Difference between revisions of "Transformer"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* [[Transformer-XL]] | * [[Transformer-XL]] | ||
* [http://github.com/huggingface/transformers Transformers] provides state-of-the-art general-purpose architectures (BERT, GPT-2, RoBERTa, XLM, DistilBert, XLNet...) for Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG) with over 32+ pretrained models in 100+ languages and deep interoperability between TensorFlow 2.0 and PyTorch. | GitHub | * [http://github.com/huggingface/transformers Transformers] provides state-of-the-art general-purpose architectures (BERT, GPT-2, RoBERTa, XLM, DistilBert, XLNet...) for Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG) with over 32+ pretrained models in 100+ languages and deep interoperability between TensorFlow 2.0 and PyTorch. | GitHub | ||
| + | * [[Generative]] Modeling | ||
| + | * [http://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2019/06/understanding-transformers-nlp-state-of-the-art-models/ How do Transformers Work in NLP? A Guide to the Latest State-of-the-Art Models | Prateek Joshi - Analytics Vidhya] | ||
| + | * [[Sequence to Sequence (Seq2Seq)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Transformer Model - uniquely have attention such that every output element is connected to every input element. The weightings between them are calculated dynamically, effectively. [http://venturebeat.com/2019/10/24/google-achieves-state-of-the-art-nlp-performance-with-an-enormous-language-model-and-data-set/ | Kyle Wiggers] The dominant sequence transduction models are based on complex recurrent or convolutional neural networks in an [[Autoencoder (AE) / Encoder-Decoder]] configuration. The best performing models also connect the encoder and decoder through an attention mechanism. We propose a new simple network architecture, the Transformer, based solely on attention mechanisms, dispensing with recurrence and convolutions entirely. Experiments on two machine translation tasks show these models to be superior in quality while being more parallelizable and requiring significantly less time to train. [http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762 Attention Is All You Need | A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A.N. Gomez, L. Kaiser, and I. Polosukhin] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Tensor2Tensor (T2T) == | ||
* Tensor2Tensor (T2T) | Google Brain | * Tensor2Tensor (T2T) | Google Brain | ||
** [http://nlp.stanford.edu/seminar/details/lkaiser.pdf Tensor2Tensor Transformers: New Deep Models for NLP | Łukasz Kaiser] | ** [http://nlp.stanford.edu/seminar/details/lkaiser.pdf Tensor2Tensor Transformers: New Deep Models for NLP | Łukasz Kaiser] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 32: | ||
Tensor2Tensor, or T2T for short, is a library of deep learning models and datasets designed to make deep learning more accessible and [accelerate ML research](https://research.googleblog.com/2017/06/accelerating-deep-learning-research.html). T2T is actively used and maintained by researchers and engineers within the [Google Brain team](https://research.google.com/teams/brain/) and a community of users. This colab shows you some datasets we have in T2T, how to download and use them, some models we have, how to download pre-trained models and use them, and how to create and train your own models. | Jay Alammar] | Tensor2Tensor, or T2T for short, is a library of deep learning models and datasets designed to make deep learning more accessible and [accelerate ML research](https://research.googleblog.com/2017/06/accelerating-deep-learning-research.html). T2T is actively used and maintained by researchers and engineers within the [Google Brain team](https://research.google.com/teams/brain/) and a community of users. This colab shows you some datasets we have in T2T, how to download and use them, some models we have, how to download pre-trained models and use them, and how to create and train your own models. | Jay Alammar] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 07:53, 9 June 2020
