|
SkyTalk - Trends, Challenges & Solutions in Aviation Security - NUCTECH
Presented by Nuctech
|
Passenger Screening
Transportation Security Administration (TSA) is evaluating the utility of advanced screening systems that use nontraditional measurement processes such as differential phase contrast X-ray, X-ray diffraction, walkthrough Advanced Imaging Technology (AIT) systems, and application of machine learning approaches to improving detection capabilities and system operational efficiency. For example, TSA is working to develop new algorithms that use machine learning approaches to discriminate between threats and benign objects, making the screening process more effective and efficient. Machine learning also offers a way to screen for all prohibited items (explosives, firearms, sharp objects, etc.) automatically. It is anticipated that machine learning algorithms not only will improve security effectiveness but also will support automation in future security systems, thereby enhancing operation efficiency and improving passenger experience through increased throughput and decreased false alarm rates. More broadly, machine learning algorithms can be applied to assess security performance and provide system-level improvements beyond performance enhancements realized at individual screening operations. Advanced Integrated Passenger and Baggage Screening Technologies | Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
Kaggle: Passenger Screening Challenge
Results have showed the effectiveness of deep learning applied to passenger screening.
Department of Homeland Security (DHS) gives notice of the availability of the “ Department of Homeland Security (DHS)’s Person Screening Algorithm Challenge Prize Competition and rules.” The DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) Homeland Security Advanced Research Projects Agency (HSARPA) Explosives Division (EXD) and the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) (Competition Sponsor) are seeking new automated detection algorithms from individuals and entities that improve the speed, accuracy, and detection of small threat objects and other prohibited items during the airport passenger screening process. Algorithms developed from this Competition, or through further research and development under a limited intellectual property use agreement, have the potential to improve the speed, the detection of prohibited items, and the accuracy of Advanced Imaging Technology (AIT) scanners. A comprehensive set of new automated detection algorithms have the potential to be integrated into the latest screening equipment.
Models idle_speculation used to win
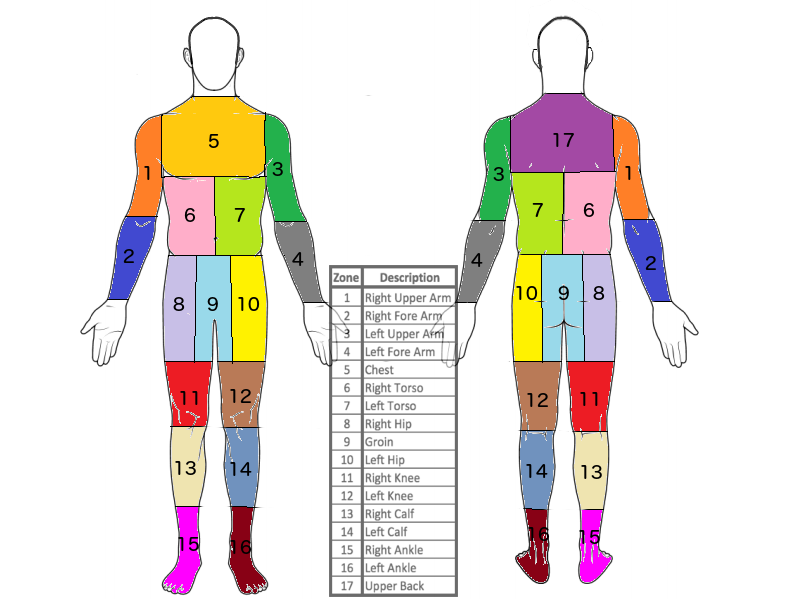
|
Copying the TSA dataset via GCS UI
Explaining how to copy the TSA dataset from GCS into your own bucket.
|
|
|
|
Building a Better TSA Screening Algorithm (Yvonne Matos) - ChiPy Mentorship Finals, Fall 2018
The current TSA body scanner passenger screening algorithm has a high rate of false positives, which leads to longer wait times at screening checkpoints. Using the TSA Kaggle dataset, I developed models to predict potential threats in two body zones of 3D body scan images. The current best model has 95% accuracy, 67% precision, and 86% recall. This is the first project I've done in Python, and am happy to say I've met many of my goals for the ChiPy mentorship program!
|
|
Using Synthetic Training Data
Old:
Development of the equipment and its associated detection algorithms is time consuming and expensive because system screening performance is difficult to accurately model. Prototype systems must be built and tested to measure and understand the interaction of sensors with explosives in various containment configurations. Development requires physical test articles to be fabricated or acquired. Suitable test articles may even be impossible to create if the explosives involved are unsafe to synthesize. Many test articles are created and scanned to build datasets for algorithm development, training, and testing. This solution is particularly labor intensive in order to generate large, representative datasets.
New:
The use of machine learning and deep learning approaches to develop algorithms to process the images generated by the screening hardware either to clear the passenger/property or to identify specific anomalies have shown significant promise in improving overall system performance. Tools can create virtual models of human travelers, their baggage and its contents. These tools/models:
- can simulate human subjects and checked baggage with all appropriate ancillaries (clothing, shoes, hair and, in the case of baggage, typical contents).
- are capable of including simulated explosives and prohibited items.
- are able to be generated in large numbers (many thousands or millions) in a reasonable amount of time (under 1 second per image).
- are used to predict the performance of emerging technologies and to train machine learning-based detection algorithms.
Biometrics
Youtube search...
