Screening; Passenger, Luggage, & Cargo
Youtube search... ...Google search
Passenger Screening
Transportation Security Administration (TSA) is evaluating the utility of advanced screening systems that use nontraditional measurement processes such as differential phase contrast X-ray, X-ray diffraction, walkthrough Advanced Imaging Technology (AIT) systems, and application of machine learning approaches to improving detection capabilities and system operational efficiency. For example, TSA is working to develop new algorithms that use machine learning approaches to discriminate between threats and benign objects, making the screening process more effective and efficient. Machine learning also offers a way to screen for all prohibited items (explosives, firearms, sharp objects, etc.) automatically. It is anticipated that machine learning algorithms not only will improve security effectiveness but also will support automation in future security systems, thereby enhancing operation efficiency and improving passenger experience through increased throughput and decreased false alarm rates. More broadly, machine learning algorithms can be applied to assess security performance and provide system-level improvements beyond performance enhancements realized at individual screening operations. Advanced Integrated Passenger and Baggage Screening Technologies | Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
- TSA gives green light to test new technology that can screen passengers from 25 feet away | Hugo Martin - Los Angeles Times
- Advanced Integrated Passenger and Baggage Screening Technologies | DHS) Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
- OIG Tells TSA to Improve Monitoring of Advanced Imaging Technology Scanners | Kylie Bielby - GTSC's Homeland Security Today
Kaggle: Passenger Screening Challenge
Results have showed the effectiveness of deep learning applied to passenger screening.
Department of Homeland Security (DHS) gives notice of the availability of the “Department of Homeland Security’s Person Screening Algorithm Challenge Prize Competition and rules.” The DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) Homeland Security Advanced Research Projects Agency (HSARPA) Explosives Division (EXD) and the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) (Competition Sponsor) are seeking new automated detection algorithms from individuals and entities that improve the speed, accuracy, and detection of small threat objects and other prohibited items during the airport passenger screening process. Algorithms developed from this Competition, or through further research and development under a limited intellectual property use agreement, have the potential to improve the speed, the detection of prohibited items, and the accuracy of Advanced Imaging Technology (AIT) scanners. A comprehensive set of new automated detection algorithms have the potential to be integrated into the latest screening equipment.
Models idle_speculation used to win
- Multi-view CNN (MVCNN) for shape recognition
- LightGBM - gradient boosting (GBDT, GBRT, GBM or MART) framework based on decision tree algorithms, used for ranking, classification, etc.
- ImageNet: VGGNet, ResNet, Inception, and Xception with Keras
- ImageNet | Wikipedia
- ResNet50 | TensorFlow Keras
- What is the (Visual Geometry Group) VGG neural network?
- VGG is a convolutional neural network in TensorFlow
- TensorFlow VGG Pretrained | Aditya Ardiya on Kaggle
- VGG-16 Pre-trained Model for Keras | Karen Simonyan, Andrew Zisserman
- Visual Geometry Group
Using Synthetic Training Data
Old:
Development of the equipment and its associated detection algorithms is time consuming and expensive because system screening performance is difficult to accurately model. Prototype systems must be built and tested to measure and understand the interaction of sensors with explosives in various containment configurations. Development requires physical test articles to be fabricated or acquired. Suitable test articles may even be impossible to create if the explosives involved are unsafe to synthesize. Many test articles are created and scanned to build datasets for algorithm development, training, and testing. This solution is particularly labor intensive in order to generate large, representative datasets.
New:
The use of machine learning and deep learning approaches to develop algorithms to process the images generated by the screening hardware either to clear the passenger/property or to identify specific anomalies have shown significant promise in improving overall system performance. Tools can create virtual models of human travelers, their baggage and its contents. These tools/models:
- can simulate human subjects and checked baggage with all appropriate ancillaries (clothing, shoes, hair and, in the case of baggage, typical contents).
- are capable of including simulated explosives and prohibited items.
- are able to be generated in large numbers (many thousands or millions) in a reasonable amount of time (under 1 second per image).
- are used to predict the performance of emerging technologies and to train machine learning-based detection algorithms.
