Difference between revisions of "Markov Decision Process (MDP)"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* [[Markov Model (Chain, Discrete Time, Continuous Time, Hidden)]] | * [[Markov Model (Chain, Discrete Time, Continuous Time, Hidden)]] | ||
| + | |||
* [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] | * [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] | ||
** [[Monte Carlo]] (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning | ** [[Monte Carlo]] (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
** [[Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms]] | ** [[Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms]] | ||
** [[Actor Critic]] | ** [[Actor Critic]] | ||
| + | *** [[Asynchronous Advantage Actor Critic (A3C)]] | ||
*** [[Advanced Actor Critic (A2C)]] | *** [[Advanced Actor Critic (A2C)]] | ||
| − | |||
*** [[Lifelong Latent Actor-Critic (LILAC)]] | *** [[Lifelong Latent Actor-Critic (LILAC)]] | ||
** [[Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)]] | ** [[Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)]] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/Markov_Decision_Process.svg/600px-Markov_Decision_Process.svg.png | http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/Markov_Decision_Process.svg/600px-Markov_Decision_Process.svg.png | ||
| + | |||
http://slideplayer.com/24/7469154/big_thumb.jpg | http://slideplayer.com/24/7469154/big_thumb.jpg | ||
Revision as of 06:22, 6 July 2020
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Monte Carlo (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning
- Markov Decision Process (MDP)
- State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)
- Q Learning
- Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) DeepRL
- Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)
- Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms
- Actor Critic
- Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)

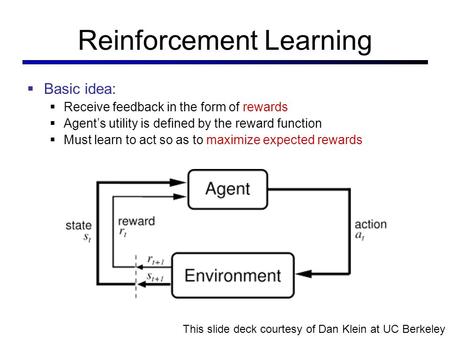
Solutions:
Used where outcomes are partly random and partly under the control of a decision maker. MDP is a discrete time stochastic control process. At each time step, the process is in some state s, and the decision maker may choose any action a that is available in state s. The process responds at the next time step by randomly moving into a new state s', and giving the decision maker a corresponding reward R_{a}(s,s')} R_a(s,s'). The probability that the process moves into its new state s' is influenced by the chosen action. Helping the convergence of certain algorithms a discount rate (factor) makes an infinite sum finite.