Difference between revisions of "Reinforcement Learning (RL)"
m |
|||
| (35 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[http://www.google.com/search?q=Reinforcement+deep+machine+learning+ML+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | [http://www.google.com/search?q=Reinforcement+deep+machine+learning+ML+artificial+intelligence ...Google search] | ||
| − | * Reinforcement Learning (RL) | + | * Reinforcement Learning (RL) |
** [[Monte Carlo]] (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning | ** [[Monte Carlo]] (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning | ||
** [[Markov Decision Process (MDP)]] | ** [[Markov Decision Process (MDP)]] | ||
| + | ** [[State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)]] | ||
** [[Q Learning]] | ** [[Q Learning]] | ||
| − | ** [[ | + | *** [[Deep Q Network (DQN)]] |
** [[Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)]] DeepRL | ** [[Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)]] DeepRL | ||
| − | |||
** [[Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)]] | ** [[Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)]] | ||
| − | |||
** [[Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms]] | ** [[Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms]] | ||
| − | ** [[Asynchronous Advantage Actor Critic (A3C)]] | + | ** [[Actor Critic]] |
| + | *** [[Asynchronous Advantage Actor Critic (A3C)]] | ||
| + | *** [[Advanced Actor Critic (A2C)]] | ||
| + | *** [[Lifelong Latent Actor-Critic (LILAC)]] | ||
** [[Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)]] | ** [[Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)]] | ||
| − | + | * [[Game Theory]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* [[Policy Gradient (PG)]] | * [[Policy Gradient (PG)]] | ||
* [[Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO)]] | * [[Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO)]] | ||
* [[Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)]] | * [[Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)]] | ||
| + | * [[Robotics]] | ||
* [http://arxiv.org/abs/1611.01578 Neural Architecture Search (NAS) with Reinforcement Learning | Barret Zoph & Quoc V. Le] ...[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neural_architecture_search#NAS_with_Reinforcement_Learning Wikipedia] | * [http://arxiv.org/abs/1611.01578 Neural Architecture Search (NAS) with Reinforcement Learning | Barret Zoph & Quoc V. Le] ...[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neural_architecture_search#NAS_with_Reinforcement_Learning Wikipedia] | ||
* [http://towardsdatascience.com/advanced-reinforcement-learning-6d769f529eb3 Beyond DQN/A3C: A Survey in Advanced Reinforcement Learning | Joyce Xu - Towards Data Science] | * [http://towardsdatascience.com/advanced-reinforcement-learning-6d769f529eb3 Beyond DQN/A3C: A Survey in Advanced Reinforcement Learning | Joyce Xu - Towards Data Science] | ||
* [[AdaNet]] | * [[AdaNet]] | ||
| + | * [[Loop#Feedback Loop - The AI Economist|Feedback Loop - The AI Economist]] | ||
___________________________________________________________ | ___________________________________________________________ | ||
| − | * [[Apprenticeship Learning - Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL)]] | + | * [[Learning Techniques]] |
| − | * [[Lifelong Learning]] | + | ** [[Apprenticeship Learning - Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL)]] |
| + | ** [[Lifelong Learning]] | ||
* [[Dopamine]] Google DeepMind | * [[Dopamine]] Google DeepMind | ||
** [[Math for Intelligence]] | ** [[Math for Intelligence]] | ||
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
* [http://www.amazon.com/Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Hands-Q-networks/dp/1788834240 Deep Reinforcement Learning Hands-On: Apply modern RL methods, with deep Q-networks, value iteration, policy gradients, TRPO, AlphaGo Zero and more | Maxim Lapan] | * [http://www.amazon.com/Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Hands-Q-networks/dp/1788834240 Deep Reinforcement Learning Hands-On: Apply modern RL methods, with deep Q-networks, value iteration, policy gradients, TRPO, AlphaGo Zero and more | Maxim Lapan] | ||
* [http://github.com/Pulkit-Khandelwal/Reinforcement-Learning-Notebooks Reinforcement-Learning-Notebooks] - A collection of Reinforcement Learning algorithms from Sutton and Barto's book and other research papers implemented in Python | * [http://github.com/Pulkit-Khandelwal/Reinforcement-Learning-Notebooks Reinforcement-Learning-Notebooks] - A collection of Reinforcement Learning algorithms from Sutton and Barto's book and other research papers implemented in Python | ||