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Attention
- The Illustrated Transformer | Jay Alammar
- What is a Transformer? | Maxime Allard - Medium
- Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
- Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Memory Networks
- Transformer-XL
- Transformers provides state-of-the-art general-purpose architectures (BERT, GPT-2, RoBERTa, XLM, DistilBert, XLNet...) for Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG) with over 32+ pretrained models in 100+ languages and deep interoperability between TensorFlow 2.0 and PyTorch. | GitHub
- Generative Modeling
- How do Transformers Work in NLP? A Guide to the Latest State-of-the-Art Models | Prateek Joshi - Analytics Vidhya
- Sequence to Sequence (Seq2Seq)
Transformer Model - uniquely have attention such that every output element is connected to every input element. The weightings between them are calculated dynamically, effectively. | Kyle Wiggers The dominant sequence transduction models are based on complex recurrent or convolutional neural networks in an Autoencoder (AE) / Encoder-Decoder configuration. The best performing models also connect the encoder and decoder through an attention mechanism. We propose a new simple network architecture, the Transformer, based solely on attention mechanisms, dispensing with recurrence and convolutions entirely. Experiments on two machine translation tasks show these models to be superior in quality while being more parallelizable and requiring significantly less time to train. Attention Is All You Need | A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A.N. Gomez, L. Kaiser, and I. Polosukhin
Contents
Tensor2Tensor (T2T)
- Tensor2Tensor (T2T) | Google Brain
Tensor2Tensor, or T2T for short, is a library of deep learning models and datasets designed to make deep learning more accessible and [accelerate ML research](https://research.googleblog.com/2017/06/accelerating-deep-learning-research.html). T2T is actively used and maintained by researchers and engineers within the [Google Brain team](https://research.google.com/teams/brain/) and a community of users. This colab shows you some datasets we have in T2T, how to download and use them, some models we have, how to download pre-trained models and use them, and how to create and train your own models. | Jay Alammar]
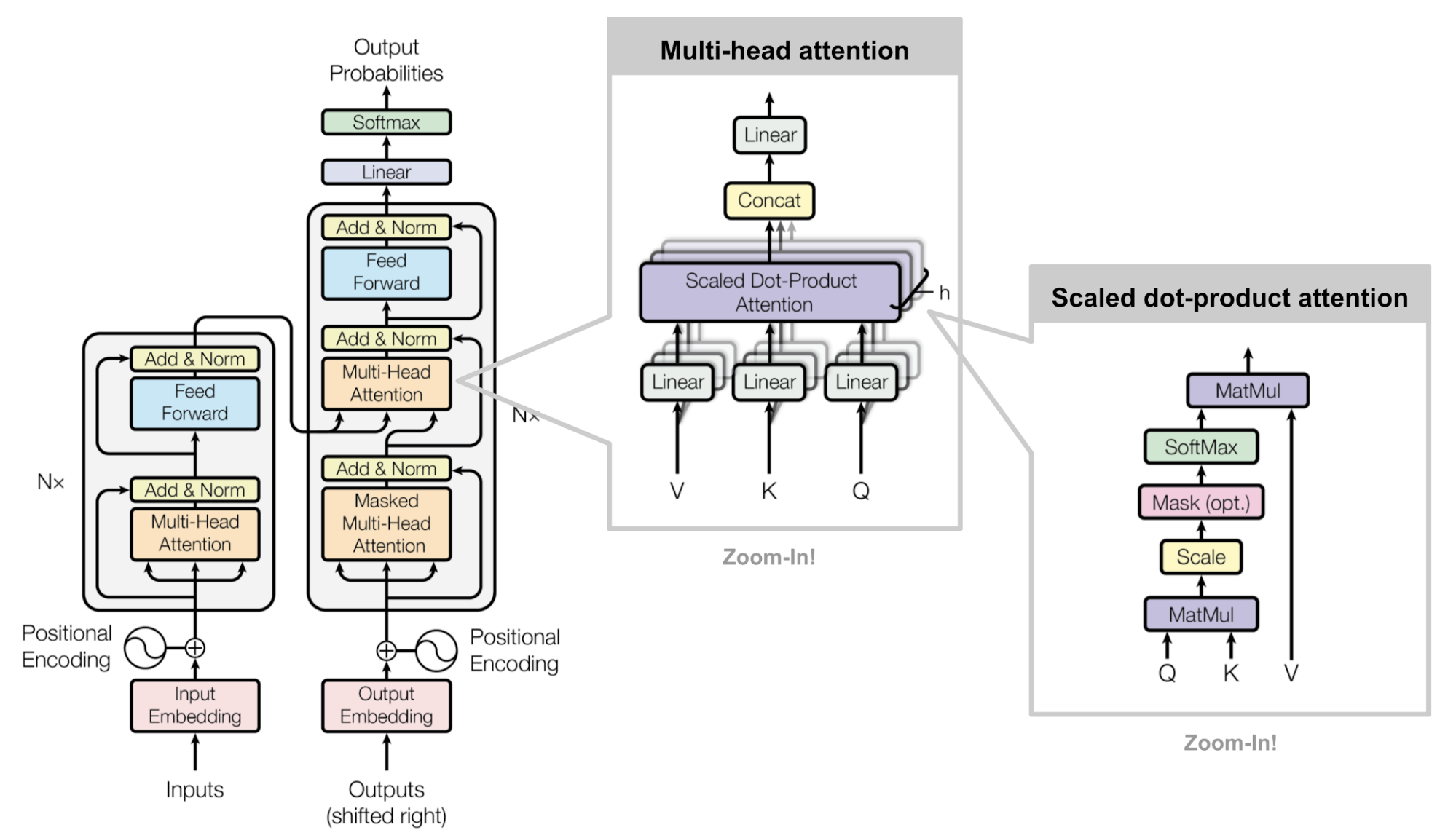
Multi-head scaled dot-product attention mechanism. (Image source: Fig 2 in Vaswani, et al., 2017)
Key, Value, and Query
“Attention is All you Need” (Vaswani, et al., 2017), without a doubt, is one of the most impactful and interesting paper in 2017. It presented a lot of improvements to the soft attention and make it possible to do Sequence to Sequence (Seq2Seq) modeling without Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) units. The proposed “transformer” model is entirely built on the Self-Attention mechanisms without using sequence-aligned recurrent architecture.
The secret recipe is carried in its model architecture
The major component in the transformer is the unit of multi-head Self-Attention mechanism. The transformer views the encoded representation of the input as a set of key-value pairs, (K,V), both of dimension n (input sequence length); in the context of NMT, both the keys and values are the encoder hidden states. In the decoder, the previous output is compressed into a query (Q of dimension m) and the next output is produced by mapping this query and the set of keys and values.
