Difference between revisions of "Loop"
m |
m |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|title=PRIMO.ai | |title=PRIMO.ai | ||
|titlemode=append | |titlemode=append | ||
| − | |keywords=artificial, intelligence, machine, learning, models, algorithms, data, singularity, moonshot, TensorFlow, Google, Nvidia, Microsoft, Azure, Amazon, AWS, Facebook | + | |keywords=artificial, intelligence, machine, learning, models, algorithms, data, singularity, moonshot, TensorFlow, Google, Nvidia, Microsoft, Azure, Amazon, AWS, Meta, Facebook |
|description=Helpful resources for your journey with artificial intelligence; videos, articles, techniques, courses, profiles, and tools | |description=Helpful resources for your journey with artificial intelligence; videos, articles, techniques, courses, profiles, and tools | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 517: | Line 517: | ||
| − | In December 2009, Google began customizing its search results for all users, and we entered a new era of personalization. With little notice or fanfare, our online experience is changing, as the websites we visit are increasingly tailoring themselves to us. In this engaging and visionary book, MoveOn.org board president Eli Pariser lays bare the personalization that is already taking place on every major website, from Facebook to AOL to ABC News. As Pariser reveals, this new trend is nothing short of an invisible revolution in how we consume information, one that will shape how we learn, what we know, and even how our democracy works. [https://www.penguinrandomhouse.com/books/309214/the-filter-bubble-by-eli-pariser/ The Filter Bubble | Eli Pariser] | + | In December 2009, Google began customizing its search results for all users, and we entered a new era of personalization. With little notice or fanfare, our online experience is changing, as the websites we visit are increasingly tailoring themselves to us. In this engaging and visionary book, MoveOn.org board president Eli Pariser lays bare the personalization that is already taking place on every major website, from [[Meta|Facebook]] to AOL to ABC News. As Pariser reveals, this new trend is nothing short of an invisible revolution in how we consume information, one that will shape how we learn, what we know, and even how our democracy works. [https://www.penguinrandomhouse.com/books/309214/the-filter-bubble-by-eli-pariser/ The Filter Bubble | Eli Pariser] |
| Line 539: | Line 539: | ||
<youtube>Zk1o2BpC79g</youtube> | <youtube>Zk1o2BpC79g</youtube> | ||
<b>Filter Bubbles and Echo Chambers | <b>Filter Bubbles and Echo Chambers | ||
| − | </b><br>You've probably heard the term Filter Bubble and/or Echo Chamber at least once or twice in the past few months. It's a term that has been circling the media for some time about Facebook and the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election. But what do they mean exactly? How does it relate to the internet or more specifically Facebook and Google? How does it affect you? Watch the video to find out! Don't forget to leave us a comment about what you think and how Filter Bubble or Echo Chamber relates to you! Scene 1 “Filter Bubble” is a theory that the algorithms from companies like Facebook and Google bases the information given to you on data acquired from things like, your search history, your past click behavior, the type of your computer and your location. Therefore, limiting the topics that reach you to a bubble of only your own formulated interests and personalized search subjects. Scene 2 The term was coined by Eli Pariser who wrote a book on this subject explaining that these algorithms are “closing us off to new ideas, new subjects and important information ”. What he means is that you are not given information outside your own political views, religious views or even other data like for example updates on women's rights and animal rights. | + | </b><br>You've probably heard the term Filter Bubble and/or Echo Chamber at least once or twice in the past few months. It's a term that has been circling the media for some time about [[Meta|Facebook]] and the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election. But what do they mean exactly? How does it relate to the internet or more specifically [[Meta|Facebook]] and Google? How does it affect you? Watch the video to find out! Don't forget to leave us a comment about what you think and how Filter Bubble or Echo Chamber relates to you! Scene 1 “Filter Bubble” is a theory that the algorithms from companies like [[Meta|Facebook]] and Google bases the information given to you on data acquired from things like, your search history, your past click behavior, the type of your computer and your location. Therefore, limiting the topics that reach you to a bubble of only your own formulated interests and personalized search subjects. Scene 2 The term was coined by Eli Pariser who wrote a book on this subject explaining that these algorithms are “closing us off to new ideas, new subjects and important information ”. What he means is that you are not given information outside your own political views, religious views or even other data like for example updates on women's rights and animal rights. |
|} | |} | ||
|}<!-- B --> | |}<!-- B --> | ||
Revision as of 22:38, 8 February 2023
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Learning
- Recommendation