Biometric Screening
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Lie Detection
- Using Deep Learning for finger-vein based biometric authentication | Ling Jin - Towards Data Science
- A Survey of Machine Learning Techniques for Behavioral-Based Biometric User Authentication | N. Mahadi, M. Mohamed, A. Mohamad, M. Makhtar, M. Kadir and M. Mamat
- European Dactyloscopy (Eurodac) European Union (EU) fingerprint database for identifying asylum seekers and irregular border-crossers.
- Entry/Exit System (EES) register entry and exit data of non-EU nationals crossing the external borders of EU Member States
- Office of the Director of National Intelligence
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Biometrics
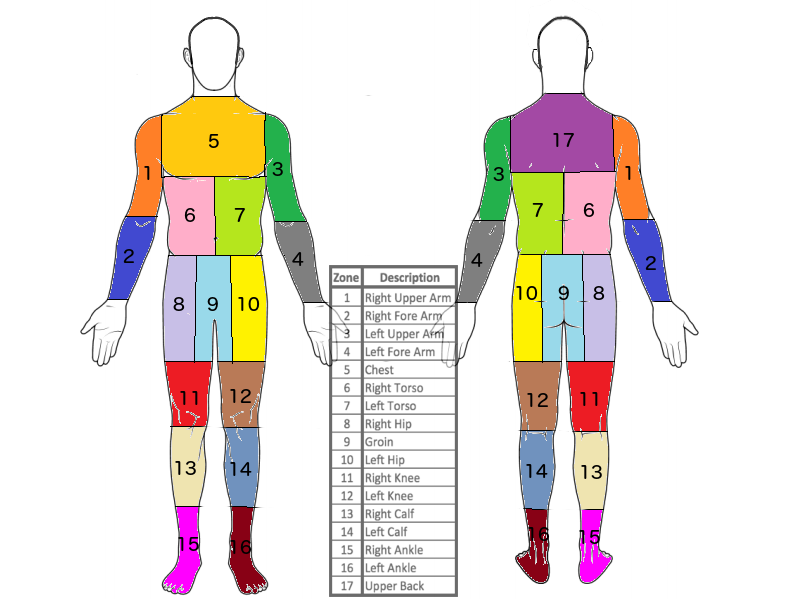
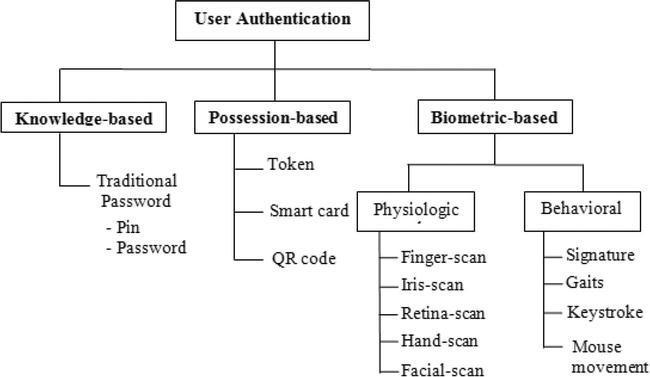
There are two categories of biometric identification and recognition solutions: Physical and behavioral. Physical biometric solutions use distinctive and measurable characteristics of particular parts of the human body, such as a person’s face, iris, DNA, vein, fingerprints, etc., and transform this information into a code understandable by the AI system. Behavioral biometric solutions operate in a similar way, except they use unique behavioral characteristics, such as a person’s typing rhythm, way of interaction with devices, gait, voice, etc. This encoded biometric information is stored in a database and digitally sampled during authentication and verification. AI in Biometrics and Security – Current Business Applications | Radhika Madhavan - emero
Biometrics is the science of analyzing physical or behavioural characteristics specific to each individual to be able to authenticate their identity. If we were to define biometry or biometrics in the most straightforward sense, we would say the "measurement of the human body." ... The electronic passport (e-passport) is a familiar biometric travel document. The second generation of such documents, also known as biometric passports, includes two fingerprints stored in addition to a passport photo. But think about it for one minute... The photo speeds up border crossing through the use of scanners, which use the principle of recognition by comparison of the face or fingerprints. Check-ins and bag-drop solutions also increase speed and efficiency while maintaining high levels of security. Needless to say, that for airports and airlines, providing passengers with a unique and enjoyable travel experience is a business priority. Biometrics provides here irrefutable evidence of the link between the passport and its holder. Biometric authentication is done by comparing the face/fingerprint(s) seen/read at the border with the face/fingerprints in the passport micro-controller. If both biometric data match, authentication is confirmed. Identification, if necessary, is done with the biographic data in the chip and printed. Besides, many countries have set up biometric infrastructures to control migration flows to and from their territories. Fingerprint scanners and cameras at border posts capture information that helps identify travellers entering the country in a more precise and reliable way. In some states, the same applies to consulates to visa applications and renewals. Data acquisition requires reliable equipment to ensure optimum capture of photos and fingerprints, essential for precision during comparison and verification. Biometrics: authentication & identification (definition, trends, use cases, laws and latest news) - 2020 review Thales
Contactless Biometrics
Youtube search... ...Google search
used to authenticate users without having to place their hands anywhere near a scanner – simply authenticating digital identity through Fingerprint, Palmprint, Iris, Retinal, Face, Speech, Speaker & Language.
Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
provides biometric identification services to protect the nation through its Office of Biometric Identity Management (OBIM), which supplies the technology for matching, storing, and sharing biometric data. OBIM is the lead designated provider of biometric identity services for DHS, and maintains the largest biometric repository in the U.S. government. This system, called the Automated Biometric Identification System (IDENT), is operated and maintained by OBIM. IDENT currently holds more than 200 million unique identities and processes more than 300,000 biometric transactions per day.
Biometric Technology Rally
Department of Homeland Security (DHS) DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) and Customs and Border Protection (CBP)’s Apex Air Entry/Exit Re-engineering (AEER) project created a partnership between S&T and CBP to test and evaluate operational processes using biometric and non-biometric technologies. The MdTF continues to support multiple projects for the DHS S&T Biometrics and Identity Technology Center including those that inform CBP, Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and external agencies to evaluate and implement solutions in their operational environments. The 2019 Biometric Technology Rally was designed to challenge industry to develop high-throughput biometric systems, meeting the requirements of fast and accurate user recognition within identity verification operations, such as security checkpoints. The 2019 Rally invited providers of biometric (face, iris, or fingerprint) acquisition systems, as well as providers of biometric matching systems that achieve defined performance targets for high-throughput use cases. MdTF | Maryland Test Facility
- 2019 Rally Results
- Secretive DHS Program Aimed at Comprehensive Biometric Surveillance, sayEFF | Alex Perala
Fingerprint
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Fingerprint | National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- On the use of convolutional neural networks for robust classification of multiple fingerprint captures | D. Peralta, I. Triguero, S. Garc´ıa, Y. Saeys, J. Benitez, and F. Herrera
- Will Artificial Intelligence Steal Your Fingerprints? | George I. Seffers - The Cyber Edge
- Fingerprints Upgraded | FingerID - Faster: Search for match in 2 billion prints within seconds
- FBI's Next Generation Identification (NGI) system accuracy more than 99.6 percent
- Biometric Fingerprint Indentification Using Artificial Neural Network | Neeraj Singla and Sugandha Sharma - International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science & Technology
Fingerprint scanners collect an image of a person’s fingerprint and record its features such as whorls, loops, and arches. Additionally, fingerprint scanners also analyze outlines of edges, furrows, and minutiae of a fingerprint. The scanned fingerprint image is then verified against a previously stored set of fingerprints. [Biometrics is smart, but AI is smarter. Here's why | Naveen Joshi - Allerin
Fingerprint identification is one of the most well-known and publicized biometrics. Because of their uniqueness and consistency over time, fingerprints have been used for identification for over a century, more recently becoming automated (i.e. a biometric) due to advancements in computing capabilities. Fingerprint identification is popular because of the inherent ease in acquisition, the numerous sources (10 fingers) available for collection, and their established use and collections by law enforcement and immigration. What is Fingerprint Identification? | Stephen Mayhew - Biometric Update.com
The practice of using fingerprints as a method of identifying individuals has been in use since the late nineteenth century when Sir Francis Galton defined some of the points or characteristics from which fingerprints can be identified. These “Galton Points” are the foundation for the science of fingerprint identification, which has expanded and transitioned over the past century. Fingerprint identification began its transition to automation in the late 1960s along with the emergence of computing technologies. With the advent of computers, a subset of the Galton Points, referred to as minutiae, has been utilized to develop automated fingerprint technology.
