Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)
Youtube search... ...Google search
- OpenAI Gym
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Monte Carlo (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning
- Markov Decision Process (MDP)
- Q Learning
- State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)
- Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)
- Deep Q Network (DQN)
- Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms
- Actor Critic
- Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)
OTHER: Policy Gradient Methods
_______________________________________________________________________________________
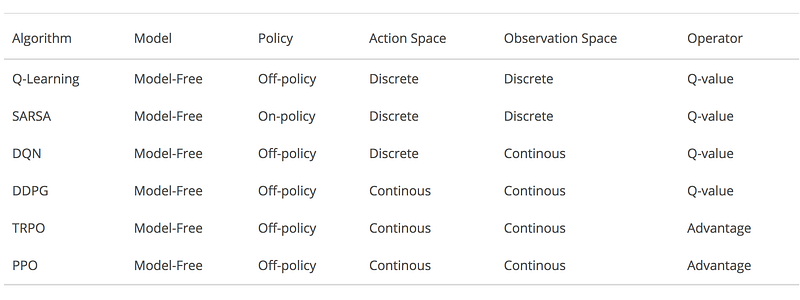
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part I (Q-Learning, SARSA, DQN, DDPG) | Steeve Huang
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part II (TRPO, PPO) | Steeve Huang
- Guide
Goal-oriented algorithms, which learn how to attain a complex objective (goal) or maximize along a particular dimension over many steps; for example, maximize the points won in a game over many moves. Reinforcement learning solves the difficult problem of correlating immediate actions with the delayed returns they produce. Like humans, reinforcement learning algorithms sometimes have to wait a while to see the fruit of their decisions. They operate in a delayed return environment, where it can be difficult to understand which action leads to which outcome over many time steps.
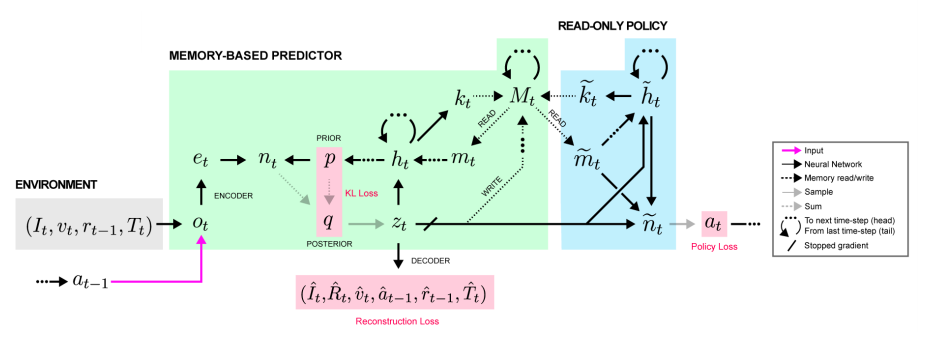
MERLIN
In deep learning, this is the driving thesis behind external, key-value-based memory stores. This idea is not new; Neural Turing Machines, one of the first and favorite papers I ever read, augmented neural nets with a differentiable, external memory store accessible via vector-valued “read” and “write” heads to specific locations. We can easily imagine this being extended into RL, where at any given time-step, an agent is given both its environment observation and memories relevant to its current state. That’s exactly what the recent MERLIN architecture extends upon. MERLIN has 2 components: a memory-based predictor (MBP), and a policy network. The MBP is responsible for compressing observations into useful, low-dimensional “state variables” to store directly into a key-value memory matrix. It is also responsible for passing relevant memories to the policy, which uses those memories and the current state to output actions.... MERLIN is not the only Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to use external memory stores — all the way back in 2016, researchers were already applying this idea in an MQN, or Memory Q-Network Beyond DQN/A3C: A Survey in Advanced Reinforcement Learning | Joyce Xu - Towards Data Science
Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architecture (IMPALA)
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Artificial General Intelligence Is Here, and Impala Is Its Name | Aaron Krumins
- DeepMind Lab
- IMPALA: Scalable Distributed Deep-RL with Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architectures
- Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architectures: Scalable Distributed DeepRL in DMLab-30
uses resources more efficiently in single-machine training but also scales to thousands of machines without sacrificing data efficiency or resource utilisation. We achieve stable learning at high throughput by combining decoupled acting and learning with a novel off-policy correction method called V-trace. IMPALA is able to achieve better performance than previous agents with less data, and crucially exhibits positive transfer between tasks as a result of its multi-task approach.

