Difference between revisions of "Poisson Regression"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
* [[AI Solver]] | * [[AI Solver]] | ||
* [[...predict values]] | * [[...predict values]] | ||
| + | * [[Capabilities]] | ||
* [http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/studio-module-reference/poisson-regression Poisson Regression? | Microsoft] | * [http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/studio-module-reference/poisson-regression Poisson Regression? | Microsoft] | ||
Revision as of 06:01, 1 June 2018
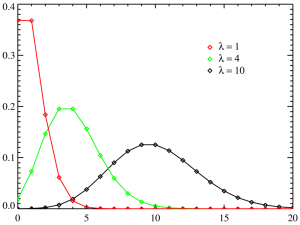
Poisson regression is used to model response variables (Y-values) that are counts. It tells you which explanatory variables have a statistically significant effect on the response variable. In other words, it tells you which X-values work on the Y-value. It’s best used for rare events, as these tend to follow a Poisson distribution (as opposed to more common events which tend to be normally distributed). For example:
- Number of colds contracted on airplanes.
- Number of bacteria found in a petri dish.
- Counts of catastrophic computer failures at a large tech firm in a calendar year.
- Number of 911 calls that end in the death of a suspect.
For large means, the normal distribution is a good approximation for the Poisson distribution. Therefore, Poisson regression is more suited to cases where the response variable is a small integer.
Poisson regression is only used for numerical, continuous data. The same technique can be used for modeling categorical explanatory variables or counts in the cells of a contingency table. When used in this way, the models are called loglinear models. What is Poisson Regression? | Statistics How To