Difference between revisions of "Math for Intelligence"
(→Explained) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
* [http://www.3blue1brown.com/ Animated Math | Grant Sanderson @ 3blue1brown.com] | * [http://www.3blue1brown.com/ Animated Math | Grant Sanderson @ 3blue1brown.com] | ||
| + | * http://machinelearningmastery.com/introduction-matrices-machine-learning/ Introduction to Matrices and Matrix Arithmetic for Machine Learning | Jason Brownlee] | ||
* [https://brilliant.org/courses/artificial-neural-networks/ Brilliant.org] | * [https://brilliant.org/courses/artificial-neural-networks/ Brilliant.org] | ||
* [http://triseum.com/variant-limits/ Varient: Limits] | * [http://triseum.com/variant-limits/ Varient: Limits] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
* Geometrically, it is the product of the Euclidean magnitudes of the two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. | * Geometrically, it is the product of the Euclidean magnitudes of the two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. | ||
| + | http://3qeqpr26caki16dnhd19sv6by6v-wpengine.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/Depection-of-Matrix-Multiplication.png | ||
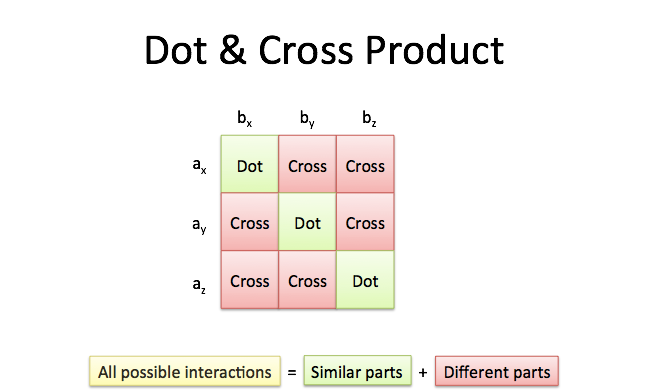
http://betterexplained.com/wp-content/uploads/crossproduct/cross-product-grid.png | http://betterexplained.com/wp-content/uploads/crossproduct/cross-product-grid.png | ||
| − | |||
<youtube>ml4NSzCQobk</youtube> | <youtube>ml4NSzCQobk</youtube> | ||
<youtube>f5liqUk0ZTw</youtube> | <youtube>f5liqUk0ZTw</youtube> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
<youtube>owuokEE9clQ</youtube> | <youtube>owuokEE9clQ</youtube> | ||
<youtube>yyNEOwEg6-I</youtube> | <youtube>yyNEOwEg6-I</youtube> | ||
| + | <youtube>5MdSE-N0bxs</youtube> | ||
<youtube>kqWCwwyeE6k</youtube> | <youtube>kqWCwwyeE6k</youtube> | ||
<youtube>sYlOjyPyX3g</youtube> | <youtube>sYlOjyPyX3g</youtube> | ||
| − | + | ||
== Siraj Raval == | == Siraj Raval == | ||
Revision as of 09:45, 29 October 2018
- Animated Math | Grant Sanderson @ 3blue1brown.com
- http://machinelearningmastery.com/introduction-matrices-machine-learning/ Introduction to Matrices and Matrix Arithmetic for Machine Learning | Jason Brownlee]
- Brilliant.org
- Varient: Limits
- Probability Cheatsheet
3blue1brown
Explained
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product Dot Product | Wikipedia]
Dot Product =
- Algebraically, the dot product is the sum of the products of the corresponding entries of the two sequences of numbers.
- Geometrically, it is the product of the Euclidean magnitudes of the two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them.

Siraj Raval
Josh Starmer - StatQuest
Quantum Algorithm