Difference between revisions of "Radial Basis Function Network (RBFN)"
(→Adversarial Attack) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{#seo: | ||
| + | |title=PRIMO.ai | ||
| + | |titlemode=append | ||
| + | |keywords=artificial, intelligence, machine, learning, models, algorithms, data, singularity, moonshot, Tensorflow, Google, Nvidia, Microsoft, Azure, Amazon, AWS | ||
| + | |description=Helpful resources for your journey with artificial intelligence; videos, articles, techniques, courses, profiles, and tools | ||
| + | }} | ||
[http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Radial+Basis+Function+Network+RBFN YouTube search...] | [http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=Radial+Basis+Function+Network+RBFN YouTube search...] | ||
| + | [http://www.google.com/search?q=Radial+Basis+Function+Network+RBFN+machine+learning+ML+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | ||
* [[Cybersecurity]] | * [[Cybersecurity]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:28, 2 February 2019
YouTube search... ...Google search
___________________________________________________
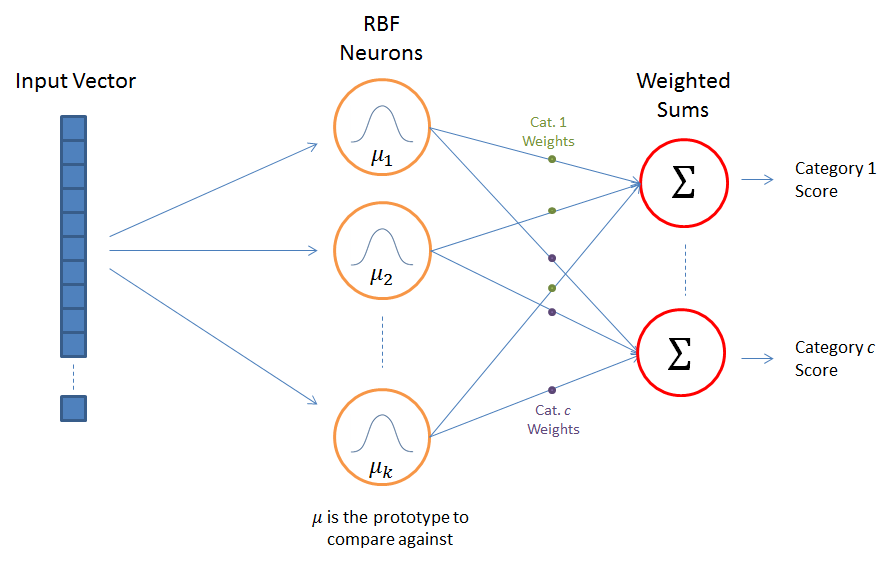
Performs classification by measuring the input’s similarity to examples from the training set. Each RBFN neuron stores a “prototype”, which is just one of the examples from the training set. When we want to classify a new input, each neuron computes the Euclidean distance between the input and its prototype. Roughly speaking, if the input more closely resembles the class A prototypes than the class B prototypes, it is classified as class A. Radial Basis Function Network (RBFN) Tutorial | Chris McCormick
Note: Support Vector Machine (SVM) represent a special case of RBFNs.
As a non-linear classifier...
Adversarial Attack Resiliency
Watch 10:15 into the following video...