| + | * [http://www.unite.ai/what-is-reinforcement-learning/ What is Reinforcement Learning? | Daniel Nelson - Unite.ai] | ||
| + | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reinforcement_learning Reinforcement Learning (RL) | Wikipedia] | ||
| + | * [http://pathmind.com/wiki/deep-reinforcement-learning A Beginner's Guide to Deep Reinforcement Learning | Chris Nicholson - A.I. Wiki pathmind] | ||
| + | * [[Capabilities]] | ||
| + | ** [[Reinforcement Learning - Games, Self-driving Vehicles, Drones, Robotics, Management, Finance]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <b>DeepMind says reinforcement learning is ‘enough’ to reach general AI</b> ...<i> | ||
| + | [http://venturebeat.com/2021/06/09/deepmind-says-reinforcement-learning-is-enough-to-reach-general-ai/ Some scientists believe that assembling multiple narrow AI modules will produce higher intelligent systems.]</i> | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | |||
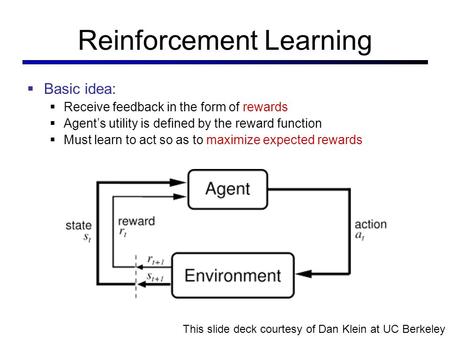
This is a bit similar to the traditional type of data analysis; the algorithm discovers through trial and error and decides which action results in greater rewards. Three major components can be identified in reinforcement learning functionality: the agent, the environment, and the actions. The agent is the learner or decision-maker, the environment includes everything that the agent interacts with, and the actions are what the agent can do. Reinforcement learning occurs when the agent chooses actions that maximize the expected reward over a given time. This is best achieved when the agent has a good policy to follow. [http://www.simplilearn.com/what-is-machine-learning-and-why-it-matters-article Machine Learning: What it is and Why it Matters | Priyadharshini @ simplilearn] | This is a bit similar to the traditional type of data analysis; the algorithm discovers through trial and error and decides which action results in greater rewards. Three major components can be identified in reinforcement learning functionality: the agent, the environment, and the actions. The agent is the learner or decision-maker, the environment includes everything that the agent interacts with, and the actions are what the agent can do. Reinforcement learning occurs when the agent chooses actions that maximize the expected reward over a given time. This is best achieved when the agent has a good policy to follow. [http://www.simplilearn.com/what-is-machine-learning-and-why-it-matters-article Machine Learning: What it is and Why it Matters | Priyadharshini @ simplilearn] | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://slideplayer.com/24/7469154/big_thumb.jpg | ||
http://s3.amazonaws.com/static2.simplilearn.com/ice9/free_resources_article_thumb/Machine_Learning_5.jpg | http://s3.amazonaws.com/static2.simplilearn.com/ice9/free_resources_article_thumb/Machine_Learning_5.jpg | ||
| + | Control-based: When running a Reinforcement Learning (RL) policy in the real world, such as controlling a physical robot on visual inputs, it is non-trivial to properly track states, obtain reward signals or determine whether a goal is achieved for real. The visual data has a lot of noise that is irrelevant to the true state and thus the equivalence of states cannot be inferred from pixel-level comparison. Self-supervised representation learning has shown great potential in learning useful state embedding that can be used directly as input to a control policy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>e3Jy2vShroE</youtube> | ||
| + | <youtube>ISk80iLhdfU</youtube> | ||
<youtube>Vz5l886eptw</youtube> | <youtube>Vz5l886eptw</youtube> | ||
| − | <youtube> | + | <youtube>w33Lplx49_A</youtube> |
| − | |||
<youtube>JgvyzIkgxF0</youtube> | <youtube>JgvyzIkgxF0</youtube> | ||
<youtube>2pWv7GOvuf0</youtube> | <youtube>2pWv7GOvuf0</youtube> | ||
<youtube>gWNeMs1Fb8I</youtube> | <youtube>gWNeMs1Fb8I</youtube> | ||
<youtube>eHipy_j29Xw</youtube> | <youtube>eHipy_j29Xw</youtube> | ||
| − | |||
<youtube>W2gaWTkpews</youtube> | <youtube>W2gaWTkpews</youtube> | ||
| + | <youtube>nSxaG_Kjw_w</youtube> | ||
| + | <youtube>313kbpBq8Sg</youtube> | ||
== [http://pythonprogramming.net/search/?q=q+learning Q Learning Algorithm and Agent - Reinforcement Learning w/ Python Tutorial | Sentdex - Harrison] == | == [http://pythonprogramming.net/search/?q=q+learning Q Learning Algorithm and Agent - Reinforcement Learning w/ Python Tutorial | Sentdex - Harrison] == | ||
| Line 81: | Line 104: | ||
* [http://github.com/philtabor/Youtube-Code-Repository/tree/master/ReinforcementLearning Code | GitHub] | * [http://github.com/philtabor/Youtube-Code-Repository/tree/master/ReinforcementLearning Code | GitHub] | ||
