and training neural networks is hard. Learn some best practices and sift through the overwhelming amount of information available with a focus on remote sensing. Talk presented by Chris Brown from [[Google]]. |
|} | |} | ||
|<!-- M --> | |<!-- M --> | ||
| Line 87: | Line 95: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>8IykL7vQ4xI</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>(M25-L) Machine Learning Best Practices From the [[Amazon]] ML Solutions Lab |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>This session will dive into key considerations for executives to think about as they design, deploy, and create a machine learning strategy. We will share customer success stories, and how to get started quickly. Session Speakers: Ryan Gavin, Larry Pizette (Session M25-L) |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| − | |||
{|<!-- T --> | {|<!-- T --> | ||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>33EiOfCRpSQ</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>Best Practices for Verification and Validation |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>In this webinar you will learn techniques and practices in Model-Based Design to verify and validate software designs and embedded code using MathWorks tools. We will address requirements driven [[development]], model coverage testing, and static code analysis of embedded software. About the Presenters: Nishaat Vasi is a product marketing manager at MathWorks. Since joining MathWorks in 2007, Nishaat has partnered with customers involved in high-integrity applications to promote the adoption of MathWorks tools for embedded software verification. He holds an M.S. in electrical engineering from University of Massachusetts and a B.E. in electronics engineering from University of Mumbai. Jay Abraham is a product marketing manager at MathWorks. His area of expertise is in software tools for the verification of critical embedded applications. He has over 20 years of software and hardware design experience. Jay has an M.S. in computer engineering from Syracuse University and a B.S. in electrical engineering from Boston University. See what's new in the latest release of MATLAB and Simulink: https://goo.gl/3MdQK1 |
| + | Download a trial: https://goo.gl/PSa78r | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Heuristics = | ||
| + | {|<!-- T --> | ||
| + | | valign="top" | | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | <youtube>ReFqFPJHLhA</youtube> | ||
| + | <b>What Are Heuristics? | ||
| + | </b><br>We all use heuristics to make everyday decisions — but sometimes they blind us to the truth. So we need to do something that doesn’t come easy: accept that our ideas might be wrong. SUBSCRIBE: https://bit.ly/2dUx6wg LEARN MORE: Behavioral Economics (video series): Join Prof. Antony Davies of Duquesne University and Erika Davies of George Mason University as they take you on a crash course of behavioral economics, discussing topics like rational choice, heuristics, nudging, and public choice economics. | ||
|} | |} | ||
|<!-- M --> | |<!-- M --> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 126: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>nSFHFfevfms</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>Types of Heuristics Availability, Representativeness & Base |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>appsychfun |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| − | |||
{|<!-- T --> | {|<!-- T --> | ||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>EKWGGDXe5MA</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>Richard Feynman Computer Heuristics Lecture |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>Richard Feynman, Winner of the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics, gives us an insightful lecture about computer heuristics: how computers work, how they file information, how they handle data, how they use their information in allocated processing in a finite amount of time to solve problems and how they actually compute values of interest to human beings. These topics are essential in the study of what processes reduce the amount of work done in solving a particular problem in computers, giving them speeds of solving problems that can outmatch humans in certain fields but which have not yet reached the complexity of human driven intelligence. The question if human thought is a series of fixed processes that could be, in principle, imitated by a computer is a major theme of this lecture and, in Feynman's trademark style of teaching, gives us clear and yet very powerful answers for this field which has gone on to consume so much of our lives today. No doubt this lecture will be of crucial interest to anyone who has ever wondered about the process of human or machine thinking and if a synthesis between the two can be made without violating logic. Donate and Support this Channel: https://www.patreon.com/muonray |
|} | |} | ||
|<!-- M --> | |<!-- M --> | ||
