Difference between revisions of "Math for Intelligence"
(→Gilbert Strang (MIT) - Linear Algebra) |
|||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
* [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hNDFwVVKVk0&list=PL221E2BBF13BECF6C YouTube Playlist] | * [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hNDFwVVKVk0&list=PL221E2BBF13BECF6C YouTube Playlist] | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>hNDFwVVKVk0</youtube> |
<youtube>gGYcSjrqbjc</youtube> | <youtube>gGYcSjrqbjc</youtube> | ||
== Quantum Algorithm == | == Quantum Algorithm == | ||
<youtube>LhtnECml-KI</youtube> | <youtube>LhtnECml-KI</youtube> | ||
Revision as of 03:40, 13 December 2018
- Animated Math | Grant Sanderson @ 3blue1brown.com
- Introduction to Matrices and Matrix Arithmetic for Machine Learning | Jason Brownlee
- Brilliant.org
- Varient: Limits
- Probability Cheatsheet
Contents
Getting Started
3blue1brown
Explained
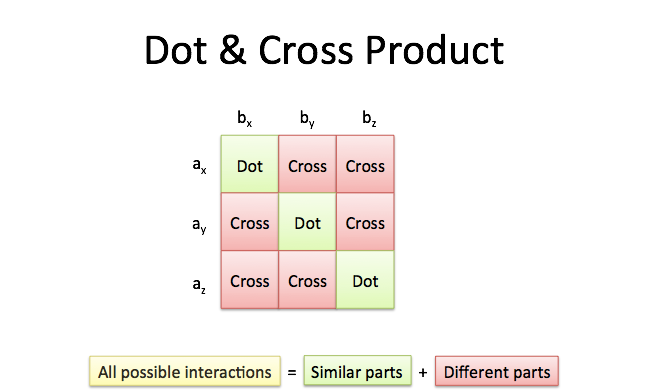
Dot Product
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product Dot Product | Wikipedia]
Dot Product =
- Algebraically, the dot product is the sum of the products of the corresponding entries of the two sequences of numbers.
- Geometrically, it is the product of the Euclidean magnitudes of the two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them.


Siraj Raval
Josh Starmer - StatQuest
Gilbert Strang (MIT) - Linear Algebra
Quantum Algorithm