| − | Reinforcement learning is an area of machine learning that involves taking right action to maximize reward in a particular situation. In this full tutorial course, you will get a solid foundation in reinforcement learning core topics. | + | Reinforcement learning is an area of machine learning that involves taking right action to maximize reward in a particular situation. In this full tutorial course, you will get a solid foundation in reinforcement learning core topics. The course covers Q learning, [[State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)]], double Q learning, [[Deep Q Learning (DQN)]], and [[Policy Gradient (PG)]] methods. These algorithms are employed in a number of environments from the open AI gym, including space invaders, breakout, and others. The deep learning portion uses [[Tensorflow]] and [[PyTorch]]. The course begins with more modern algorithms, such as deep q learning and [[Policy Gradient (PG)]] methods, and demonstrates the power of reinforcement learning. Then the course teaches some of the fundamental concepts that power all reinforcement learning algorithms. These are illustrated by coding up some algorithms that predate deep learning, but are still foundational to the cutting edge. These are studied in some of the more traditional environments from the [[OpenAI#OpenAI Gym | OpenAI Gym]], like the cart pole problem. |
| − | |||
| − | The course covers Q learning, [[State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)]], double Q learning, [[Deep Q Learning (DQN)]], and [[Policy Gradient (PG)]] methods. These algorithms are employed in a number of environments from the open AI gym, including space invaders, breakout, and others. The deep learning portion uses [[Tensorflow]] and [[PyTorch]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | The course begins with more modern algorithms, such as deep q learning and [[Policy Gradient (PG)]] methods, and demonstrates the power of reinforcement learning. | ||
| − | |||
| − | Then the course teaches some of the fundamental concepts that power all reinforcement learning algorithms. These are illustrated by coding up some algorithms that predate deep learning, but are still foundational to the cutting edge. These are studied in some of the more traditional environments from the [[OpenAI Gym]], like the cart pole problem. | ||
⌨️ ([http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ELE2_Mftqoc&t=0s 00:00:00]) Introduction | ⌨️ ([http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ELE2_Mftqoc&t=0s 00:00:00]) Introduction | ||
Revision as of 06:14, 10 June 2021
YouTube search... ...Google search
- Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Monte Carlo (MC) Method - Model Free Reinforcement Learning
- Markov Decision Process (MDP)
- State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA)
- Q Learning
- Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) DeepRL
- Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning (DDRL)
- Evolutionary Computation / Genetic Algorithms
- Actor Critic
- Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL)
- Game Theory
- Policy Gradient (PG)
- Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO)
- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
- Robotics
- Neural Architecture Search (NAS) with Reinforcement Learning | Barret Zoph & Quoc V. Le ...Wikipedia
- Beyond DQN/A3C: A Survey in Advanced Reinforcement Learning | Joyce Xu - Towards Data Science
- AdaNet
- Feedback Loop - The AI Economist
___________________________________________________________
- Learning Techniques
- Dopamine Google DeepMind
- Inside Out - Curious Optimistic Reasoning
- World Models
- Google DeepMind AlphaGo Zero
- Google’s AI picks which machine learning models will produce the best results | Kyle Wiggers - VentureBeat off-policy classification,” or OPC, which evaluates the performance of AI-driven agents by treating evaluation as a classification problem
- Deep Reinforcement Learning Hands-On: Apply modern RL methods, with deep Q-networks, value iteration, policy gradients, TRPO, AlphaGo Zero and more | Maxim Lapan
- Reinforcement-Learning-Notebooks - A collection of Reinforcement Learning algorithms from Sutton and Barto's book and other research papers implemented in Python
- What is Reinforcement Learning? | Daniel Nelson - Unite.ai
- Reinforcement Learning (RL) | Wikipedia
- A Beginner's Guide to Deep Reinforcement Learning | Chris Nicholson - A.I. Wiki pathmind
- Capabilities
DeepMind says reinforcement learning is ‘enough’ to reach general AI ... Some scientists believe that assembling multiple narrow AI modules will produce higher intelligent systems.
