Difference between revisions of "Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[http://www.google.com/search?q=reinforcement+machine+learning+ML+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | [http://www.google.com/search?q=reinforcement+machine+learning+ML+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | ||
| + | * [[IMPALA (Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architecture)]] | ||
* [[OpenAI Gym]] | * [[OpenAI Gym]] | ||
* [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] | * [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
** [[State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)]] | ** [[State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)]] | ||
** [[Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)]] DeepRL | ** [[Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)]] DeepRL | ||
| − | |||
** [[Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)]] | ** [[Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)]] | ||
** [[Deep Q Network (DQN)]] | ** [[Deep Q Network (DQN)]] | ||
Revision as of 15:10, 1 September 2019
Youtube search... ...Google search
- IMPALA (Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architecture)
- OpenAI Gym
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Monte Carlo (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning
- Markov Decision Process (MDP)
- Q Learning
- State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)
- Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) DeepRL
- Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)
- Deep Q Network (DQN)
- Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms
- Asynchronous Advantage Actor Critic (A3C)
- Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)
- MERLIN
OTHER: Policy Gradient Methods
_______________________________________________________________________________________
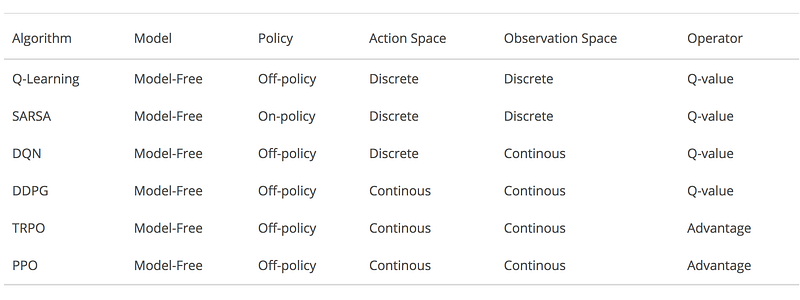
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part I (Q-Learning, SARSA, DQN, DDPG) | Steeve Huang
- Introduction to Various Reinforcement Learning Algorithms. Part II (TRPO, PPO) | Steeve Huang
- Guide
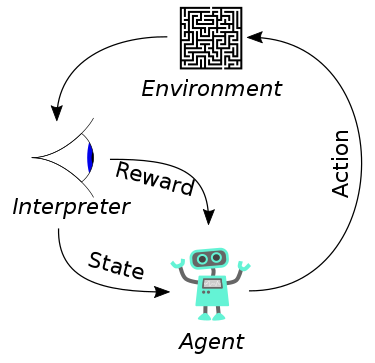
Goal-oriented algorithms, which learn how to attain a complex objective (goal) or maximize along a particular dimension over many steps; for example, maximize the points won in a game over many moves. Reinforcement learning solves the difficult problem of correlating immediate actions with the delayed returns they produce. Like humans, reinforcement learning algorithms sometimes have to wait a while to see the fruit of their decisions. They operate in a delayed return environment, where it can be difficult to understand which action leads to which outcome over many time steps.