...Google search
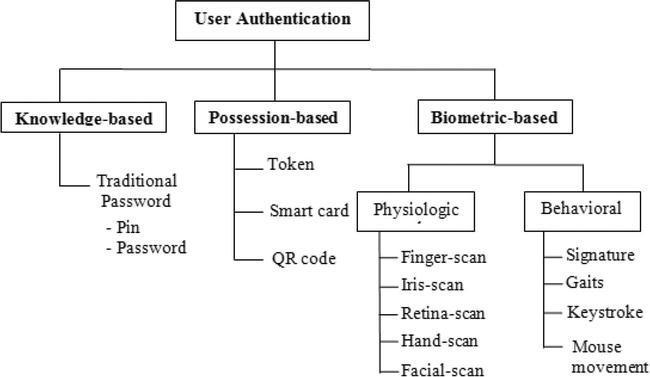
Biometrics is the science of analyzing physical or behavioural characteristics specific to each individual to be able to authenticate their identity. If we were to define biometry or biometrics in the most straightforward sense, we would say the "measurement of the human body."
There are two categories of biometric identification and recognition solutions: Physical and behavioral. Physical biometric solutions use distinctive and measurable characteristics of particular parts of the human body, such as a person’s face, iris, DNA, vein, fingerprints, etc., and transform this information into a code understandable by the AI system. Behavioral biometric solutions operate in a similar way, except they use unique behavioral characteristics, such as a person’s typing rhythm, way of interaction with devices, gait, voice, etc. This encoded biometric information is stored in a database and digitally sampled during authentication and verification. AI in Biometrics and Security – Current Business Applications | Radhika Madhavan - emero
Biometric Screening
The electronic passport (e-passport) is a familiar biometric travel document. The second generation of such documents, also known as biometric passports, includes two fingerprints stored in addition to a passport photo. But think about it for one minute... The photo speeds up border crossing through the use of scanners, which use the principle of recognition by comparison of the face or fingerprints. Check-ins and bag-drop solutions also increase speed and efficiency while maintaining high levels of security. Needless to say, that for airports and airlines, providing passengers with a unique and enjoyable travel experience is a business priority. Biometrics provides here irrefutable evidence of the link between the passport and its holder. Biometric authentication is done by comparing the face/fingerprint(s) seen/read at the border with the face/fingerprints in the passport micro-controller. If both biometric data match, authentication is confirmed. Identification, if necessary, is done with the biographic data in the chip and printed. Besides, many countries have set up biometric infrastructures to control migration flows to and from their territories. Fingerprint scanners and cameras at border posts capture information that helps identify travellers entering the country in a more precise and reliable way. In some states, the same applies to consulates to visa applications and renewals. Data acquisition requires reliable equipment to ensure optimum capture of photos and fingerprints, essential for precision during comparison and verification. Biometrics: authentication & identification (definition, trends, use cases, laws and latest news) - 2020 review Thales
Contactless Biometrics
Youtube search...
...Google search
used to authenticate users without having to place their hands anywhere near a scanner – simply authenticating digital identity through Fingerprint, Palmprint, Iris, Retinal, Face, Speech, Speaker & Language.
|
AISecureTech contactless AI integrated Facial recognition and temperature scanning solution
May 23, 2020
|
|
|
|
ZKTeco Touchless Biometrics Solutions for Access Control
Along with the latest launch of our touchless #biometrics product series with mask and body temperature detection, we have prepared a video demonstrating how these products work and contribute to help improve early detection, exposure and prevention. This video covers our #AccessControl terminals, turnstile and metal detector in order to show the entire solution in practical usage. Key features for access point #security: Body Temperature Detection Masked #FaceRecognition Computer Vision 3-in-1
|
|
|
Contactless 3D Fingerprint AI Scanner: FingerID SWIPE
Identify any fingerprint from 2 billion ones in 1 second
|
|
|
|
RamcoGEEK - Contactless Attendance with Facial Recognition, Voice Recording and Thermal Screening
Did you know that Coronavirus can survive on plastic surfaces for up to 3 days? The attendance swipe cards and the thumb-based biometric systems can easily be a reason for spread of such acute viral respiratory diseases! Switch to Ramco’s Touchless Attendance System integrated with Facial Recognition, Voice Recording, Thermal Screening and IoT based Door Sensor technology to address the crucial aspect of hygiene and health of employees.
|
|
|
Biometric Examples in Movies
Biometric Examples
|
|
|
|
Minority Report iLens scan
Eye scanning the Apple iLens concept - Minority Report
|
|
Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
provides biometric identification services to protect the nation through its Office of Biometric Identity Management (OBIM), which supplies the technology for matching, storing, and sharing biometric data. OBIM is the lead designated provider of biometric identity services for DHS, and maintains the largest biometric repository in the U.S. government. This system, called the Automated Biometric Identification System (IDENT), is operated and maintained by OBIM. IDENT currently holds more than 200 million unique identities and processes more than 300,000 biometric transactions per day.