| Line 124: | Line 143: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>v2SDBbtFp3c</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>The Heuristics Revolution – Gerd Gigerenzer at Summer Institute 2018 |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>Decision problems come in two kinds: risk and uncertainty. Risk applies to situations that are well structured and stable, such as gambles, lotteries, and cancer screening, and has been tamed by the probabilistic revolution in the sciences since the beginning of the 17th century. Uncertainty applies to situations that are ill structured and instable, such as human interaction, investment, and business. Although this is an old distinction, most economists and psychologists have ignored it and used the probability theory as the sole tool for dealing with both. Part of the problem was that no theory of decision-making under uncertainty existed until recently. Based on Herbert Simon’s work, we are now developing such a theory of intelligent heuristics that are able to deal with situations of uncertainty. The science of heuristics addresses three questions. The first is descriptive: What are the heuristics in the adaptive toolbox of a species, an organization, or an individual, and how do people choose between heuristics? The second is normative: In which situations is a heuristic better than a complex strategy? This question is known as the study of the ecological rationality of heuristics, which proceeds using analysis and simulation. The third question is one of intuitive design: How can systems be designed that help experts and laypeople make better decisions, be it in developing simple rules for safer financial regulation or improving medical diagnosis? The methodological tools are threefold: formal models of heuristics (instead of vague labels such as “System 1”), competitive testing of heuristics against complex strategies (instead of null hypothesis testing), and tests of the predictive power of heuristics (instead of data fitting). The heuristic revolution complements the probabilistic revolution and overcomes the earlier misconception of heuristics as biases. |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
| − | = | + | = Pareto = |
| − | * [ | + | [https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Pareto+Principle+artificial+intelligence+Deep+Machine+Learning+AI YouTube search...] |
| − | + | [https://www.google.com/search?q=Pareto+Principle+artificial+intelligence+Deep+Machine+Learning+AI ...Google search] | |
| − | + | ||
| + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_principle Pareto Principle | Wikipedia] | ||
| + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_distribution Pareto Distribution | Wikipedia] | ||
| + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_chart Pareto Chart | Wikipedia] | ||
| + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_priority_index https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_priority_index Pareto Priority Index | Wikipedia] | ||
| + | * [https://hbr.org/2017/02/ai-is-going-to-change-the-8020-rule AI Is Going to Change the 80/20 Rule | Michael Schrage - Harvard Business Review] | ||
| + | * [https://vigir.missouri.edu/~gdesouza/Research/Conference_CDs/IEEE_SSCI_2007/CI%20and%20Games%20-%20CIG%202007/data/papers/CIG/S002P003.pdf Pareto Evolution and Co-Evolution in Cognitive Neural Agents Synthesis for Tic-Tac-Toe | Y. Yau, J. Teo and P. Anthony] | ||
| + | * [https://www.aaai.org/Papers/JAIR/Vol21/JAIR-2104.pdf Competitive Coevolution through Evolutionary Complexification | Kenneth O. Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen] | ||
| + | * [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952197601000367 A Pareto-optimal genetic algorithm for warehouse multi-objective optimization | P.N. Poulos, G.G. Rigatos, S.G. Tzafestas, and A.K. Koukos - ScienceDirect] | ||
| + | * [https://www.kdnuggets.com/2019/03/pareto-principle-data-scientists.html The Pareto Principle for Data Scientists | Pradeep Gulipalli - Tiger Analytics KDnuggets] | ||
| + | * [https://medium.com/@mittajithendra46/pareto-distribution-to-normal-distribution-24cf3657a551 Pareto Distribution to Normal Distribution | result of strain - Medium] | ||
| + | * [https://resumelab.com/career-advice/pareto-principle Pareto Principle & the 80/20 Rule (Updated for 2020) | Maciej Duszynski - ResumeLab] | ||
| + | * [https://qctraininginc.com/7-basic-quality-tools-the-pareto-chart/ 7 Quality Tools – The Pareto Chart | Steven Bonacorsi - QC Training Services, Inc.] | ||
| + | * [https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.10782 AI Feynman 2.0: Pareto-optimal symbolic regression exploiting graph modularity | S. Udrescu, A. Tan, J. Feng, O. Neto, T. Wu, and M. Tegmark] | ||
| + | |||
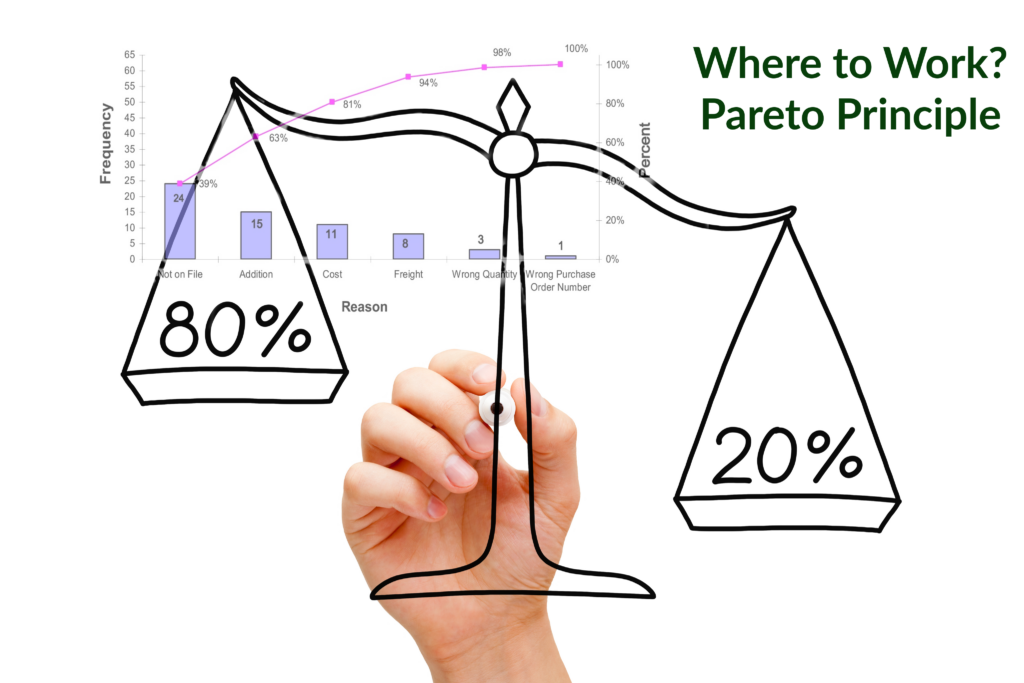
