Difference between revisions of "Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* [http://thegradient.pub/the-promise-of-hierarchical-reinforcement-learning The Promise of Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning | Yannis Flet-Berliac - The Gradient] | * [http://thegradient.pub/the-promise-of-hierarchical-reinforcement-learning The Promise of Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning | Yannis Flet-Berliac - The Gradient] | ||
* [http://www.slideshare.net/DavidJardim/hierarchical-reinforcement-learning Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning | David Jardim] | * [http://www.slideshare.net/DavidJardim/hierarchical-reinforcement-learning Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning | David Jardim] | ||
| − | * [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] | + | |
| + | * [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] | ||
** [[Monte Carlo]] (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning | ** [[Monte Carlo]] (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning | ||
** [[Markov Decision Process (MDP)]] | ** [[Markov Decision Process (MDP)]] | ||
| + | ** [[State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)]] | ||
** [[Q Learning]] | ** [[Q Learning]] | ||
| − | ** [[ | + | *** [[Deep Q Network (DQN)]] |
** [[Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)]] DeepRL | ** [[Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)]] DeepRL | ||
** [[Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)]] | ** [[Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)]] | ||
| − | |||
** [[Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms]] | ** [[Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms]] | ||
** [[Actor Critic]] | ** [[Actor Critic]] | ||
| + | *** [[Asynchronous Advantage Actor Critic (A3C)]] | ||
*** [[Advanced Actor Critic (A2C)]] | *** [[Advanced Actor Critic (A2C)]] | ||
| − | |||
*** [[Lifelong Latent Actor-Critic (LILAC)]] | *** [[Lifelong Latent Actor-Critic (LILAC)]] | ||
** Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL) | ** Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL) | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | traditional [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] methods to solve more complex tasks. | + | HRL is a promising approach to extend traditional [[Reinforcement Learning (RL)]] methods to solve more complex tasks. |
<youtube>x_QjJry0hTc</youtube> | <youtube>x_QjJry0hTc</youtube> | ||
Revision as of 06:17, 6 July 2020
Youtube search... ...Google search
- The Promise of Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning | Yannis Flet-Berliac - The Gradient
- Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning | David Jardim
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Monte Carlo (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning
- Markov Decision Process (MDP)
- State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)
- Q Learning
- Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) DeepRL
- Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)
- Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms
- Actor Critic
- Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)
HRL is a promising approach to extend traditional Reinforcement Learning (RL) methods to solve more complex tasks.
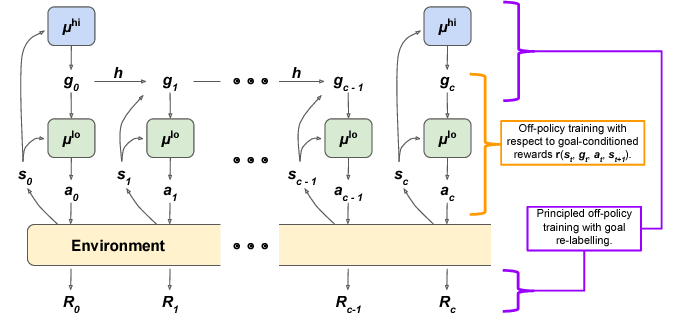
HIerarchical Reinforcement learning with Off-policy correction (HIRO)
- Beyond DQN/A3C: A Survey in Advanced Reinforcement Learning | Joyce Xu - Towards Data Science
- Data-Efficient Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning | O. Nachum, S. Gu, H. Lee, and S. Levine - Google Brain
HIRO can be used to learn highly complex behaviors for simulated robots, such as pushing objects and utilizing them to reach target locations, learning from only a few million samples, equivalent to a few days of real-time interaction. In comparisons with a number of prior HRL methods.