Biometric Technology Rally
Department of Homeland Security (DHS) DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) and Customs and Border Protection (CBP)’s Apex Air Entry/Exit Re-engineering (AEER) project created a partnership between S&T and CBP to test and evaluate operational processes using biometric and non-biometric technologies. The MdTF continues to support multiple projects for the DHS S&T Biometrics and Identity Technology Center including those that inform CBP, Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and external agencies to evaluate and implement solutions in their operational environments. The 2019 Biometric Technology Rally was designed to challenge industry to develop high-throughput biometric systems, meeting the requirements of fast and accurate user recognition within identity verification operations, such as security checkpoints. The 2019 Rally invited providers of biometric (face, iris, or fingerprint) acquisition systems, as well as providers of biometric matching systems that achieve defined performance targets for high-throughput use cases. MdTF | Maryland Test Facility
|
DHS S&T's Biometric Technology Rally
Balancing speed and security at checkpoints, like airports, is essential to ensuring safe, reliable travel. Many of these checkpoints are increasingly using biometric technology to improve speed and reliability. While recent improvements in biometrics have lowered failure to match rates, many systems fail to quickly acquire biometric information in the first place. The Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Directorate’s (S&T) first Biometric Technology Rally, held in March at S&T’s Maryland Test Facility (MdTF), aimed to eliminate these obstacles by testing face and face/iris recognition systems.
|
|
|
|
>
Biometric Technology Rally 2020 - Announcement
he U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) is calling for submissions to the 2020 Biometric Technology Rally (Rally). Started in 2018, the Rally challenges industry to deliver fast, accurate, and easy-to-use biometric recognition capabilities to improve security and user facilitation of checkpoint processing. This video provides an overview of the 2020 Biometric Technology Rally application process and requirements.
|
|
|
2019 Biometric Technology Rally Acquisitions Systems
Detailed results (for acquisition systems) from the 2019 Biometric Technology Rally. The Biometric Technology Rally, held in May, challenged industry to meet specific DHS use cases and is an opportunity to foster innovation and create partnerships across government and industry.
|
|
|
|
2019 Bio Tech Rally Matching System Results
Detailed results (for matching systems) from the 2019 Biometric Technology Rally. The Biometric Technology Rally, held in May, challenged industry to meet specific DHS use cases and is an opportunity to foster innovation and create partnerships across government and industry.
|
|
|
Delta launching first biometric terminal at Atlanta airport
Some Delta Air Lines passengers will soon go through airport check-in and security just by showing their faces. The nation's first biometric airport terminal launches Saturday in Atlanta. But the new technology also raises privacy concerns. Kris Van Cleave reports.
|
|
|
|
OneScreen GoSafe Body Temperature & Facial Recognition Scanner
Why GoSafe? Securely scan in less than one second with on-board AI The only scanner with live video assistance for real time entry approval Provides access control integration for automatic doors Centralized management for multiple scanners, data and attendance Free, unlimited help & training
|
|
Fingerprint
Youtube search...
...Google search
Fingerprint scanners collect an image of a person’s fingerprint and record its features such as whorls, loops, and arches. Additionally, fingerprint scanners also analyze outlines of edges, furrows, and minutiae of a fingerprint. The scanned fingerprint image is then verified against a previously stored set of fingerprints. [Biometrics is smart, but AI is smarter. Here's why | Naveen Joshi - Allerin
Fingerprint identification is one of the most well-known and publicized biometrics. Because of their uniqueness and consistency over time, fingerprints have been used for identification for over a century, more recently becoming automated (i.e. a biometric) due to advancements in computing capabilities. Fingerprint identification is popular because of the inherent ease in acquisition, the numerous sources (10 fingers) available for collection, and their established use and collections by law enforcement and immigration. What is Fingerprint Identification? | Stephen Mayhew - Biometric Update.com
The practice of using fingerprints as a method of identifying individuals has been in use since the late nineteenth century when Sir Francis Galton defined some of the points or characteristics from which fingerprints can be identified. These “Galton Points” are the foundation for the science of fingerprint identification, which has expanded and transitioned over the past century. Fingerprint identification began its transition to automation in the late 1960s along with the emergence of computing technologies. With the advent of computers, a subset of the Galton Points, referred to as minutiae, has been utilized to develop automated fingerprint technology.
A fingerprint usually appears as a series of dark lines that represent the high, peaking portion of the friction ridge skin, while the valley between these ridges appears as white space and are the low, shallow portion of the friction ridge skin. Fingerprint identification is based primarily on the minutiae, or the location and direction of the ridge endings and bifurcations (splits) along a ridge path.
A variety of sensor types —
- optical
- capacitive
- ultrasound
- thermal
— are used for collecting the digital image of a fingerprint surface. Optical sensors take an image of the fingerprint, and are the most common sensor today.
The two main categories of fingerprint matching techniques are:
- minutiae-based matching
- pattern matching.
Pattern matching simply compares two images to see how similar they are. Pattern matching is usually used in fingerprint systems to detect duplicates. The most widely used recognition technique, minutiae-based matching, relies on the minutiae points, specifically the location and direction of each point.
|
FingerPrint Recognition Using Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) Deep learning
This video depicts how the Realtime fingerprint Recognition System using [[(Deep) Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN/CNN)|Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) Deep learning].
|
|
|
|
fingerprint detection using CNN Deep Learning Explanation
This video includes the working of the fingerprint recognition system and also the challenges in the fingerprint recognition system. Implementation is Done in Python using Tensorflow API.
|
|
Palmprint
Youtube search...
