Difference between revisions of "Poisson Regression"
m |
m |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|title=PRIMO.ai | |title=PRIMO.ai | ||
|titlemode=append | |titlemode=append | ||
| − | |keywords=artificial, intelligence, machine, learning, models | + | |keywords=ChatGPT, artificial, intelligence, machine, learning, GPT-4, GPT-5, NLP, NLG, NLC, NLU, models, data, singularity, moonshot, Sentience, AGI, Emergence, Moonshot, Explainable, TensorFlow, Google, Nvidia, Microsoft, Azure, Amazon, AWS, Hugging Face, OpenAI, Tensorflow, OpenAI, Google, Nvidia, Microsoft, Azure, Amazon, AWS, Meta, LLM, metaverse, assistants, agents, digital twin, IoT, Transhumanism, Immersive Reality, Generative AI, Conversational AI, Perplexity, Bing, You, Bard, Ernie, prompt Engineering LangChain, Video/Image, Vision, End-to-End Speech, Synthesize Speech, Speech Recognition, Stanford, MIT |description=Helpful resources for your journey with artificial intelligence; videos, articles, techniques, courses, profiles, and tools |
| − | |description=Helpful resources for your journey with artificial intelligence; videos, articles, techniques, courses, profiles, and tools | + | |
| + | <!-- Google tag (gtag.js) --> | ||
| + | <script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=G-4GCWLBVJ7T"></script> | ||
| + | <script> | ||
| + | window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || []; | ||
| + | function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);} | ||
| + | gtag('js', new Date()); | ||
| + | |||
| + | gtag('config', 'G-4GCWLBVJ7T'); | ||
| + | </script> | ||
}} | }} | ||
[http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Poisson+Regression YouTube search...] | [http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Poisson+Regression YouTube search...] | ||
| Line 10: | Line 19: | ||
* [[AI Solver]] | * [[AI Solver]] | ||
** [[...predict values]] | ** [[...predict values]] | ||
| − | |||
* [[Regression]] Analysis | * [[Regression]] Analysis | ||
* [[Math for Intelligence]] ... [[Finding Paul Revere]] | * [[Math for Intelligence]] ... [[Finding Paul Revere]] | ||
Revision as of 20:44, 5 July 2023
YouTube search... ...Google search
- AI Solver
- Regression Analysis
- Math for Intelligence ... Finding Paul Revere
- Poisson Regression? | Microsoft
- Choosing the Correct Type of Regression Analysis | Jim Frost
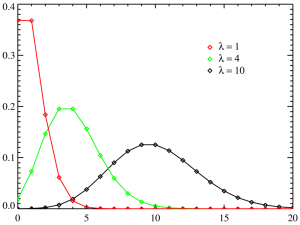
Poisson regression is used to model response variables (Y-values) that are counts. It tells you which explanatory variables have a statistically significant effect on the response variable. In other words, it tells you which X-values work on the Y-value. It’s best used for rare events, as these tend to follow a Poisson distribution (as opposed to more common events which tend to be normally distributed). For example:
- Number of colds contracted on airplanes.
- Number of bacteria found in a petri dish.
- Counts of catastrophic computer failures at a large tech firm in a calendar year.
- Number of 911 calls that end in the death of a suspect.
For large means, the normal distribution is a good approximation for the Poisson distribution. Therefore, Poisson regression is more suited to cases where the response variable is a small integer.
Poisson regression is only used for numerical, continuous data. The same technique can be used for modeling categorical explanatory variables or counts in the cells of a contingency table. When used in this way, the models are called loglinear models. What is Poisson Regression? | Statistics How To