Difference between revisions of "Word2Vec"
m |
m |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* [[TensorFlow]] | * [[TensorFlow]] | ||
** [http://projector.tensorflow.org/ Embedding Projector] | ** [http://projector.tensorflow.org/ Embedding Projector] | ||
| − | * [[Embedding]] | + | * [[Embedding]] ... [[Fine-tuning]] ... [[Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)|RAG]] ... [[Agents#AI-Powered Search|Search]] ... [[Clustering]] ... [[Recommendation]] ... [[Anomaly Detection]] ... [[Classification]] ... [[Dimensional Reduction]]. [[...find outliers]] |
** [http://pathmind.com/wiki/word2vec A Beginner's Guide to Word2Vec and Neural Word Embeddings | Chris Nicholson - A.I. Wiki pathmind] | ** [http://pathmind.com/wiki/word2vec A Beginner's Guide to Word2Vec and Neural Word Embeddings | Chris Nicholson - A.I. Wiki pathmind] | ||
* [http://towardsdatascience.com/introduction-to-word-embedding-and-word2vec-652d0c2060fa Introduction to Word Embedding and Word2Vec | Dhruvil Karani - Towards Data Science - Medium] | * [http://towardsdatascience.com/introduction-to-word-embedding-and-word2vec-652d0c2060fa Introduction to Word Embedding and Word2Vec | Dhruvil Karani - Towards Data Science - Medium] | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 13 September 2023
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Large Language Model (LLM) ... Natural Language Processing (NLP) ...Generation ... Classification ... Understanding ... Translation ... Tools & Services
- Doc2Vec
- Node2Vec
- Skip-Gram
- Global Vectors for Word Representation (GloVe)
- Bag-of-Words (BoW)
- Continuous Bag-of-Words (CBoW)
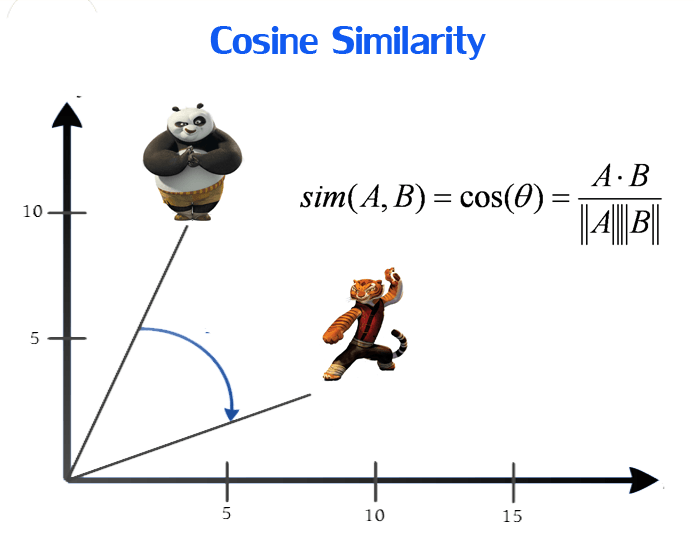
- Similarity
- TensorFlow
- Embedding ... Fine-tuning ... RAG ... Search ... Clustering ... Recommendation ... Anomaly Detection ... Classification ... Dimensional Reduction. ...find outliers
- Introduction to Word Embedding and Word2Vec | Dhruvil Karani - Towards Data Science - Medium
- Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality | Tomas Mikolov - Google
a shallow, two-layer neural networks which is trained to reconstruct linguistic contexts of words. It takes as its input a large corpus of words and produces a vector space, typically of several hundred dimensions, with each unique word in the corpus being assigned a corresponding vector in the space.