The transformer adopts the scaled Dot Product Attention: the output is a weighted sum of the values, where the weight assigned to each value is determined by the Dot Product of the query with all the keys:
Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(QK⊤n−−√)V
Multi-Head Self-Attention
Multi-head scaled Dot Product Attention
Rather than only computing the Attention once, the multi-head mechanism runs through the scaled Dot Product Attention multiple times in parallel. The independent Attention outputs are simply concatenated and linearly transformed into the expected dimensions. I assume the motivation is because ensembling always helps? ;) According to the paper, “multi-head Attention allows the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces at different positions. With a single Attention head, averaging inhibits this.” Attention? Attention! | Lilian Weng
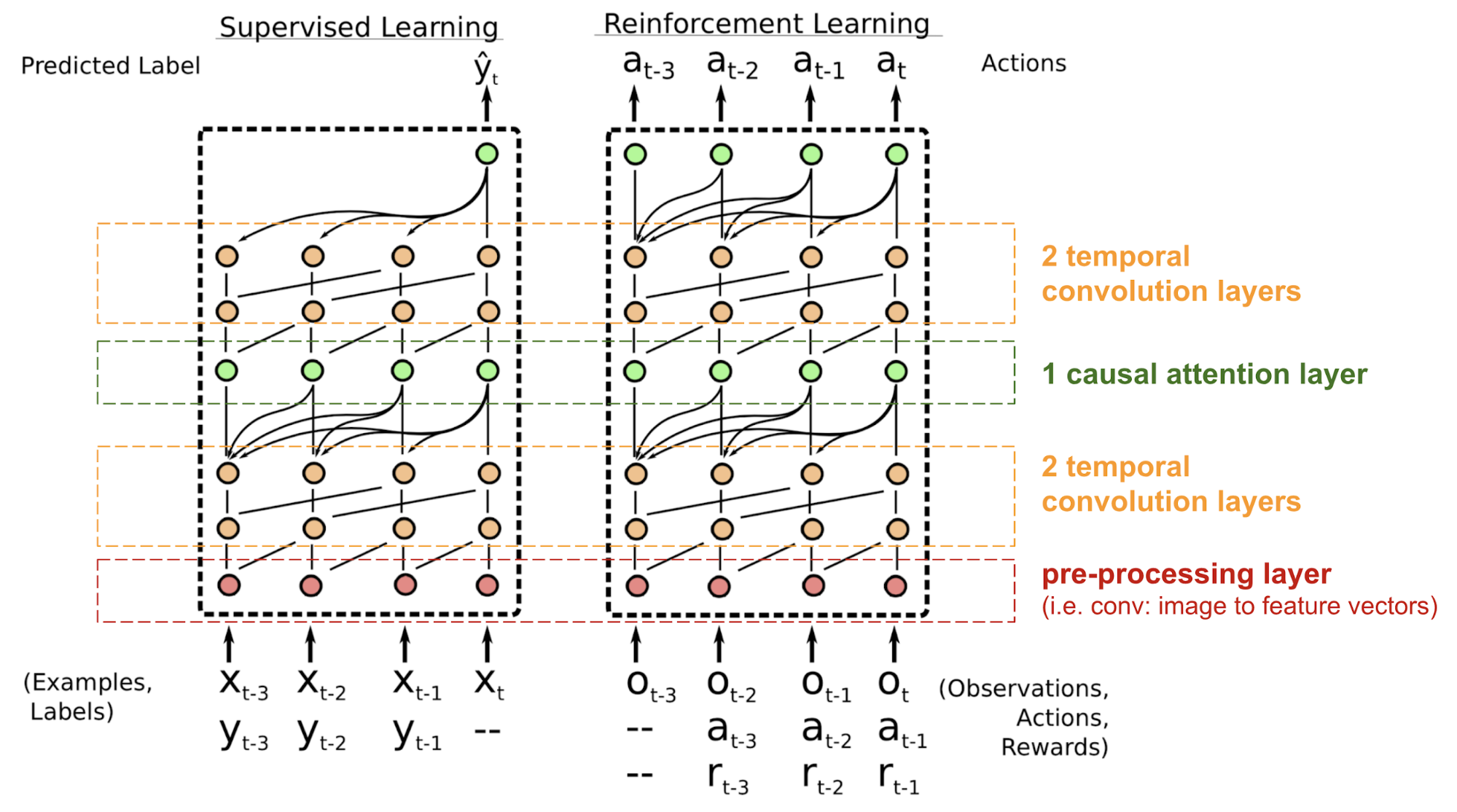
SNAIL
The transformer has no Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) or (Deep) Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN/CNN) structure, even with the positional encoding added to the embedding vector, the sequential order is only weakly incorporated. For problems sensitive to the positional dependency like Reinforcement Learning (RL), this can be a big problem.
The Simple Neural Attention Meta-Learner (SNAIL) (Mishra et al., 2017) was developed partially to resolve the problem with positioning in the transformer model by combining the self-attention Attention in transformer with temporal convolutions. It has been demonstrated to be good at both Supervised learning and Reinforcement Learning (RL) tasks. Attention? Attention! | Lilian Weng