Difference between revisions of "Matrix Factorization"
m |
m |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* [[Embedding]]: [[Agents#AI-Powered Search|Search]] ... [[Clustering]] ... [[Recommendation]] ... [[Anomaly Detection]] ... [[Classification]] ... [[Dimensional Reduction]] ... [[...find outliers]] | * [[Embedding]]: [[Agents#AI-Powered Search|Search]] ... [[Clustering]] ... [[Recommendation]] ... [[Anomaly Detection]] ... [[Classification]] ... [[Dimensional Reduction]] ... [[...find outliers]] | ||
| − | * [[AI Solver]] | + | * [[AI Solver]] ... [[Algorithms]] ... [[Algorithm Administration|Administration]] ... [[Model Search]] ... [[Discriminative vs. Generative]] ... [[Optimizer]] ... [[Train, Validate, and Test]] |
* [[Alternating Least Squares (ALS)]] | * [[Alternating Least Squares (ALS)]] | ||
| − | * | + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matrix_factorization_(recommender_systems) Matrix factorization (recommender systems) | Wikipedia] |
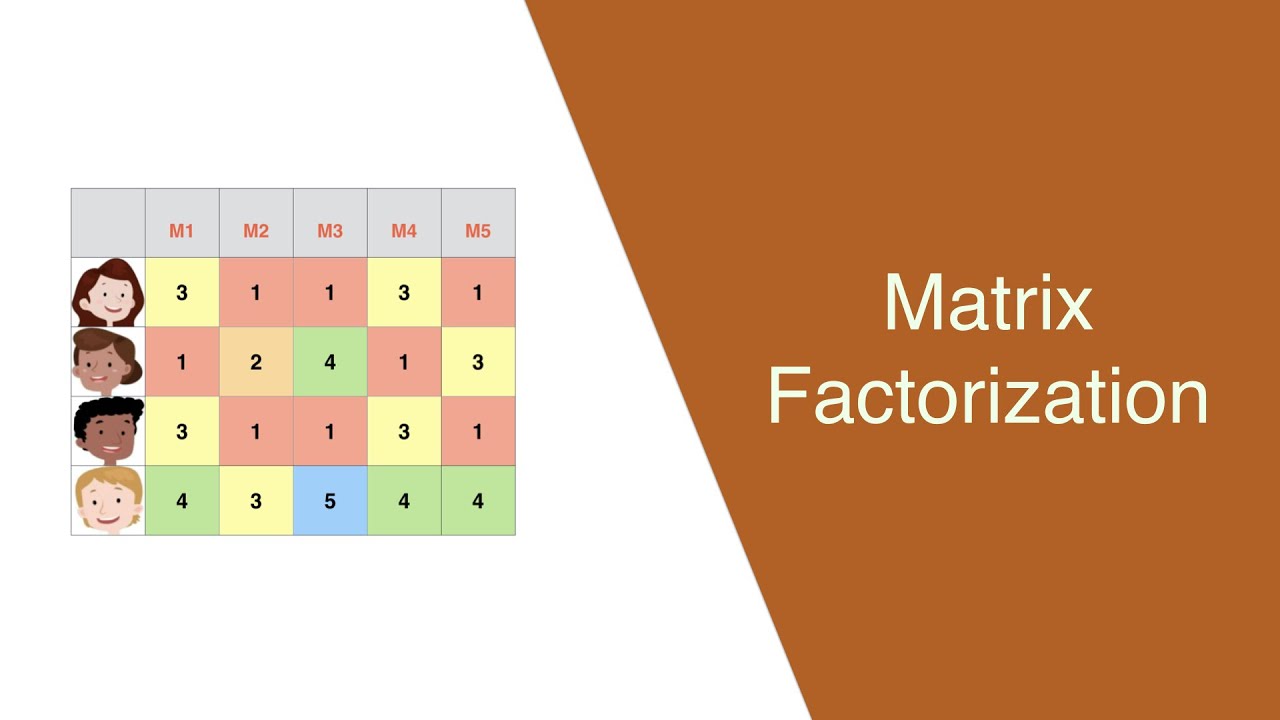
a class of collaborative filtering algorithms used in recommender systems. Matrix factorization algorithms work by decomposing the user-item interaction matrix into the product of two lower dimensionality rectangular matrices | a class of collaborative filtering algorithms used in recommender systems. Matrix factorization algorithms work by decomposing the user-item interaction matrix into the product of two lower dimensionality rectangular matrices | ||
Revision as of 20:36, 12 July 2023
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Embedding: Search ... Clustering ... Recommendation ... Anomaly Detection ... Classification ... Dimensional Reduction ... ...find outliers
- AI Solver ... Algorithms ... Administration ... Model Search ... Discriminative vs. Generative ... Optimizer ... Train, Validate, and Test
- Alternating Least Squares (ALS)
- Matrix factorization (recommender systems) | Wikipedia
a class of collaborative filtering algorithms used in recommender systems. Matrix factorization algorithms work by decomposing the user-item interaction matrix into the product of two lower dimensionality rectangular matrices