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Causation vs. Correlation
- Algorithm Administration
- Network Pattern
- Process Patterns, Loops and Emergence | Carlos E. Perez - Medium
Contents
- 1 Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop
- 2 Feedback Loop
- 3 Multi-Loop Learning
- 4 Triple Golden OODA
- 5 Feedback Loop - Peer Learning
- 6 Feedback Loop - Creating Consciousness
- 7 Feedback Loop - Scientific Discovery
- 8 Feedback Loop - Stock Market Predictions
- 9 Feedback Loop - The AI Economist
- 10 Feedback Loop - Synthetic
- 11 Recursion
- 12 Unintended Feedback Loop
- 13 Using the OODA Loop - Purple Team with Cybersecurity
- 14 OODA Loop - Security Approaches
Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop
YouTube search... ...Google search
The OODA loop is the cycle: Observe–Orient–Decide–Act ...emphasized that "the loop" is actually a set of interacting loops that are to be kept in continuous operation... developed by military strategist and United States Air Force Colonel John Boyd. Boyd applied the concept to the combat operations process, often at the operational level during military campaigns. It is now also often applied to understand commercial operations and learning processes. The approach explains how agility can overcome raw power in dealing with human opponents. It is especially applicable to cyber security and cyberwarfare. Wikipedia ... A Discourse On Winning and Losing | John R. Boyd - Air University Press
We’ve historically focused automation efforts on the “Act” portion but the real potential for new technologies is to address the prior 3 steps: Improving Observation: Improve the data itself with better sensing accuracy, timeliness, relevance, etc or improve our ability to use the data with higher throughput learning processes Improving Orientation: Improve the classification of the current state and the prediction of future states
Improving Decision: Improve the ability to choose between paths via better objective functions. How Artificial Intelligence is Closing the Loop with Better Predictions | Erik Trautman - HackerNoon]
|
|
Feedback Loop
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Feedback | Wikipedia
- Closing the Loop: How Feedback Loops Help to Maintain Quality Long-Term AI Results | Natalie Fletcher - Clarifai
- So, What Actually Is a Feedback Loop? | Tina Nord - Ultimate Knowledge ...With feedback loops, a system is constantly in dialogue with itself.
- AI in the Feedback Loop: A Survey of Alternative Approaches | Karl-ErikÅrzén - ScienceDirect ...paper gives special attention to fuzzy control and expert control.
- Feedback Loops in Machine Learning | Ankur Goyal - Impair ...in spite of the immense benefits that Machine Learning offers, this technology has been very slow to take off, particularly in the enterprise world. At Impira, we believe a key reason for this is the lack of well-designed feedback loops that serve to continuously improve machine learning models.
- HP200A | Wikipedia ...oscillator to use a simple light bulb as the temperature-dependent resistor in its feedback network. Walt Disney bought eight HP200A for use in the production of Fantasia
- The Air Force Research Lab wants tools, techniques and innovative ideas for shortening the OODA Loop. | Aaron Boyd - Nextgov
any process where the outputs of a system are plugged back in and used as iterative inputs. Feedback loops exist just about everywhere. In nature, the evolutionary "arms race" between predators and prey is a classic example. In business, the practice of taking customer feedback (the output of a product or service) and using it to improve future processes is another commonly used feedback loop. Today, rapid advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are helping businesses do more with data. These systems — and their ability to analyze an inhuman amount of data — allow businesses to adjust algorithms, workflows and processes on the fly. Get More Out Of Feedback Loops With AI | Arka Dhar - Forbes
|
|
Multi-Loop Learning
YouTube search... ...Google search
- How Artificial Intelligence Will Redefine Management | V. Kolbjørnsrud, R. Amico and R.J. Thomas
- Chris Argyris: theories of action, double-loop learning and organizational learning | Infed.org
- Donald Schon (Schön): learning, reflection and change | Infed.org
- Organisational learning: a critical review | Catherine L. Wang, Pervaiz K. Ahmed
- Single and double loop learning | Organizational Learning
- Double-loop learning | Wikipedia
- Re-Framing Perspectives | Patrick A. Trottier - The Institute Of Emergent Organizational Development and Emergent Change®
- Working visually: Record, Reflect, Reframe, Part 1 Part 2 | Kim S van den Berg
- Different Kinds of Learning (Loops of Learning) Adapted from “Field Guide to Consulting and Organizational Development”

|
|
|
|
|
|
Triple Golden OODA
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Framing Context
- Multi-Loop Learning
- Start With Why | Simon Sinek ...Wikipedia
- Observe–Orient–Decide–Act (OODA) Loop ...Wikipedia
The Triple Golden OODA loop diagram depicts a hybrid of concepts from the Triple Loop concept inspired by Chris Argyris & Donald Schön's work on the Double Loop, Simon Sinek's Golden Circle in 'Start with Why', and Colonel John Boyd's Observe, Orient, Decide and Act (OODA) Loop from his ‘A Discourse On Winning and Losing'.