...Google search
The NGI System’s latent functionality uses a Friction Ridge Investigative File composed of all retained events for an individual as opposed to one composite image set per identity. These multiple events in the repository result in three times the previous latent search accuracy and allow for additional event image retrieval to support difficult casework. In May 2013, the FBI established the National Palm Print System (NPPS). This system contains palm prints that are searchable to law enforcement nationwide.
|
Palmprint Recognition using Deep Learning
pantechsolutions
|
|
|
|
Computer Vision Palm Recognition by ZKTeco
In 2019, ZKTeco made a breakthrough in palm recognition technology. The new technology has been combined with palm, palm-print and palm-vein recognition to set a new bar for the next-gen palm recognition
|
|
Eye: Iris/Retinal
Youtube search...
...Google search
Two methods:
- Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance.
- Retinal scanning is a different, ocular-based biometric technology that uses the unique patterns on a person's retina blood vessels and is often confused with iris recognition. Iris recognition uses video camera technology with subtle near infrared illumination to acquire images of the detail-rich, intricate structures of the iris which are visible externally.
|
Deep Learning E89 - Iris Recognition for Identification
This is a long video on my presentation on Iris Recognition for E89-Deep Learning class.
|
|
|
|
Iris Recognition
A.J. Hensman
|
|
|
Unlock Doors With Your EYES: Eyelock
Until now, only Wesley Snipes' character in "Demolition Man" understood the importance of retina scan. Today, Eyelock is announcing a device that puts dual-retina scan on your computer.
|
|
|
|
What is Retinal Scanning?
In this episode you will learn what is Retinal Scanning?
The human retina is a thin tissue composed of neuralcells that is located in the posterior portion of the eye. Because of the complex structure of the capillaries that supply the retina with blood, each person’s retina is unique. The network of blood vessels in the retina is so complex that even identical twins do not share a similar pattern. Although retinal patterns may be altered in cases of diabetes, glaucoma or retinal degenerative disorders, the retina typically remains unchanged from birth until death. A biometric identifier known as a retinal scan is used to map the unique patterns of a person’s retina. The blood vessels within the retina absorb light more readily than the surrounding tissue and are easily identified with appropriate lighting. A retinal scan is performed by casting an unperceived beam of low-energy infrared light into a person’s eye as they look through the scanner’s eyepiece. This beam of light traces a standardized path on the retina. Because retinal blood vessels are more absorbent of this light than the rest of the eye, the amount of reflection varies during the scan. The pattern of variations is converted to computer code and stored in a database.
|
|
Face
See Facial Recognition page
Speech, Speaker & Language
Youtube search...
...Google search
The implementation of AI in voice recognition can train the biometric systems using millions of voice samples of different users. AI and biometrics like voice recognition can evaluate a person’s biometric voice signature by analyzing their voice patterns such as speed, accent, tone, and pitch. Such biometrics can be quick and authenticate individuals precisely. Such AI-powered voice recognition can be used in workplaces for authentication and attendance purposes. [Biometrics is smart, but AI is smarter. Here's why | Naveen Joshi - Allerin
Biometric authentication, unlike passwords or token-based authentication, uses unique biological characteristics to verify an individual’s identity. It’s harder to spoof and generally more convenient for users since they don’t have to remember passwords or carry a physical token that can easily be lost or stolen. The authenticator is part of the individual. Aware
Voice recognition (also called speaker recognition or voice authentication) applies analyzes of a person’s voice to verify their identity. Airways and soft-tissue cavities, as well as the shape and movement of the mouth and jaw, influence voice patterns to create a unique “voiceprint.”
Speaker recognition is a type of voice recognition technology. However, it is not the same as speech recognition, which is the technology used in speech-to-text applications and virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa. Speech recognition can make sense of verbal language, but it can’t verify the identity of the speaker based on his or her unique vocal attributes; voice biometrics can.
Speaker recognition methods -
There are two main approaches to voice authentication:
- Text independent: Voice authentication is performed using any spoken passphrase or other speech content.
- Text-dependent: The same passphrases are used in enrollment and for verification. This means that a speaker cannot say anything he or she would like to authenticate, but will be asked to speak a predetermined phrase. In static text-dependent voice authentication, the same passphrase is used for every verification. In dynamic text-dependent voice authentication, a randomized passphrase such as a number sequence is generated for the user. This content must also be enrolled.
Enrollment and verification -
A voice biometric sample must be captured and enrolled using a microphone to create a reference template to compare against samples for future authentication attempts. Unique vocal qualities are then analyzed;, such as :
- Duration
- Intensity
- Dynamics
- Pitch
|
Identify Speaker Voice Machine learning model Neural Networks in Keras/TensorFlow (2019)
Learn to build a Keras model for speech classification. Audio is the field that ignited industry interest in deep learning. In this model, we are working with sounds WAV files, extract MFCC features upload to the dataset file fo training. Two different classification problem we are solving : 1- Identify speaker voice (Biometric authentication). 2- recognize spoken digit (0-9). University of Toronto School of Continuing Studies
|
|
|
|
Synaptics Smart Edge AI™ - Voice Identification
Secure Edge Computing SoC with Machine Learning Voice Identification
|
|
Luggage Screening
Youtube search...