A fingerprint usually appears as a series of dark lines that represent the high, peaking portion of the friction ridge skin, while the valley between these ridges appears as white space and are the low, shallow portion of the friction ridge skin. Fingerprint identification is based primarily on the minutiae, or the location and direction of the ridge endings and bifurcations (splits) along a ridge path.
A variety of sensor types —
- optical
- capacitive
- ultrasound
- thermal
— are used for collecting the digital image of a fingerprint surface. Optical sensors take an image of the fingerprint, and are the most common sensor today.
The two main categories of fingerprint matching techniques are:
- minutiae-based matching
- pattern matching.
Pattern matching simply compares two images to see how similar they are. Pattern matching is usually used in fingerprint systems to detect duplicates. The most widely used recognition technique, minutiae-based matching, relies on the minutiae points, specifically the location and direction of each point.
Palmprint
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Toward Unconstrained Palmprint Recognition on Consumer Devices: A Literature Review | A. Ungureanu , S. Salahuddin, and P. Corcoran - IEEE Access
- FBI's Next Generation Identification (NGI) system three times the previous latent search accuracy
- Palmprint image registration using convolutional neural networks and Hough transform | Mohsen Ahmadi and Hossein Soleimani
- Palmprint and Palmvein Recognition Based on DCNN and A New Large-Scale Contactless Palmvein Dataset | L. Zhang, Z. Cheng, Y. Shen, and D. Wang
The NGI System’s latent functionality uses a Friction Ridge Investigative File composed of all retained events for an individual as opposed to one composite image set per identity. These multiple events in the repository result in three times the previous latent search accuracy and allow for additional event image retrieval to support difficult casework. In May 2013, the FBI established the National Palm Print System (NPPS). This system contains palm prints that are searchable to law enforcement nationwide.
Eye: Iris/Retinal
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Iris | National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- An intelligent method for iris recognition using supervised machine learning techniques | N. Ahmadi, M. Nilashi, S. Samad, T. Rashid, and H. Ahmadi
- DeepIris: Iris Recognition Using A Deep Learning Approach | Shervin Minaee and Amirali Abdolrashidi
Two methods:
- Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance.
- Retinal scanning is a different, ocular-based biometric technology that uses the unique patterns on a person's retina blood vessels and is often confused with iris recognition. Iris recognition uses video camera technology with subtle near infrared illumination to acquire images of the detail-rich, intricate structures of the iris which are visible externally.
Face
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Face | National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- Deep Learning For Face Recognition: A Critical Analysis | Andrew Jason Shepley
- Facial Recognition And AI: Latest Developments And Future Directions | Oleksii Kharkovyna - Being Human - Medium
- Rekognition
- Neural Architecture Search for Deep Face Recognition | Ning Zhu
- Deep Face Recognition: A Survey | Mei Wang, Weihong Deng - School of Information and Communication Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing, China
- Amazon’s Face Recognition Falsely Matched 28 Members of Congress With Mugshots | Jacob Snow - ACLU
- A Flawed Facial-Recognition System Sent This Man to Jail | Sidney Fussell - Wired
- OpenCV Open Computer Vision
- Interactive map shows where facial recognition surveillance is happening | Fightforthefuture.org
