Difference between revisions of "(Boosted) Decision Tree"
(Created page with "[http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=+Linear+Regression+artificial+intelligence YouTube search...] * AI Solver ** ...predict categories * Capabilities *...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=+ | + | [http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=boosted+decision+tree+artificial+intelligence YouTube search...] |
* [[AI Solver]] | * [[AI Solver]] | ||
** [[...predict categories]] | ** [[...predict categories]] | ||
* [[Capabilities]] | * [[Capabilities]] | ||
| − | * [http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/studio-module-reference/ | + | * [http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/studio-module-reference/two-class-boosted-decision-tree Two-Class Boosted Decision Tree | Microsoft] |
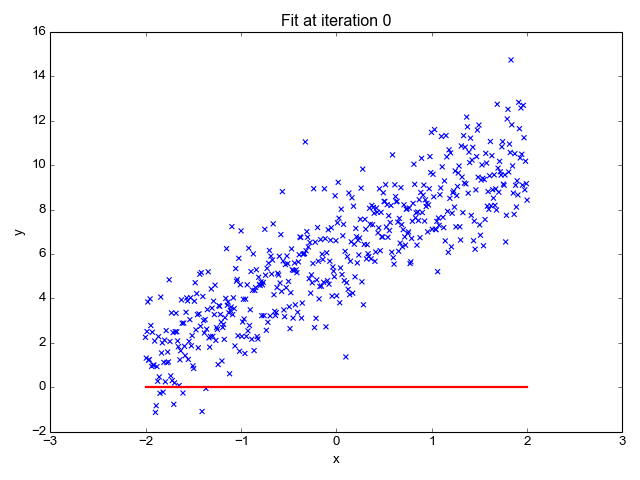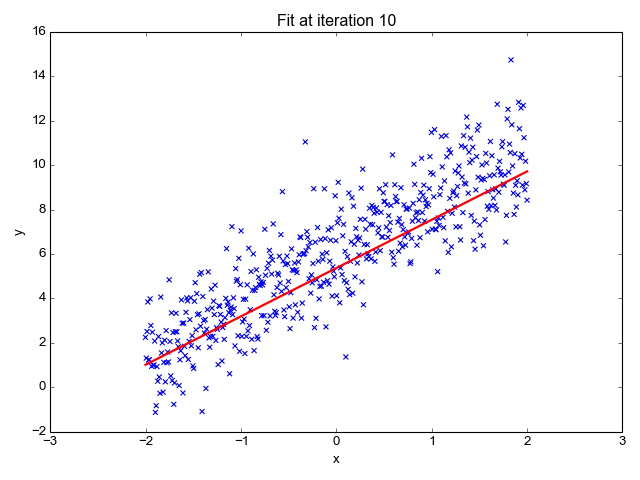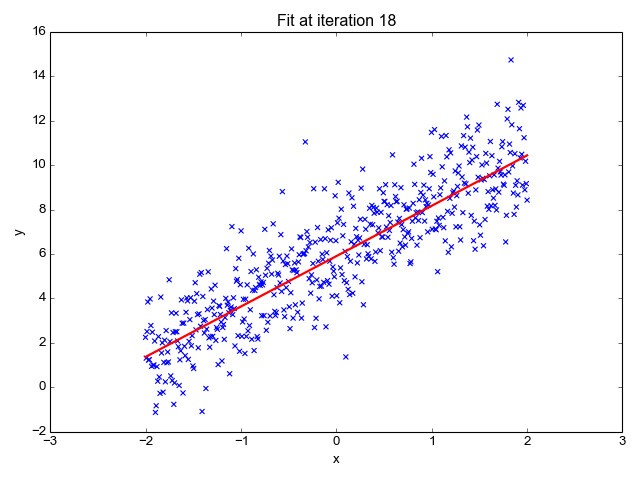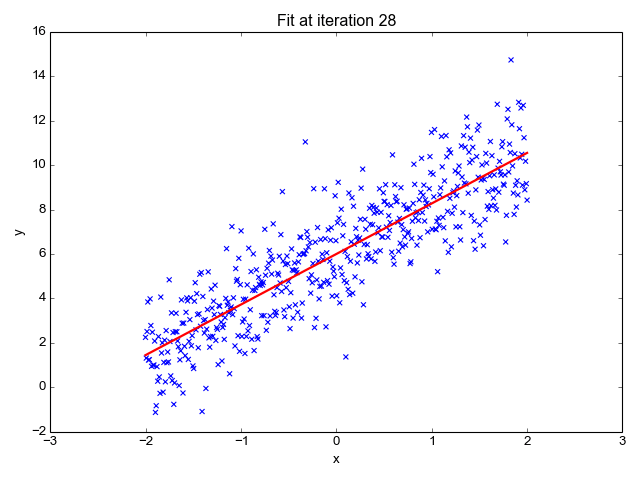
| − | + | A boosted decision tree is an ensemble learning method in which the second tree corrects for the errors of the first tree, the third tree corrects for the errors of the first and second trees, and so forth. Predictions are based on the entire ensemble of trees together that makes the prediction. For further technical details, see the Research section of this article. Generally, when properly configured, boosted decision trees are the easiest methods with which to get top performance on a wide variety of machine learning tasks. However, they are also one of the more memory-intensive learners, and the current implementation holds everything in memory. Therefore, a boosted decision tree model might not be able to process the very large datasets that some linear learners can handle. | |
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/640/1*eeIvlwkMNG1wSmj3FR6M2g.gif | https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/640/1*eeIvlwkMNG1wSmj3FR6M2g.gif | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>mzcS_UT-UQ0</youtube> |
| − | |||
Revision as of 21:10, 2 June 2018
A boosted decision tree is an ensemble learning method in which the second tree corrects for the errors of the first tree, the third tree corrects for the errors of the first and second trees, and so forth. Predictions are based on the entire ensemble of trees together that makes the prediction. For further technical details, see the Research section of this article. Generally, when properly configured, boosted decision trees are the easiest methods with which to get top performance on a wide variety of machine learning tasks. However, they are also one of the more memory-intensive learners, and the current implementation holds everything in memory. Therefore, a boosted decision tree model might not be able to process the very large datasets that some linear learners can handle.