...Google search
- 3D Model ...Point Cloud
- Image Retrieval / Object Detection
- (Deep) Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN/CNN)
- (Deep) Residual Network (DRN) - ResNet
- 3D Point Cloud Feature Explanations Using Gradient-Based Methods | A. Gupta, S. Watson, H. Yin ...Voxception-ResNet
- 3D Deep Learning | Kuixu
- Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks | S. Ren, K. He, R. Girshick, and J. Sun
- Object Detection with RetinaNet | Srihari Humbarwadi
- Azure Custom Vision ...an AI service and end-to-end platform for applying computer vision
- Towards Automatic Threat Detection: A Survey of Advances of Deep Learning within X-ray Security Imaging | Samet Akcay and Toby P. Breckon - Durham University, UK
- A Model-Based 3D Multi-slice Helical CT Reconstruction Algorithm for Transportation Security Application | P. chen, E. Haneda, C. Bouman, and K. Sauer
- The US Transportation Security Administration has recently introduced new computed tomography (CT) scanners, which use AI to help target threats, at Los Angeles International Airport, John F. Kennedy and Phoenix airports. How can AI help speed up airport security? | Airport Technology
- Computed Tomography (CT) | TSA
- Object Recognition and Adaptive Algorithms for Airport Passenger Property Screening Solicitation
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) in XIS-6040 X-ray Baggage Scanners | Astrophysics– Syntech Solutions
- DHS Awards $200K for AI-Based Object Recognition Proof-of-Concept | Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate (S&T)
- TSA Machine Learning Opportunities | Frank Cartwright - Office of Requirements and Capabilities Analysis, TSA
- Future Baggage Scanners Will Tell Us What Things Are Made Of | J. Greenberg, A. Ashok and M. Gehm - IEEE Spectrum
- DHS S&T Awards $142K to Cignal for Artificial Intelligence Model Training | GTSC's Homeland Security Today
- A Comparison of 3D Interest Point Descriptors with Application to Airport Baggage Object Detection in Complex CT Imagery | G. Flitton, T. Breckon, and N. Megherbi
- Automated Deep Learning for Threat Detection in Luggage from X-ray Images | Alessio Petrozziello and Ivan Jordanov
- DCNNs: A Transfer Learning comparison of Full Weapon Family threat detection forDual-Energy X-Ray Baggage Imagery | A. Williamson, P. Dickinson, T. Lambrou, and J. C. Murray
Computed Tomography (CT) scanning has ...found an application in transport security (predominantly airport security where it is currently used in a materials analysis context for explosives detection CTX (explosive-detection device) and is also under consideration for automated baggage/parcel security scanning using computer vision based object recognition algorithms that target the detection of specific threat items based on 3D appearance (e.g. guns, knives, liquid containers) CT scan | Wikipedia
In the last two decades, baggage scanning has globally become one of the prime aviation security concerns. Manual screening of the baggage items is tedious, error-prone, and compromise privacy. Hence, many researchers have developed X-ray imagery-based autonomous systems to address these shortcomings. This paper presents a cascaded structure tensor framework that can automatically extract and recognize suspicious items in heavily occluded and cluttered baggage. The proposed framework is unique, as it intelligently extracts each object by iteratively picking contour-based transitional information from different orientations and uses only a single feed-forward convolutional neural network for the recognition. The proposed framework has been rigorously evaluated using a total of 1,067,381 X-ray scans from publicly available GDXray and SIXray datasets where it outperformed the state-of-the-art solutions by achieving the mean average precision score of 0.9343 on GDXray and 0.9595 on SIXray for recognizing the highly cluttered and overlapping suspicious items. Furthermore, the proposed framework computationally achieves 4.76\% superior run-time performance as compared to the existing solutions based on publicly available object detectors. Cascaded Structure Tensor Framework for Robust Identification of Heavily Occluded Baggage Items from X-ray Scans | T. Hassan, S. Akcay, M. Bennamoun, S. Khan, and N. Werghi
X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) based 3D imaging is widely used in airports for aviation security screening whilst prior work on prohibited item detection focuses primarily on 2D X-ray imagery. In this paper, we aim to evaluate the possibility of extending the automatic prohibited item detection from 2D X-ray imagery to volumetric 3D CT baggage security screening imagery. To these ends, we take advantage of 3D Convolutional Neural Neworks (CNN) and popular object detection frameworks such as RetinaNet and Faster R-CNN in our work. As the first attempt to use 3D CNN for volumetric 3D CT baggage security screening, we first evaluate different CNN architectures on the classification of isolated prohibited item volumes and compare against traditional methods which use hand-crafted features. Subsequently, we evaluate object detection performance of different architectures on volumetric 3D CT baggage images. The results of our experiments on Bottle and Handgun datasets demonstrate that 3D CNN models can achieve comparable performance (98% true positive rate and 1.5% false positive rate) to traditional methods but require significantly less time for inference (0.014s per volume). Furthermore, the extended 3D object detection models achieve promising performance in detecting prohibited items within volumetric 3D CT baggage imagery with 76% mAP for bottles and 88% mAP for handguns, which shows both the challenge and promise of such threat detection within 3D CT X-ray security imagery. On the Evaluation of Prohibited Item Classification and Detection in Volumetric 3D Computed Tomography Baggage Security Screening Imagery | Q. Wang, N. Bhowmik, and T. Breckon

The benefits of adopting 3D technology for checkpoint security screening | Smiths Detection ...Guide: CT: What Is It And What Does It Deliver? | Smiths Detection
|
Azure AI and Machine Learning | Using Azure Stack Edge to help stop animal trafficking
Take a look at Azure Stack Edge and its growing application for AI and machine learning workloads. Find out how it’s being piloted, as part of Microsoft's AI For Good program, at London’s Heathrow Airport, to prevent illegal wildlife trafficking by inspecting passenger luggage for positive matches. All this is achieved using Azure Custom Vision AI models running locally on Azure Stack Edge. Matt McSpirit, Senior Program Manager for Azure Stack, joins Jeremy Chapman to share how the Azure AI Customer Engineering Team has been working with Heathrow to build a solution, combining a 3D scanner with AI models created in Azure, that cuts time and optimizes the process of early detection.