- Facial recognition system | Wikipedia
- ICE Outlines How Investigators Rely on Third-Party Facial Recognition Services | Aaron Boyd - Nextgov
Facial recognition is a biometric software application capable of uniquely identifying or verifying a person by comparing and analyzing patterns based on the person’s facial contours. There are different facial recognition techniques in use, such as the generalized matching face detection method and the adaptive regional blend matching method. Most facial recognition systems function based on the different nodal points on a human face. The values measured against the variable associated with points of a person’s face help in uniquely identifying or verifying the person. With this technique, applications can use data captured from faces and can accurately and quickly identify target individuals. Facial recognition techniques are quickly evolving with new approaches such as 3-D modeling, helping to overcome issues with existing techniques. There are many advantages associated with facial recognition. Compared to other biometric techniques, facial recognition is of a non-contact nature. Face images can be captured from a distance and can be analyzed without ever requiring any interaction with the user/person. As a result, no user can successfully imitate another person. Facial recognition can serve as an excellent security measure for time tracking and attendance. Facial recognition is also cheap technology as there is less processing involved, like in other biometric techniques. Machine Learning on Facial Recognition - Damilola Omoyiwola - Medium
Face detection is one of the important tasks of object detection. Typically detection is the first stage of pattern recognition and identity authentication. In recent years, deep learning-based algorithms in object detection have grown rapidly. These algorithms can be generally divided into two categories, i.e., two-stage detector like Faster R-CNN and one-stage detector like You Only Look Once (YOLO). Although YOLO and its varieties are not so good as two-stage detectors in terms of accuracy, they outperform the counterparts by a large margin in speed. YOLO performs well when facing normal size objects, but is incapable of detecting small objects. The accuracy decreases notably when dealing with objects that have large-scale changing like faces. Aimed to solve the detection problem of varying face scales, we propose a face detector named YOLO-face based on YOLOv3 to improve the performance for face detection. The present approach includes using anchor boxes more appropriate for face detection and a more precise regression loss function. The improved detector significantly increased accuracy while remaining fast detection speed. Experiments on the WIDER FACE and the FDDB datasets show that our improved algorithm outperforms YOLO and its varieties. YOLO-face: a real-time face detector | W. Chen, H. Huang, S. Peng, C. Zhou & C. Zhang - The Visual Computer Deep learning based Face detection using the YOLOv3 algorithm | Ayoosh Kathuria - GitHub ... YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement | Joseph Redmon, Ali Farhadi - University of Washington
Ethnus Codemithra Masterclass
Face Recognition @ Scale
Youtube search... ...Google search
References:
Scaling Training:
- Federated Learning
- Distributed Learning
Scaling Evaluation:
- Shared nothing architecture
- Neural network/classifier rarely change
- Load balancing pattern
- Partitioning data if needed
- High demands for speed and accuracy:
- identify any one of its 1.3 billion citizens within three seconds
- someone’s face to their ID photo with about 90 per cent accuracy
- accuracy of the photo that most closely matched the face being searched for was below 60 per cent.
- with the top 20 matches the accuracy rate remained below 70 per cent