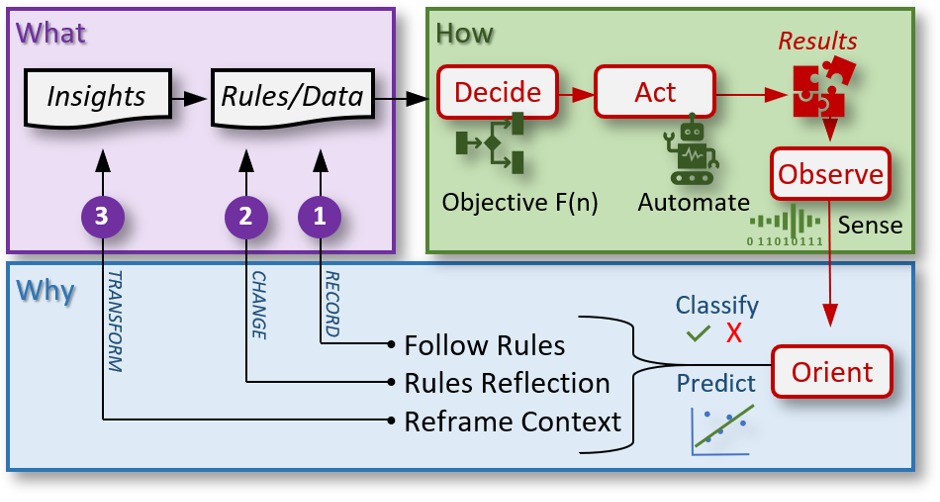
|
|
Feedback Loop - Peer Learning
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Education
- Decentralized: Federated & Distributed Learning
- FeedbackFruits
- The NIPS experiment | Eric Price - A blog on machine learning very broadly construed by Moritz Hardt
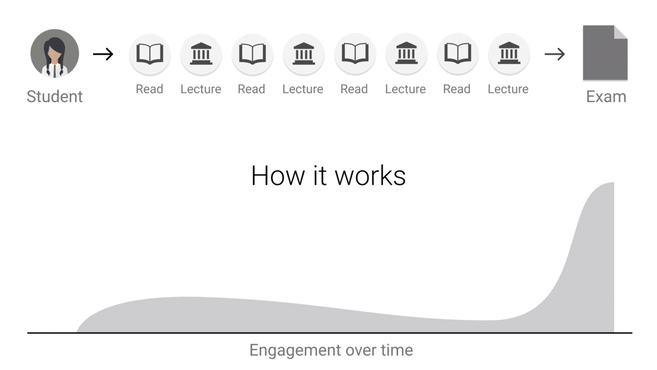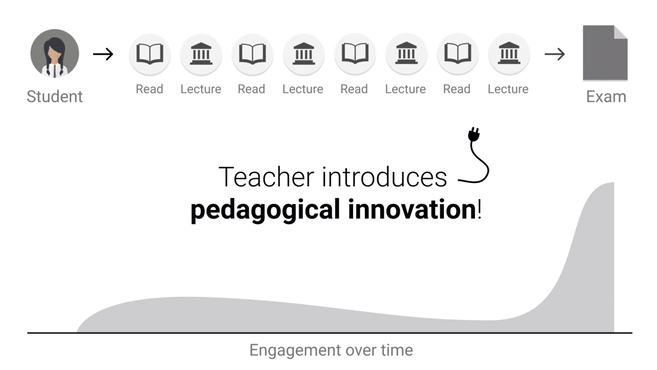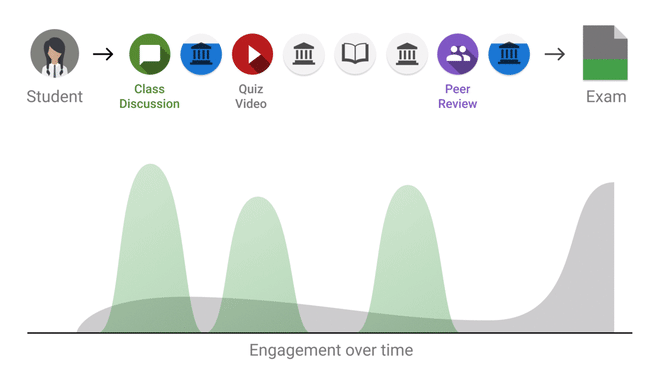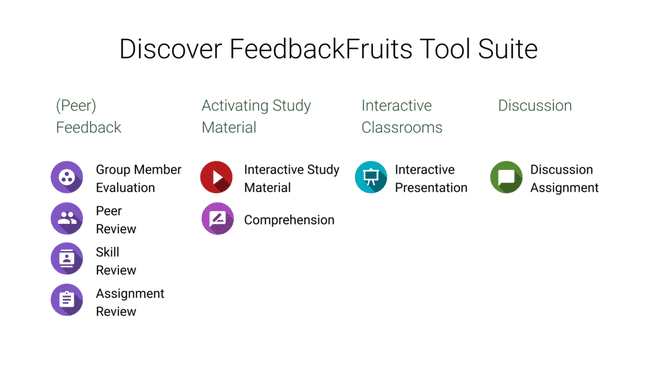
|
|
|
|
Feedback Loop - Creating Consciousness
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Michio Kaku and the Mysteries of the Mind | Alyson Sheppard - Popular Mechanics ...The Future of the Mind: The Scientific Quest to Understand, Enhance, and Empower the Mind
- A Theory of Consciousness | Tyler Neylon - Medium
- Do Loops Explain Consciousness? | Martin Gardner - AMS.org ...Review of I Am a Strange Loop
- Strange Loop | Wikipedia ...The "strangeness" of a strange loop comes from our way of perception
- Godel, Escher, Bach: an Eternal Golden Braid | Douglas R. Hofstadter
- Generative ...Simulated Environment Learning
|
|
|
|
Feedback Loop - Scientific Discovery
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Scientific discovery must be redefined. Quantum and AI can help | Dario Gil - World Economic Forum
- Can Artificial Intelligence Make Scientific Discoveries? | Kartik Hosanagar - The Scientist
- Can artificial intelligence lead scientific discoveries? | University of Konstanz - EurekAlert!
