Difference between revisions of "Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)"
(→OpenAI Gym and Universe) |
(→OpenAI Gym and Universe) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
* [http://gym.openai.com/ Gym] | [http://openai.com/ OpenAI] | * [http://gym.openai.com/ Gym] | [http://openai.com/ OpenAI] | ||
| + | * [http://medium.freecodecamp.org/how-to-build-an-ai-game-bot-using-openai-gym-and-universe-f2eb9bfbb40a How to build an AI Game Bot using OpenAI Gym and Universe | Harini Janakiraman] | ||
<youtube>mGYU5t8MO7s</youtube> | <youtube>mGYU5t8MO7s</youtube> | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 26 January 2019
OTHER: Learning; MDP, Q, and SARSA
- Markov Decision Process (MDP)
- Deep Q Learning (DQN)
- Neural Coreference
- State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)
OTHER: Policy Gradient Methods
- Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG)
- Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO)
- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
_______________________________________________________________________________________
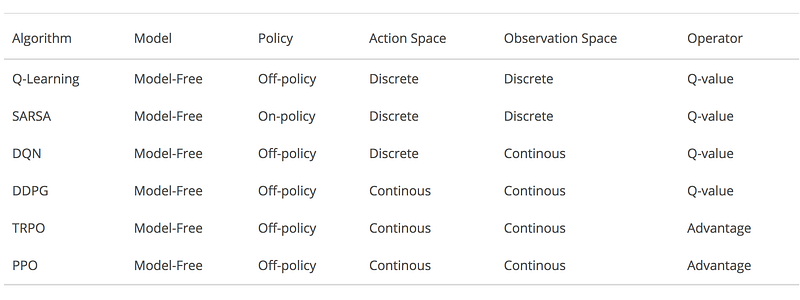
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part I (Q-Learning, SARSA, DQN, DDPG) | Steeve Huang
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part II (TRPO, PPO) | Steeve Huang
- Guide
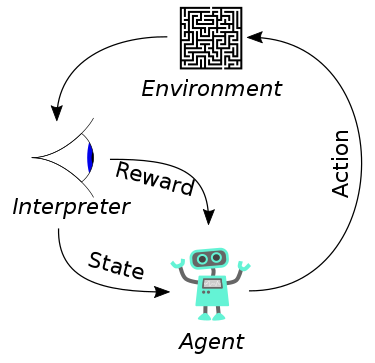
Goal-oriented algorithms, which learn how to attain a complex objective (goal) or maximize along a particular dimension over many steps; for example, maximize the points won in a game over many moves. Reinforcement learning solves the difficult problem of correlating immediate actions with the delayed returns they produce. Like humans, reinforcement learning algorithms sometimes have to wait a while to see the fruit of their decisions. They operate in a delayed return environment, where it can be difficult to understand which action leads to which outcome over many time steps.
OpenAI Gym and Universe