Difference between revisions of "Math for Intelligence"
m (→Dot Product) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* [http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html Neural Networks and Deep Learning - online book | Michael A. Nielsen] | * [http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html Neural Networks and Deep Learning - online book | Michael A. Nielsen] | ||
* [http://bloomberg.github.io/foml/#lectures Bloomberg Lectures] | * [http://bloomberg.github.io/foml/#lectures Bloomberg Lectures] | ||
| + | * [http://lagunita.stanford.edu/courses/HumanitiesSciences/StatLearning/Winter2016/about Statistical Learning | Trevor Hastie, Rob Tibshirani - Stanford] | ||
* Fundamentals: | * Fundamentals: | ||
** [http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-06sc-linear-algebra-fall-2011/ Linear Algebra] | ** [http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-06sc-linear-algebra-fall-2011/ Linear Algebra] | ||
Revision as of 04:56, 13 December 2018
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Animated Math | Grant Sanderson @ 3blue1brown.com
- Google's Crash Course
- Introduction to Matrices and Matrix Arithmetic for Machine Learning | Jason Brownlee
- Brilliant.org
- Varient: Limits
- Probability Cheatsheet
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning - online book | Michael A. Nielsen
- Bloomberg Lectures
- Statistical Learning | Trevor Hastie, Rob Tibshirani - Stanford
- Fundamentals:
Contents
Getting Started
3blue1brown
Explained
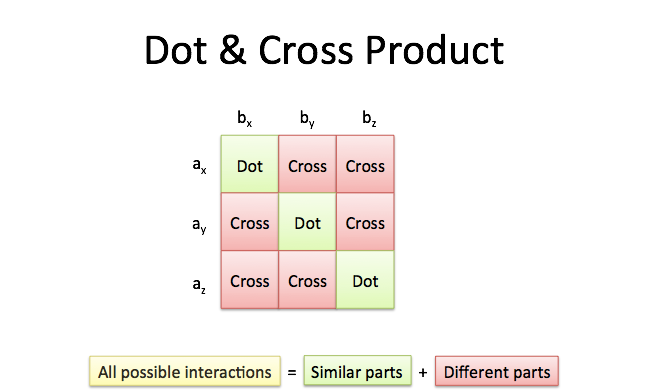
Dot Product
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product Dot Product | Wikipedia]
Dot Product =
- Algebraically, the dot product is the sum of the products of the corresponding entries of the two sequences of numbers.
- Geometrically, it is the product of the Euclidean magnitudes of the two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them.


Siraj Raval
Josh Starmer - StatQuest
Gilbert Strang (MIT) - Linear Algebra
Quantum Algorithm