The paradigm shift will be from AI used for analysing the data which has already been obtained, to AI deciding what to measure next. Why Artificial Intelligence Will Enable New Scientific Discoveries - Andrew Briggs - Graphcore
Quantum Computing and AI to Enable Our Sustainable Future | Katia Moskvitch - IBM
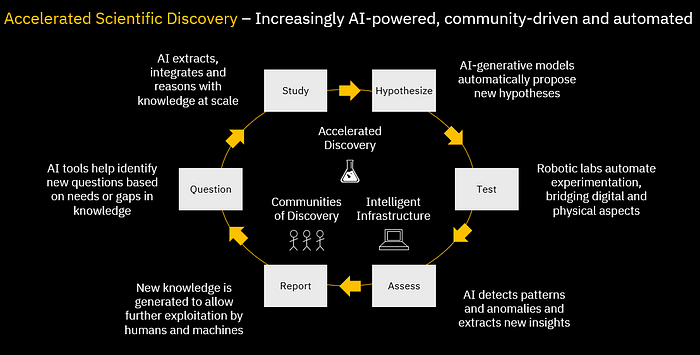

|
|
Feedback Loop - Stock Market Predictions
YouTube search... ...Google search
Why you can beat the market, even when it does not seem so. The importance of loops, patterns, and predictable events. Random events are don’t measure risks, and should not affect your decision making. Some traders follow the trend, and some go against it. At I Know First we work on algorithmic strategies which are neither, we simply try an assess where the next opportunity is and provide stock market predictions. If this means to do what everyone else does, than why not. If it means going against when everyone else does, this is also fine. The tricky part is determining where this opportunities are, this article will discuss how to find opportunities in what can seem as total randomness. Markets are Complex, but not Unpredictable! There are two major misconceptions about the stock market. The first one is connected to the classical economic theory which claims markets to be efficient, and as such unpredictable. In this case trying to select one stock over another becomes useless, as no opportunity is ever better than the other. Both stocks are perfectly priced according to their opportunity and risk, with everyone having all information. However, the truth of the matter is that some people profit trading stocks while others lose – this by itself proves the market to be inefficient, and thus exploitable. While US markets are very efficient, and most information is available, not everyone interprets this information the same. Stock Market Predictions: Where In The Feedback Loop Is Your Portfolio? | I Know First
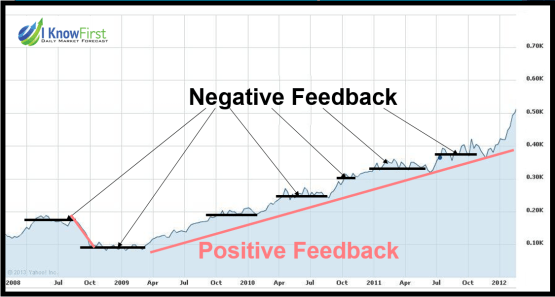
|
Feedback Loop - The AI Economist
YouTube search... ...Google search
Optimal Tax Design as Learned Reward Design Using Reinforcement Learning. Reinforcement learning is a powerful framework in which agents learn from experience collected through trial-and-error. We use model-free RL, in which agents do not use any prior world knowledge or modeling assumptions. Another benefit of RL is that agents can optimize for any objective. In our setting, this means that a tax policy can be learned that optimizes any social objective, and without knowledge of workers’ utility functions or skills. The AI Economist: Improving Equality and Productivity with AI-Driven Tax Policies | S. Zheng, A. Trott, S. Srinivasa, N. Naik, M. Gruesbeck, D. Parkes, and R. Socher - Einstein.ai]

|
Feedback Loop - Synthetic
YouTube search... ...Google search
|
Recursion
YouTube search... ...Google search

|
|
|
|
Unintended Feedback Loop
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Bias and Variances
- Unintended consequences from existing AI | Wikipedia
- Weapons of Math Destruction: How Big Data Increases Inequality and Threatens Democracy | Cathy O'Neil
- The Toxic Potential of YouTube’s Feedback Loop | Guillaume Chaslot - Wired
- The Unintended Consequences of Machine Learning | Frank Kane - Sundog Education - KDnuggets
- Dangerous Feedback Loops in ML | David Blaszka - Towards Data Science
- The Negative Feedback Loop: Technology Needs To Know When It Gets Things Wrong | Fiona McEvoy - You The Data ...This is not a secret problem. AI developers are painfully aware that there is currently no straightforward way to combat biased data or solicit full feedback. However, increasingly they are making efforts to harvest this critical information wherever and however they can. Not just in the name of ethics, but also to ensure that their creations perform as accurately as possible.

Models that are an integrated part of a product experience, or what we referred to as data products, often involve feedback loops. When done right, feedback loops can help us to create better experiences. However, feedback loops can also create unintended negative consequences, such as bias or inaccurate model performance measurements... Getting Better at Machine Learning | Robert Chang - Medium
Leaders hoping to shift their posture from hindsight to foresight need to better understand the types of risks they are taking on, their interdependencies, and their underlying causes... Confronting the risks of artificial intelligence | B. Cheatham, K. Javanmardian, and H. Samandari - Mckinsey & Company
One of the key features of live ML systems is that they often end up influencing their own behavior if they update over time. This leads to a form of analysis debt, in which it is difficult to predict the behavior of a given model before it is released. These feedback loops can take different forms, but they are all more difficult to detect and address if they occur gradually over time, as may be the case when models are updated infrequently.