|
|
|
|
Prohibited Item Detection in Volumetric 3D Computed Tomography Baggage Security Screening Imagery
On the Evaluation of Prohibited Item Classification and Detection in Volumetric 3D Computed Tomography Baggage Security Screening Imagery (Q. Wang, N. Bhowmik, T.P. Breckon), In Proc. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IEEE, 2020. Author / Originator / Copyright: Qian Wang & Toby Breckon, Durham University
|
|
|
TSA Testing 3D Scanners to Speed up Security Line
Tests in European airports have indicated that security lines may be able to move at double their current speed if the 3D scanners are introduced, but the biggest hurdle to widespread implementation is their price. One model, made by Analogic, costs $300,000, which is double the price of a standard x-ray scanner. American Airlines is planning to test the machines at Phoenix Sky Harbor airport before expanding the trials next year.
|
|
|
|
Prohibited Item Detection in Volumetric 3D Computed Tomography Baggage Security Imagery (demo)
On the Evaluation of Prohibited Item Classification and Detection in Volumetric 3D Computed Tomography Baggage Security Screening Imagery (Q. Wang, N. Bhowmik, T.P. Breckon), In Proc. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IEEE, 2020 - https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.12625 Author / Originator / Copyright: Qian Wang / Toby Breckon, Durham University
|
|
|
Computed tomography - Image reconstruction backprojection
Very Nice explanation with brilliant visualization.
|
|
|
|
|
CT (Computed Tomography) Scans - A Level Physics
A basic description of the mechanism of CT (computed tomography) scans for medical use in remote sensing. Part of the A Level Physics revision series.
|
|
|
|
Rigaku CT Webinar: X-ray Computed Tomography for Materials Science 2: Data Analysis
An overview of X-ray CT data analysis techniques starting with basic image processing and leading to traditional segmentation, machine learning based segmentation and quantitative analysis. A number of commonly used data analysis and visualization programs will be discussed and demonstrated to help beginners to get an idea of where to start and select the right analysis tool for their needs.
|
|
|
TSA to debut new baggage scanners
The TSA is launching new technology that could change the way bags are scanned at airports across the country. The goal is to replace aging X-ray scanners with new 3D carry-on bag scanners that use the same technology as cat scans. Kris van cleave reports.
|
|
|
|
High tech TSA scanners give a closer look at airport baggage
The Oakland International Airport is testing out a $350,000 CT scanner that lets Transportation Security Administration agents take a more detailed look at the contents of carry-on luggage.
|
|
|
Analogic Checkpoint CT
Analogic's Checkpoint CT screening systems offer airports the highest level of threat detection and dramatically better passenger throughput and reliability. CT has become the gold standard for high speed automatic threat detection screening for checked luggage at airports worldwide; why not at the checkpoint?
|
|
|
|
Autoclear X-ray Security Scanner Training Video - Basic Operation
Demonstration of the basic steps to operate an Autoclear x-ray scanner. Please note...this is NOT sufficient training for effective threat detection...only for proper machine operation. Thanks to Alan Martin for producing and starring in this video.
|
|
Trace Detection
Youtube search...
...Google search
- IONSCAN 500DT Explosives and narcotics trace detection | Smiths Detection
- Improving the Chemical Selectivity of an Electronic Nose to TNT, DNT and RDX Using Machine Learning | A. Gradišek, M.van Midden, M. Koterle, V. Prezelj, D. Strle, B. Štefane, H. Brodnik, M. Trifkovič, I. Kvasić, E. Zupanič, and I. Muševič
- Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology (S&T)'s Secondary Screening
Ion-Mobility Spectrometry (IMS) has been applied, for example, to the localization of fatty acyl and double bond positions (Castro-Perez et al., 2011), and works well in combination with hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and reversed phase chromatography for increased resolution, specificity, and signal-to-noise ratio (Baker et al., 2014). | Science Direct
Mass spectrometry (MS) a new, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL)-developed method provides direct, real-time detection of trace amounts of explosives such as RDX, PETN and C-4. The method selectively ionizes a sample before passing the sample through a mass spectrometer to detect explosive vapors. The method could be used at airports to improve aviation security.
|
Tech Talk: Explosives Trace Detection
The Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Directorate’s (S&T) Secondary Screening Program works with the Transportation Security Administration, U.S. Customs and Border Protection and others across the Homeland Security Enterprise, as well as with academia and industry. The goal is to develop technology that can detect trace particles or residues of explosives left on surfaces -- like clothing or electronics or bags that can't be seen.
|
|
|
|
Real-time Classification of Explosive Transients Using Deep Recurrent Neural Networks
Real-time classification of explosive transients using deep recurrent neural networks by Daniel Muthukrishna (University of Cambridge) on 08/03/2019.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Advancing Explosives Detection Capabilities: Vapor Detection
A new, PNNL-developed method provides direct, real-time detection of trace amounts of explosives such as RDX, PETN and C-4. The method selectively ionizes a sample before passing the sample through a mass spectrometer to detect explosive vapors. The method could be used at airports to improve aviation security.
