Difference between revisions of "Manifold Hypothesis"
m (→Manifold Learning) |
m (→Manifold Learning) |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
Manifold learning is based on the assumption that many high-dimensional datasets lie on a low-dimensional manifold, which is a curved surface that is embedded in a higher-dimensional space. It is particularly useful for datasets that lie on a low-dimensional manifold, even if the manifold is non-linear. Manifold learning algorithms aim to find a low-dimensional embedding of the data that preserves the intrinsic geometry of the manifold. This can be useful for visualization, data analysis, and machine learning tasks. Some popular manifold learning algorithms include: | Manifold learning is based on the assumption that many high-dimensional datasets lie on a low-dimensional manifold, which is a curved surface that is embedded in a higher-dimensional space. It is particularly useful for datasets that lie on a low-dimensional manifold, even if the manifold is non-linear. Manifold learning algorithms aim to find a low-dimensional embedding of the data that preserves the intrinsic geometry of the manifold. This can be useful for visualization, data analysis, and machine learning tasks. Some popular manifold learning algorithms include: | ||
| − | * <b> | + | * <b>[[Local Linear Embedding (LLE)]]</b>: LLE constructs a local linear model for each data point and then finds a low-dimensional embedding that preserves the local structure of the data. |
| − | * <b>Isomap</b>: Isomap constructs a graph of the data points based on their pairwise distances and then uses multidimensional scaling (MDS) to find a low-dimensional embedding of the graph. | + | * <b>[[Isomap]]</b>: Isomap constructs a graph of the data points based on their pairwise distances and then uses multidimensional scaling (MDS) to find a low-dimensional embedding of the graph. |
| − | * <b> | + | * <b>[[T-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE)]]</b>: t-SNE uses a probabilistic approach to find a low-dimensional embedding of the data that preserves the local and global structure of the data. |
Manifold learning algorithms have been used in a wide variety of applications, including: | Manifold learning algorithms have been used in a wide variety of applications, including: | ||
Revision as of 14:29, 16 September 2023
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Backpropagation ... FFNN ... Forward-Forward ... Activation Functions ...Softmax ... Loss ... Boosting ... Gradient Descent ... Hyperparameter ... Manifold Hypothesis ... PCA
- Embedding ... Fine-tuning ... RAG ... Search ... Clustering ... Recommendation ... Anomaly Detection ... Classification ... Dimensional Reduction. ...find outliers
- Objective vs. Cost vs. Loss vs. Error Function
- Optimization Methods
- Embedding ... Fine-tuning ... RAG ... Search ... Clustering ... Recommendation ... Anomaly Detection ... Classification ... Dimensional Reduction. ...find outliers
- Manifold Wikipedia
- Manifolds and Neural Activity: An Introduction | Kevin Luxem - Towards Data Science
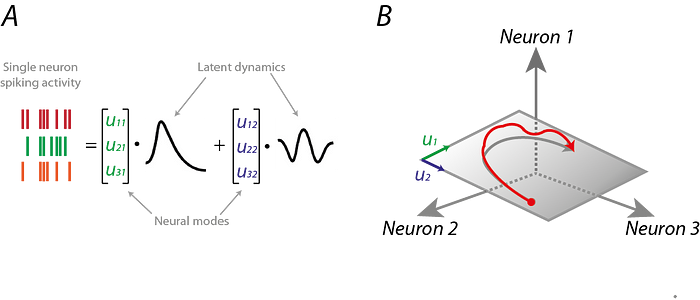
The Manifold Hypothesis states that real-world high-dimensional data (images, neural activity) lie on low-dimensional manifolds
manifolds embedded within the high-dimensional space. ...manifolds are topological spaces that look locally like Euclidean spaces.
The Manifold Hypothesis explains (heuristically) why machine learning techniques are able to find useful features and produce accurate predictions from datasets that have a potentially large number of dimensions ( variables). The fact that the actual data set of interest actually lives on in a space of low dimension, means that a given machine learning model only needs to learn to focus on a few key features of the dataset to make decisions. However these key features may turn out to be complicated functions of the original variables. Many of the algorithms behind machine learning techniques focus on ways to determine these (embedding) functions. What is the Manifold Hypothesis? | DeepAI
|
|
Manifold Learning
Manifold learning is an approach to non-linear dimensionality reduction. Algorithms for this task are based on the idea that the dimensionality of many data sets is only artificially high. Manifold learning | SciKitLearn
Manifold learning is based on the assumption that many high-dimensional datasets lie on a low-dimensional manifold, which is a curved surface that is embedded in a higher-dimensional space. It is particularly useful for datasets that lie on a low-dimensional manifold, even if the manifold is non-linear. Manifold learning algorithms aim to find a low-dimensional embedding of the data that preserves the intrinsic geometry of the manifold. This can be useful for visualization, data analysis, and machine learning tasks. Some popular manifold learning algorithms include:
- Local Linear Embedding (LLE): LLE constructs a local linear model for each data point and then finds a low-dimensional embedding that preserves the local structure of the data.
- Isomap: Isomap constructs a graph of the data points based on their pairwise distances and then uses multidimensional scaling (MDS) to find a low-dimensional embedding of the graph.
- T-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE): t-SNE uses a probabilistic approach to find a low-dimensional embedding of the data that preserves the local and global structure of the data.
Manifold learning algorithms have been used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Image processing: Manifold learning can be used to reduce the dimensionality of images without losing important information. This can be useful for image compression, classification, and retrieval.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Manifold learning can be used to reduce the dimensionality of text data without losing important information. This can be useful for text classification, clustering, and machine translation.
- Bioinformatics: Manifold learning can be used to reduce the dimensionality of biological data, such as gene expression data and protein structure data. This can be useful for identifying disease biomarkers and developing new drugs.
Manifold Alignment
Manifold - Defenses Against Adversarial Attacks
The reformer network moves adversarial examples towards the manifold of normal examples, which is effective for correctly classifying adversarial examples with small perturbation.