- when a photo, gender and age range are inputted accuracy level higher than 88 per cent
- launched by the Ministry of Public Security in 2015
- cloud facilities to connect with data storage and processing centres distributed across the country
- portrait information of each Chinese citizen (1.3 billion), amounts to 13 terabytes
- the size of the full database with detailed personal information does not exceed 90 terabytes
- Isvision will use an algorithm developed by Seetatech Technology Co., a start-up established by several researchers from the Institute of Computing Technology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing
- University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC) - Wikipedia
- Journal of Electronic Science and Technology - ScienceDirect
faced is a proof of concept that you don’t always need to rely on general purpose trained models in scenarios were these models are an overkill to your problem and performance issues are involved. Don’t overestimate the power of spending time designing custom neural network architectures that are specific to your problem. These specific networks will be a much better solution than the general ones. faced: CPU Real Time face detection using Deep Learning | Ivan Itzcovich - Towards Data Science
Haar Cascade [left] vs faced [right]

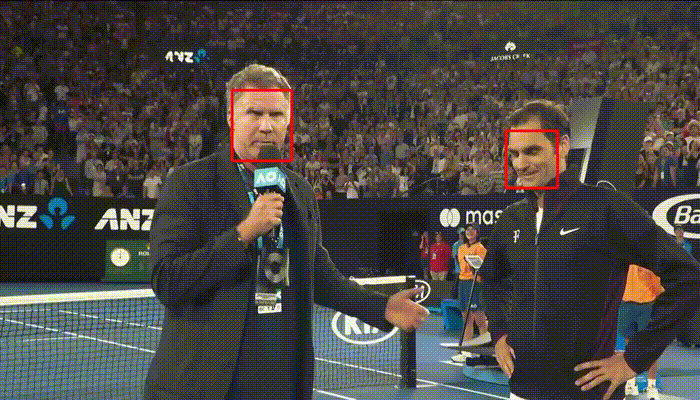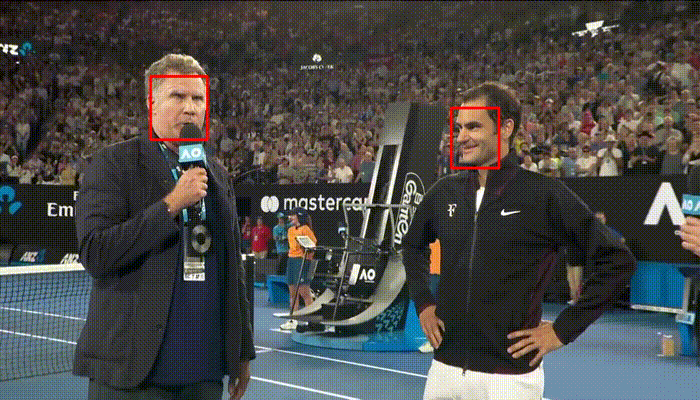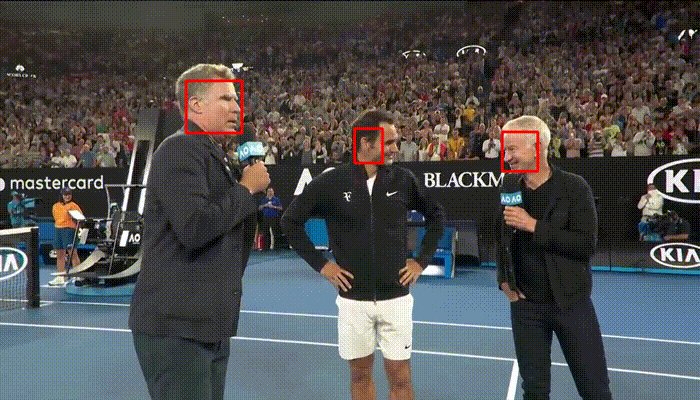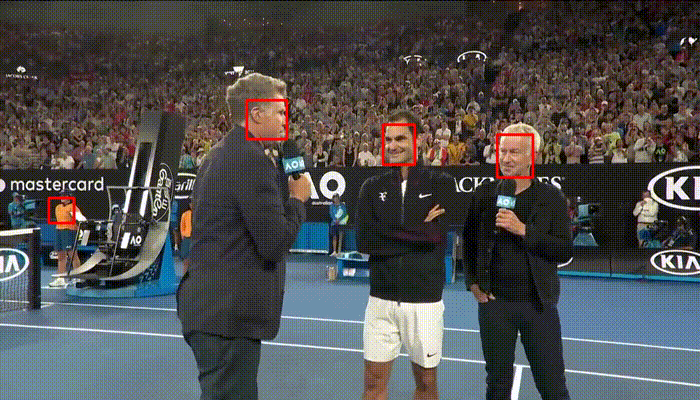
Liveness Detection
Youtube search... ...Google search
an AI computer system’s ability to determine that it is interfacing with a physically present human being and not an inanimate spoof artifact. Liveness Detection has become a necessary component of any authentication system that is based on face biometric technology where a trusted human is not supervising the authentication attempt.
- Facial Recognition is for surveillance; it's the 1-to-N matching of images captured with cameras the user doesn't control, like those in a casino or an airport. And it only provides "possible" matches for the surveilled person from face photos stored in an existing database.
- Face Authentication (1:1 Matching+Liveness), on the other hand, takes User-initiated data collected from a device they do control and confirms that User's identity for their own direct benefit, like, for example, secure account access.
Speech, Speaker & Language
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Speaker and Language Recognition | National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- Speech Analytics | National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- The Future of Voice | Michal Hrab - Biometric Update.com
The implementation of AI in voice recognition can train the biometric systems using millions of voice samples of different users. AI and biometrics like voice recognition can evaluate a person’s biometric voice signature by analyzing their voice patterns such as speed, accent, tone, and pitch. Such biometrics can be quick and authenticate individuals precisely. Such AI-powered voice recognition can be used in workplaces for authentication and attendance purposes. [Biometrics is smart, but AI is smarter. Here's why | Naveen Joshi - Allerin
Biometric authentication, unlike passwords or token-based authentication, uses unique biological characteristics to verify an individual’s identity. It’s harder to spoof and generally more convenient for users since they don’t have to remember passwords or carry a physical token that can easily be lost or stolen. The authenticator is part of the individual. Aware
Voice recognition (also called speaker recognition or voice authentication) applies analyzes of a person’s voice to verify their identity. Airways and soft-tissue cavities, as well as the shape and movement of the mouth and jaw, influence voice patterns to create a unique “voiceprint.”