|
|
|
1st Detect Launches the Tracer 1000™ – the First Mass Spectrometer Explosives Trace Detector
BusinessWire
|
|
|
|
Fast, easy, cheap explosives detection: Kelley Peters at TEDxFIU
In the spirit of ideas worth spreading, TEDx is a program of local, self-organized events that bring people together to share a TED-like experience.
|
|
|
Short Introductory Video to the Smiths Detection Ionscan 500DT
The IONSCAN 500DT fills the growing need of security professionals to have the ability to detect a wide range of substances and to be able to adapt as threats change. By incorporating two IMS detectors in a single unit, the IONSCAN 500DT is capable of detecting and identifying explosives and narcotics during a single analysis, giving you the ability to detect a broader range of substances.
|
|
|
|
IONSCAN 600
Portable desktop system used to detect and identify trace amounts of explosives. Non-radioactive IMS source - Easy to use interface requires minimal raining - Small, lightweight and portable - Fully operational, hot-swappable battery - Cost effective swabs Learn more about the IONSCAN 600 - https://www.smithsdetection.com/produ... ABOUT SMITHS DETECTION Smiths Detection is a global leader in threat detection and screening technologies for aviation, ports and borders, urban security and defence. Our mission is to help make the world a safer place – with technology solutions and services that protect life, safeguard society and uphold the free flow of trade. For more information visit https://www.smithsdetection.com..
|
|
Standoff Detection
Youtube search...
...Google search
Demand for new surveillance capabilities for usage in airport screenings and battlefield security check-points has led to the development of terahertz imagers and sensors. There are several advantages of imaging at terahertz frequencies compared to microwave or infrared: the wavelengths in this regime are short enough to provide high resolution with modest apertures, yet long enough to penetrate clothing. Moreover, unlike in infrared, the terahertz frequencies are not affected by dust, fog, and rain.
|
Have you got a minute? - Automatic Weapons Detection Using Artificial Intelligence
Smiths Detection is committed to the development of next-generation solutions which improve operational efficiency, support resource planning and ensure the highest level of threat detection. We have recently added weapon detection to the innovative iCMORE family of smart and adaptable object recognition algorithms. Watch this short video to learn how artificial intelligence reduces the burden on image analysts and increases efficiency and detection accuracy.
|
|
|
|
Millimeter-Wave Remote Biometric Identification and Tracking (RBIT) System for Security Applications
Argonne, in collaboration with Northwestern University, has developed the first heart/respiration/movement biometric system that remotely identifies and tracks moving individuals by using a novel mmW sensor, facial-recognition video sensor/camera, and feature-extraction and data-analysis software. The portable RBIT system can be rapidly deployed for security screening, health of soldiers in battlefield and disaster rescue efforts. For more information: Millimeter-Wave Remote Biometric Identification and Tracking (RBIT) System for Security Applications
|
|
|
Millimeter Wave Technology And AI Are Key To Detecting Concealed Threats
Senior Vice President Carl speaks with Dale Jackson on CEO Report, explaining how millimeter wave technology and AI are key to detecting concealed threats.
|
|
|
|
Prof. Eric Grossman - Terahertz and Millimeter-wave Imaging - Technion lecture
Prof. Eric Grossman of National Institute of Standards and Technology, Boulder, CO, USA - Terahertz and Millimeter-wave Imaging - lecture from February 8, 2012 - Electrical Engineering faculty, Technion
|
|
|
Terahertz Radar for Stand-Off Through-Clothes Imaging
Demand for new surveillance capabilities for usage in airport screenings and battlefield security check-points has led to the development of terahertz imagers and sensors. There are several advantages of imaging at terahertz frequencies compared to microwave or infrared: the wavelengths in this regime are short enough to provide high resolution with modest apertures, yet long enough to penetrate clothing. Moreover, unlike in infrared, the terahertz frequencies are not affected by dust, fog, and rain. Several groups around the world are working on the development of terahertz imagers for various applications. One option is to use passive imaging techniques, which were very successful at millimeter-wave frequencies, by scaling in frequencies to terahertz range. However, the background sky is much warmer at terahertz frequencies due to high atmospheric absorption. Since passive imagers detect small differences in temperatures from the radiating object against the sky background, at these frequencies passive imagers do not provide enough scene contrast for short integration times. On the other hand, in an active imager, the object is illuminated with a terahertz source and the resulting reflected/scattered radiation is detected to make an image. However, the glint from the background clutter in an active terahertz imager makes it hard to provide high fidelity images without a fortunate alignment between the imaging system and the target. We have developed an ultra wideband radar based terahertz imaging system that addresses many of these issues and produces high resolution through-clothes images at stand-off distances. The system uses a 675 GHz solid-state transmit/receive system in a frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar mode working at room temperature. The imager has sub-centimeter range resolution by utilizing a 30 GHz bandwidth. It has comparable cross-range resolution at a 25m stand-off distance with a 1m aperture mirror. A fast rotating small secondary mirror rapidly steers the projected beam over a 50 x 50 cm target at range to produce images at frame rates exceeding 1 Hz. In this talk we will explain in detail the design and implementation of the terahertz imaging radar system. We will show how by using a time delay multiplexing of two beams, we achieved a two-pixel imaging system using a single transmit/receive pair. Moreover, we will also show how we improved the signal to noise of the radar system by a factor of 4 by using a novel polarizing wire grid and grating reflector. The research described herein was carried out at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA, under contract with National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
|
|
|
|
Securing Surface Transportation - Electromagnetic Wave Sensors
DHS Science and Technology Directorate What’s hiding behind the advertisements on the subway? A network of electromagnetic sensors that might save your life. Watch this brief segment from the new short video, “Securing Surface Transportation” to learn more about the innovative technologies that S&T is developing to protect rail travelers from terrorism.
