Difference between revisions of "Markov Decision Process (MDP)"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query= | + | {{#seo: |
| + | |title=PRIMO.ai | ||
| + | |titlemode=append | ||
| + | |keywords=artificial, intelligence, machine, learning, models, algorithms, data, singularity, moonshot, Tensorflow, Google, Nvidia, Microsoft, Azure, Amazon, AWS | ||
| + | |description=Helpful resources for your journey with artificial intelligence; videos, articles, techniques, courses, profiles, and tools | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | [http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Markov+Decision+Process+MDP Youtube search...] | ||
| + | [http://www.google.com/search?q=Markov+Decision+Process+MDP+machine+learning+ML+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | ||
* [[Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)]] | * [[Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)]] | ||
Revision as of 23:16, 2 February 2019
Youtube search... ...Google search

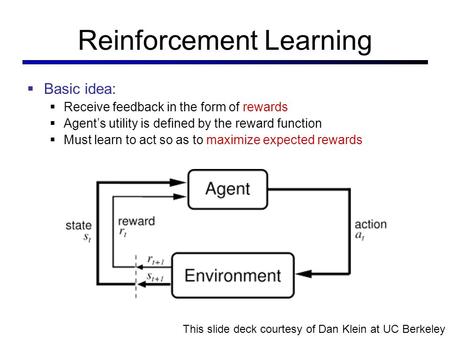
Solutions:
Used where outcomes are partly random and partly under the control of a decision maker. MDP is a discrete time stochastic control process. At each time step, the process is in some state s, and the decision maker may choose any action a that is available in state s. The process responds at the next time step by randomly moving into a new state s', and giving the decision maker a corresponding reward R_{a}(s,s')} R_a(s,s'). The probability that the process moves into its new state s' is influenced by the chosen action. Helping the convergence of certain algorithms a discount rate (factor) makes an infinite sum finite.