This is a bit similar to the traditional type of data analysis; the algorithm discovers through trial and error and decides which action results in greater rewards. Three major components can be identified in reinforcement learning functionality: the agent, the environment, and the actions. The agent is the learner or decision-maker, the environment includes everything that the agent interacts with, and the actions are what the agent can do. Reinforcement learning occurs when the agent chooses actions that maximize the expected reward over a given time. This is best achieved when the agent has a good policy to follow. Machine Learning: What it is and Why it Matters | Priyadharshini @ simplilearn

Control-based: When running a Reinforcement Learning (RL) policy in the real world, such as controlling a physical robot on visual inputs, it is non-trivial to properly track states, obtain reward signals or determine whether a goal is achieved for real. The visual data has a lot of noise that is irrelevant to the true state and thus the equivalence of states cannot be inferred from pixel-level comparison. Self-supervised representation learning has shown great potential in learning useful state embedding that can be used directly as input to a control policy.
Contents
Q Learning Algorithm and Agent - Reinforcement Learning w/ Python Tutorial | Sentdex - Harrison
Reinforcement Learning | Phil Tabor
Reinforcement learning is an area of machine learning that involves taking right action to maximize reward in a particular situation. In this full tutorial course, you will get a solid foundation in reinforcement learning core topics. The course covers Q learning, State-Action-Reward-State-Action (SARSA), double Q learning, Deep Q Learning (DQN), and Policy Gradient (PG) methods. These algorithms are employed in a number of environments from the open AI gym, including space invaders, breakout, and others. The deep learning portion uses Tensorflow and PyTorch. The course begins with more modern algorithms, such as deep q learning and Policy Gradient (PG) methods, and demonstrates the power of reinforcement learning. Then the course teaches some of the fundamental concepts that power all reinforcement learning algorithms. These are illustrated by coding up some algorithms that predate deep learning, but are still foundational to the cutting edge. These are studied in some of the more traditional environments from the OpenAI Gym, like the cart pole problem.
⌨️ (00:00:00) Introduction
⌨️ (00:01:30) Intro to Deep Q Learning
⌨️ (00:08:56) How to Code Deep Q Learning in Tensorflow
⌨️ (00:52:03) Deep Q Learning with Pytorch Part 1: The Q Network
⌨️ (01:06:21) Deep Q Learning with Pytorch part 2: Coding the Agent
⌨️ (01:28:54) Deep Q Learning with Pytorch part 3
⌨️ (01:46:39) Intro to Policy Gradients 3: Coding the main loop
⌨️ (01:55:01) How to Beat Lunar Lander with Policy Gradients
⌨️ (02:21:32) How to Beat Space Invaders with Policy Gradients
⌨️ (02:34:41) How to Create Your Own Reinforcement Learning Environment Part 1
⌨️ (02:55:39) How to Create Your Own Reinforcement Learning Environment Part 2
⌨️ (03:08:20) Fundamentals of Reinforcement Learning
⌨️ (03:17:09) Markov Decision Processes
⌨️ (03:23:02) The Explore Exploit Dilemma
⌨️ (03:29:19) Reinforcement Learning in the Open AI Gym: SARSA
⌨️ (03:39:56) Reinforcement Learning in the Open AI Gym: Double Q Learning
⌨️ (03:54:07) Conclusion
Jump Start
Lunar Lander: Deep Q learning is Easy in PyTorch
Lunar Lander: How to Beat Lunar Lander with Policy Gradients | Tensorflow Tutorial
Breakout: How to Code Deep Q Learning in Tensorflow (Tutorial)
Gridworld: How To Create Your Own Reinforcement Learning Environments