- Direct Feedback Loops. A model may directly influence the selection of its own future training data. It is common practice to use standard supervised algorithms, although the theoretically correct solution would be to use bandit algorithms. The problem here is that bandit algorithms (such as contextual bandits) do not necessarily scale well to the size of action spaces typically required for real-world problems. It is possible to mitigate these effects by using some amount of randomization, or by isolating certain parts of data from being influenced by a given model.
- Hidden Feedback Loops. Direct feedback loops are costly to analyze, but at least they pose a statistical challenge that ML researchers may find natural to investigate. A more difficult case is hidden feedback loops, in which two systems influence each other indirectly through the world. One example of this may be if two systems independently determine facets of a web page, such as
one selecting products to show and another selecting related reviews. Improving one system may lead to changes in behavior in the other, as users begin clicking more or less on the other components in reaction to the changes. Note that these hidden loops may exist between completely disjoint systems. Consider the case of two stock-market prediction models from two different investment companies. Improvements (or, more scarily, bugs) in one may influence the bidding and buying behavior of the other. Hidden Technical Debt in Machine Learning Systems | D. Sculley, G. Holt, D. Golovin, E. Davydov, T. Phillips, D. Ebner, V. Chaudhary, M. Young, J. Crespo, and D. Dennison - Google


When the system is retrained on future data, it may become not less but more detrimental to historically disadvantaged groups. In order to build AI systems that are aligned with desirable long-term societal outcomes, we need to understand when and why such negative feedback loops occur, and we need to learn how to prevent them. When bias begets bias: A source of negative feedback loops in AI systems | Lydia T. Liu - University of California, Berkeley - Microsoft Research Blog
|
|
Unintended Feedback Loop - Filter Bubbles
YouTube search... ...Google search
In December 2009, Google began customizing its search results for all users, and we entered a new era of personalization. With little notice or fanfare, our online experience is changing, as the websites we visit are increasingly tailoring themselves to us. In this engaging and visionary book, MoveOn.org board president Eli Pariser lays bare the personalization that is already taking place on every major website, from Facebook to AOL to ABC News. As Pariser reveals, this new trend is nothing short of an invisible revolution in how we consume information, one that will shape how we learn, what we know, and even how our democracy works. The Filter Bubble | Eli Pariser
In news media, echo chamber is a metaphorical description of a situation in which beliefs are amplified or reinforced by communication and repetition inside a closed system. Filter Bubble | Wikipedia
|
|
|
|
Using the OODA Loop - Purple Team with Cybersecurity
YouTube search... ...Google search
- MITRE ATT&CK™
- The Cyber OODA Loop, How Your Attacker Should Help You Design Your Defense | Tony Sager - The Center for Internet Security - NIST
- The 4 Phases of Effective Incident Response Decision Making | Andrew Cook - Praetorian
- OODA and Cybersecurity | INFOSEC
- Red Team VS Blue Team: What’s The Difference? | Jason Firch - PurpleSec
- Purple Team: When Red and Blue Teams Work Together | Packetlabs
Modern security organizations create new capabilities within an overall cyber defense team by organizing themselves around a fundamental concept of an “OODA loop” — enabling teams to quickly make necessary decisions as they are responding to live or simulated incidents. ... Handling incidents effectively requires this sort of cyclical and quick decision making. In this quick-decision cycle, the IR team becomes the Blue Team, the “attackers” comprise the Red Team and run attack scenarios, and an even more novel third team called the Purple Team proactively hunts the attackers. This structure allows organizations to “train like they fight,” enabling them to prepare for increasingly more advanced adversarial techniques....Purple Teams help optimize security detection processes within an organization by reproducing attacks, determining if successful detection of these attacks occurred, and exposing existing deficiencies within the organization’s IR plan. Improving Cyber Defense by Purple Team using OODA loop | Ozren (Oz) Bogovac - Medium

|
|
OODA Loop - Security Approaches
YouTube search... ...Google search
|
|