For more information, visit: https://go.usa.gov/xRuNF
|
|
Video Forensics
Youtube search...
...Google search
An action movie opens to a scene on the metro platform where a bag has been left unattended, raising suspicion in the metro’s security control room. Video cameras zero in and, through movie magic, security personnel track the footage backward to identify who left the bag. Now, they can track the suspect’s movements to catch the culprit and save the day.
A video algorithm that detects bags left behind and cutting-edge video forensic tools securing train stations and protecting the traveling public. The Forensic Video Exploitation and Analysis (FOVEA) tool developed by MIT Lincoln Laboratory, enables security personnel to tag a person to a left-behind item and then reconstruct the path of that individual across multiple camera views. With FOVEA, hours of video can be scanned much faster than it would normally take, making the process more efficient and more effective. These tools are being tested now by WMATA and Amtrak. Snapshot: DHS S&T’s Unique Video Forensic Tools Implemented by Mass Transit Authorities | Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology (S&T)
|
Securing Surface Transportation - Video Forensics
A video algorithm that detects bags left behind and cutting-edge video forensic tools are some of the technologies featured in “Securing Surface Transportation,” a new short video from S&T about securing train stations and protecting the traveling public. Learn more by watching this brief excerpt from the video. For more information, visit: https://go.usa.gov/xRuNF
|
|
|
|
Package Left Behind Detection
Terrorist Prevention. Multi target detection.
|
|
"Snow White", which enables looking into the past in detail
|
Deja Vu - Official Trailer
It is deja vu that unexpectedly guides ATF agent Doug Carlin through an investigation into a shattering crime. Called in to recover evidence after a bomb sets off a cataclysmic explosion on a New Orleans Ferry, Carlin is about to discover that what most people believe is only in their heads is actually something far more powerful.
|
|
|
|
Minority Report 2002
Full Movie HD
|
|
Cargo Screening
Youtube search...
...Google search
Neutrons are the preferred probing radiation when material specificity is required, which is most often the case. Great strides have been made in neutron based inspection techniques. Fast and thermal neutrons, whether in steady state or in microsecond, or even nanosecond pulses are being employed to interrogate, at high speeds, for explosives, drugs, chemical agents, and nuclear and many other smuggled materials. A Review of Neutron Based Non-Intrusive Inspection Techniques | Tsahi Gozani
New scanners not only can tell the shape of objects inside bags, but also, what they are made of. Now, from a glance of a screen, airport staff can tell "bag of flour from a bag of explosive".
In March 2013, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), an agency of the United Nations, revised an international air cargo security standard to require that that the same security screening measures apply to cargo traveling on passenger as on all-cargo aircraft (previously, the applicable screening measures differed). Under the new standard, all international air cargo transported on commercial aircraft — whether passenger or cargo — must either be (1) screened to a level intended to identify and/or detect the presence of concealed explosive devices or (2) under appropriate security controls throughout the cargo supply chain to prevent the introduction of concealed explosive devices. These new requirements must be implemented in all ICAO member states (including the United States) no later than June 30, 2021. TSA Explores Ways to Streamline International Air Cargo Screening | Cozen O'Connor - Lexology
|
The New Technology Behind Airport Security
Cargo Scanner (2012): Does our technology match the threats that terrorism poses?
|
|
|
|
PEO security: Full 3D Cargo Inspection using the MVCT (Multi-View CT) from Astrophysics
The Astrophysics 3D Multi-View CT (MVCT) X-ray inspection system is a unique, breakthrough solution for screening medium-to-high density cargo. By combining two complementary techniques, multi-view radiographic (X-ray) transmission and 3D computed tomography (CT), this high-powered system allows rapid and effective cargo inspections for: airlines; freight forwarders; customs and border control; harbours;
and government agencies.
|
|
General
PHOENIX –The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) announced today that Alfie, a four-year-old yellow lab and explosive detection K9 who works at Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport (PHX), was voted the winner of TSA’s “cutest K9” contest. The votes are in! TSA’s “cutest K9” is PHX’s Alfie
|
The Science of Airport Security
Long lines, being patted down, and having your hands swabbed don’t make for a wonderful day, but Michael Aranda explains the machines you encounter in airport security and the science and technology behind them.
|
|
|
|
Long Lines, Short Patience: The TSA Airport Screening Experience
The aviation sector remains the crown jewel of targets to terrorist groups like ISIS. The speculation about the crash of Egyptair Flight 804 being a terrorist event is a sobering reminder of the important mission of the Transportation Security Administration (TSA). However, balancing good customer service with strict security screening is not mutually exclusive. With approximately 220 million passengers expected to pass through security checkpoints during peak travel season this summer, aviation stakeholders remain concerned that TSA’s staffing challenges will cause very long lines and wait times. These wait times will cause travelers and airlines inconvenient delays or missed flights. This hearing will examine TSA Administrator Neffenger’s plans to deal with the challenges at TSA. The hearing will also provide an opportunity to discuss how to empower local airports and eliminate bureaucratic roadblocks to provide excellent customer service and effective screening procedures to the traveling public.
|
|
Passenger Aviation Security Layers | William Johnstone - Elsevier

|



