Difference between revisions of "Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)"
(→MERLIN) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[http://www.google.com/search?q=reinforcement+machine+learning+ML+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | [http://www.google.com/search?q=reinforcement+machine+learning+ML+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | ||
| − | |||
* [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] | * [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] | ||
** [[Monte Carlo]] (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning | ** [[Monte Carlo]] (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
** [[Actor Critic]] | ** [[Actor Critic]] | ||
** [[Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)]] | ** [[Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)]] | ||
| + | * [[Inside Out - Curious Optimistic Reasoning#MERLIN|MERLIN]] | ||
| + | * [[OpenAI Gym]] | ||
==== OTHER: Policy Gradient Methods ==== | ==== OTHER: Policy Gradient Methods ==== | ||
Revision as of 20:53, 1 September 2019
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Monte Carlo (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning
- Markov Decision Process (MDP)
- Q Learning
- State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)
- Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)
- Deep Q Network (DQN)
- Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms
- Actor Critic
- Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)
- MERLIN
- OpenAI Gym
OTHER: Policy Gradient Methods
_______________________________________________________________________________________
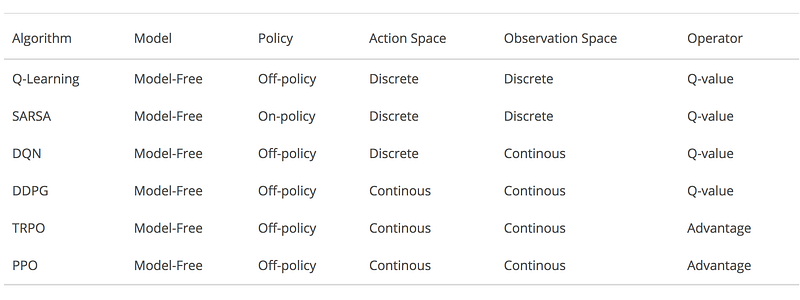
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part I (Q-Learning, SARSA, DQN, DDPG) | Steeve Huang
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part II (TRPO, PPO) | Steeve Huang
- Guide
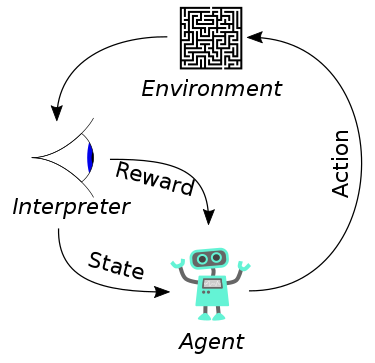
Goal-oriented algorithms, which learn how to attain a complex objective (goal) or maximize along a particular dimension over many steps; for example, maximize the points won in a game over many moves. Reinforcement learning solves the difficult problem of correlating immediate actions with the delayed returns they produce. Like humans, reinforcement learning algorithms sometimes have to wait a while to see the fruit of their decisions. They operate in a delayed return environment, where it can be difficult to understand which action leads to which outcome over many time steps.
Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architecture (IMPALA)
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Artificial General Intelligence Is Here, and Impala Is Its Name | Aaron Krumins
- DeepMind Lab
- IMPALA: Scalable Distributed Deep-RL with Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architectures
- Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architectures: Scalable Distributed DeepRL in DMLab-30
uses resources more efficiently in single-machine training but also scales to thousands of machines without sacrificing data efficiency or resource utilisation. We achieve stable learning at high throughput by combining decoupled acting and learning with a novel off-policy correction method called V-trace. IMPALA is able to achieve better performance than previous agents with less data, and crucially exhibits positive transfer between tasks as a result of its multi-task approach.