Speaker recognition is a type of voice recognition technology. However, it is not the same as speech recognition, which is the technology used in speech-to-text applications and virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa. Speech recognition can make sense of verbal language, but it can’t verify the identity of the speaker based on his or her unique vocal attributes; voice biometrics can.
Speaker recognition methods - There are two main approaches to voice authentication:
- Text independent: Voice authentication is performed using any spoken passphrase or other speech content.
- Text-dependent: The same passphrases are used in enrollment and for verification. This means that a speaker cannot say anything he or she would like to authenticate, but will be asked to speak a predetermined phrase. In static text-dependent voice authentication, the same passphrase is used for every verification. In dynamic text-dependent voice authentication, a randomized passphrase such as a number sequence is generated for the user. This content must also be enrolled.
Enrollment and verification -
A voice biometric sample must be captured and enrolled using a microphone to create a reference template to compare against samples for future authentication attempts. Unique vocal qualities are then analyzed;, such as :
- Duration
- Intensity
- Dynamics
- Pitch
Luggage Screening
Youtube search... ...Google search
- A Model-Based 3D Multi-slice Helical CT Reconstruction Algorithm for Transportation Security Application | P. chen, E. Haneda, C. Bouman, and K. Sauer
- The US Transportation Security Administration has recently introduced new computed tomography (CT) scanners, which use AI to help target threats, at Los Angeles International Airport, John F. Kennedy and Phoenix airports. How can AI help speed up airport security? | Airport Technology
- Computed Tomography (CT) | TSA
- Object Recognition and Adaptive Algorithms for Airport Passenger Property Screening Solicitation
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) in XIS-6040 X-ray Baggage Scanners | Astrophysics– Syntech Solutions
- DHS Awards $200K for AI-Based Object Recognition Proof-of-Concept | Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate (S&T)
- TSA Machine Learning Opportunities | Frank Cartwright - Office of Requirements and Capabilities Analysis, TSA
- Future Baggage Scanners Will Tell Us What Things Are Made Of | J. Greenberg, A. Ashok and M. Gehm - IEEE Spectrum
- DHS S&T Awards $142K to Cignal for Artificial Intelligence Model Training | GTSC's Homeland Security Today
Computed Tomography (CT) scanning has ...found an application in transport security (predominantly airport security where it is currently used in a materials analysis context for explosives detection CTX (explosive-detection device)[106][107][108][109] and is also under consideration for automated baggage/parcel security scanning using computer vision based object recognition algorithms that target the detection of specific threat items based on 3D appearance (e.g. guns, knives, liquid containers) CT scan | Wikipedia
Cargo Screening
Youtube search... ...Google search
- Cargo Screening | Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
- Non-Intrusive Inspection Systems Program (NII) | Department of Homeland Security (DHS) U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
Neutrons are the preferred probing radiation when material specificity is required, which is most often the case. Great strides have been made in neutron based inspection techniques. Fast and thermal neutrons, whether in steady state or in microsecond, or even nanosecond pulses are being employed to interrogate, at high speeds, for explosives, drugs, chemical agents, and nuclear and many other smuggled materials. A Review of Neutron Based Non-Intrusive Inspection Techniques | Tsahi Gozani
New scanners not only can tell the shape of objects inside bags, but also, what they are made of. Now, from a glance of a screen, airport staff can tell "bag of flour from a bag of explosive".
In March 2013, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), an agency of the United Nations, revised an international air cargo security standard to require that that the same security screening measures apply to cargo traveling on passenger as on all-cargo aircraft (previously, the applicable screening measures differed). Under the new standard, all international air cargo transported on commercial aircraft — whether passenger or cargo — must either be (1) screened to a level intended to identify and/or detect the presence of concealed explosive devices or (2) under appropriate security controls throughout the cargo supply chain to prevent the introduction of concealed explosive devices. These new requirements must be implemented in all ICAO member states (including the United States) no later than June 30, 2021. TSA Explores Ways to Streamline International Air Cargo Screening | Cozen O'Connor - Lexology
General
PHOENIX –The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) announced today that Alfie, a four-year-old yellow lab and explosive detection K9 who works at Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport (PHX), was voted the winner of TSA’s “cutest K9” contest. The votes are in! TSA’s “cutest K9” is PHX’s Alfie
