Difference between revisions of "Natural Language Generation (NLG)"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
* [http://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1510/1510.04420.pdf Narrative Science Systems: A Review | P. Sarao, P. Mittal, R. Kaur] | * [http://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1510/1510.04420.pdf Narrative Science Systems: A Review | P. Sarao, P. Mittal, R. Kaur] | ||
* [[Generative Pre-trained Transformer-2 (GPT-2)]] | * [[Generative Pre-trained Transformer-2 (GPT-2)]] | ||
| + | * [http://www.informationweek.com/big-data/big-data-analytics/nlp-for-analytics-its-not-just-about-text/a/d-id/1336184 NLP for Analytics: It's Not Just About Text | Lisa Morgan - InformationWeek] | ||
| + | |||
* Companies: | * Companies: | ||
Revision as of 13:06, 3 November 2019
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- The Future of Writing, With Robots | Garrett Grams
- Using Natural Language Processing for Smart Question Generation | Aditya S -Intel AI Academy
- Neural text generation: How to generate text using conditional language models | Neil Yager
- Narrative Science Systems: A Review | P. Sarao, P. Mittal, R. Kaur
- Generative Pre-trained Transformer-2 (GPT-2)
- NLP for Analytics: It's Not Just About Text | Lisa Morgan - InformationWeek
- Companies:
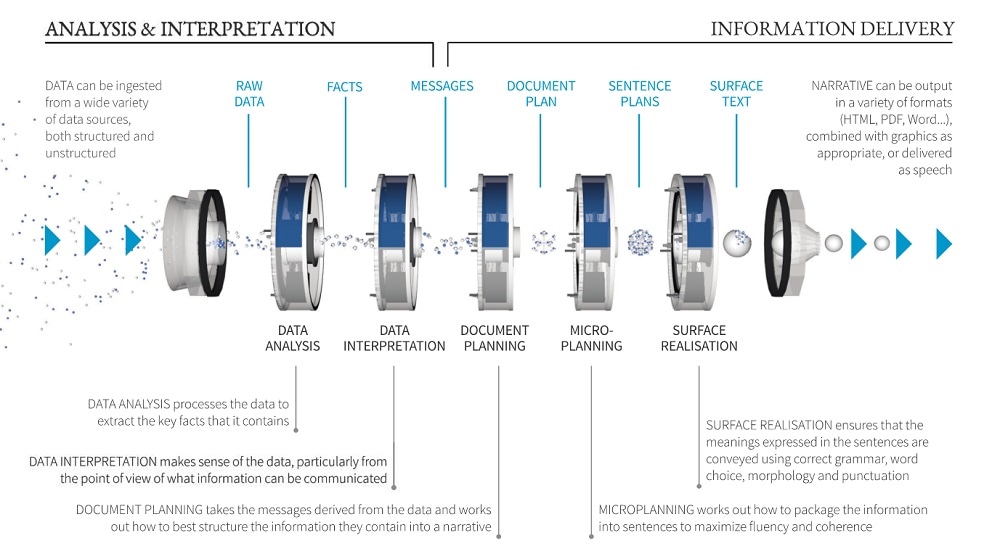
Natural-language generation (NLG) is the natural-language processing task of generating natural language from a machine-representation system such as a knowledge base or a logical form. Psycholinguists prefer the term language production when such formal representations are interpreted as models for mental representations. It could be said an NLG system is like a translator that converts data into a natural-language representation. However, the methods to produce the final language are different from those of a compiler due to the inherent expressivity of natural languages. ...NLG may be viewed as the opposite of natural-language understanding: whereas in natural-language understanding, the system needs to disambiguate the input sentence to produce the machine representation language, in NLG the system needs to make decisions about how to put a concept into words. Wikipedia
Mapping the Field of Algorithmic Journalism | Konstantin N. Dörr

- Artificial intelligence in healthcare: an interview with Dr Ehud Reiter | News Medical Life Sciences
- Arria NLG Engine