| + | If we consider the <b>Pareto Principle</b> when leveraging AI, we would employ human skills such as strategy, creativity, and collaboration for the <b>20 percent of tasks that drive 80 percent of business impact</b>. Then, apply AI to the 80 percent of tasks that are routine-oriented and structured, making them ideal for automation. [https://www.marchex.com/blog/artificial-intelligence-jobs-and-the-pareto-principle/#:~:text=If%20we%20consider%20the%20Pareto,making%20them%20ideal%20for%20automation. Artificial Intelligence, jobs and the Pareto Principle | Erin Murphy - Marchex] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <img src="https://qctraininginc.com/wp-content/uploads/80_20-Rule-Pareto-1024x683.png" width="800"> | ||
| + | |||
{|<!-- T --> | {|<!-- T --> | ||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>AabUVkYsV2s</youtube> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>COVID-19 |
| − | </b><br> | + | </b><br>nETSETOS This video describes Pareto Distribution with given topics:- - 80-20 rule with graph - Parameter of Pareto Distribution - Application of Pareto Principle' - COVID - 19 Analysis with Pareto - How to Plot Pareto On [[Jupyter]] - Testing Pareto with the help of QQPlot |
| + | |} | ||
| + | |<!-- M --> | ||
| + | | valign="top" | | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 550px;" | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | <youtube>pkJkHB_c3nA</youtube> | ||
| + | <b>AI for physics & physics for AI | ||
| + | </b><br>Max Tegmark, MIT | ||
| + | Abstract: After briefly reviewing how machine learning is becoming ever-more widely used in physics, I explore how ideas and methods from physics can help improve machine learning, focusing on automated discovery of mathematical formulas from data. I present a method for unsupervised learning of equations of motion for objects in raw and optionally distorted unlabeled video. I also describe progress on symbolic regression, i.e., finding a symbolic expression that matches data from an unknown function. Although this problem is likely to be NP-hard in general, functions of practical interest often exhibit symmetries, separability, compositionality and other simplifying properties. In this spirit, we have developed a recursive multidimensional symbolic regression algorithm that combines neural network fitting with a suite of physics-inspired techniques that discover and exploit these simplifying properties, enabling significant improvement of state-of-the-art performance. | ||
| + | Related papers: AI Feynman: a Physics-Inspired Method for Symbolic Regression - https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11481 AI Feynman 2.0: Pareto-optimal symbolic regression exploiting graph modularity - https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.10782 Symbolic Pregression: Discovering Physical Laws from Raw Distorted Video - https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11212 | ||
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
Latest revision as of 04:48, 30 April 2024
YouTube search... ... Quora search ...Google search ...Google News ...Bing News
- Strategy & Tactics ... Project Management ... Best Practices ... Checklists ... Project Check-in ... Evaluation ... Measures
- Leadership
- Risk, Compliance and Regulation ... Ethics ... Privacy ... Law ... AI Governance ... AI Verification and Validation
- Data Science ... Governance ... Preprocessing ... Exploration ... Interoperability ... Master Data Management (MDM) ... Bias and Variances ... Benchmarks ... Datasets
- Rules of Machine Learning: Best Practices for ML Engineering | Martin Zinkevich - Google
- Best practices for performance and cost optimization for machine learning | Google
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heuristics
|
|
|
|
Pareto
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Pareto Principle | Wikipedia
- Pareto Distribution | Wikipedia
- Pareto Chart | Wikipedia
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_priority_index Pareto Priority Index | Wikipedia
- AI Is Going to Change the 80/20 Rule | Michael Schrage - Harvard Business Review
- Pareto Evolution and Co-Evolution in Cognitive Neural Agents Synthesis for Tic-Tac-Toe | Y. Yau, J. Teo and P. Anthony
- Competitive Coevolution through Evolutionary Complexification | Kenneth O. Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen
- A Pareto-optimal genetic algorithm for warehouse multi-objective optimization | P.N. Poulos, G.G. Rigatos, S.G. Tzafestas, and A.K. Koukos - ScienceDirect
- The Pareto Principle for Data Scientists | Pradeep Gulipalli - Tiger Analytics KDnuggets
- Pareto Distribution to Normal Distribution | result of strain - Medium
- Pareto Principle & the 80/20 Rule (Updated for 2020) | Maciej Duszynski - ResumeLab
- 7 Quality Tools – The Pareto Chart | Steven Bonacorsi - QC Training Services, Inc.
- AI Feynman 2.0: Pareto-optimal symbolic regression exploiting graph modularity | S. Udrescu, A. Tan, J. Feng, O. Neto, T. Wu, and M. Tegmark
If we consider the Pareto Principle when leveraging AI, we would employ human skills such as strategy, creativity, and collaboration for the 20 percent of tasks that drive 80 percent of business impact. Then, apply AI to the 80 percent of tasks that are routine-oriented and structured, making them ideal for automation. Artificial Intelligence, jobs and the Pareto Principle | Erin Murphy - Marchex
|
|