Difference between revisions of "Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)"
(→Q-learning & SARSA) |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
* [[Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)]] | * [[Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)]] | ||
| − | https:// | + | https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1b/Reinforcement_learning_diagram.svg/375px-Reinforcement_learning_diagram.svg.png |
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1*BEby_oK1mU8Wq0HABOqeVQ.png | https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/1*BEby_oK1mU8Wq0HABOqeVQ.png | ||
Revision as of 05:40, 27 May 2018
- Gym | OpenAI
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part I (Q-Learning, SARSA, DQN, DDPG) | Steeve Huang
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part II (TRPO, PPO) | Steeve Huang
- Guide
Q-learning & SARSA
Policy Gradient Methods
- Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG)
- Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO)
- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
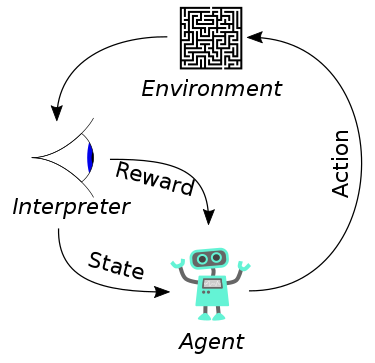
Goal-oriented algorithms, which learn how to attain a complex objective (goal) or maximize along a particular dimension over many steps; for example, maximize the points won in a game over many moves. Reinforcement learning solves the difficult problem of correlating immediate actions with the delayed returns they produce. Like humans, reinforcement learning algorithms sometimes have to wait a while to see the fruit of their decisions. They operate in a delayed return environment, where it can be difficult to understand which action leads to which outcome over many time steps.